News
Data Centre Architecture Insights & Best Practices
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
News
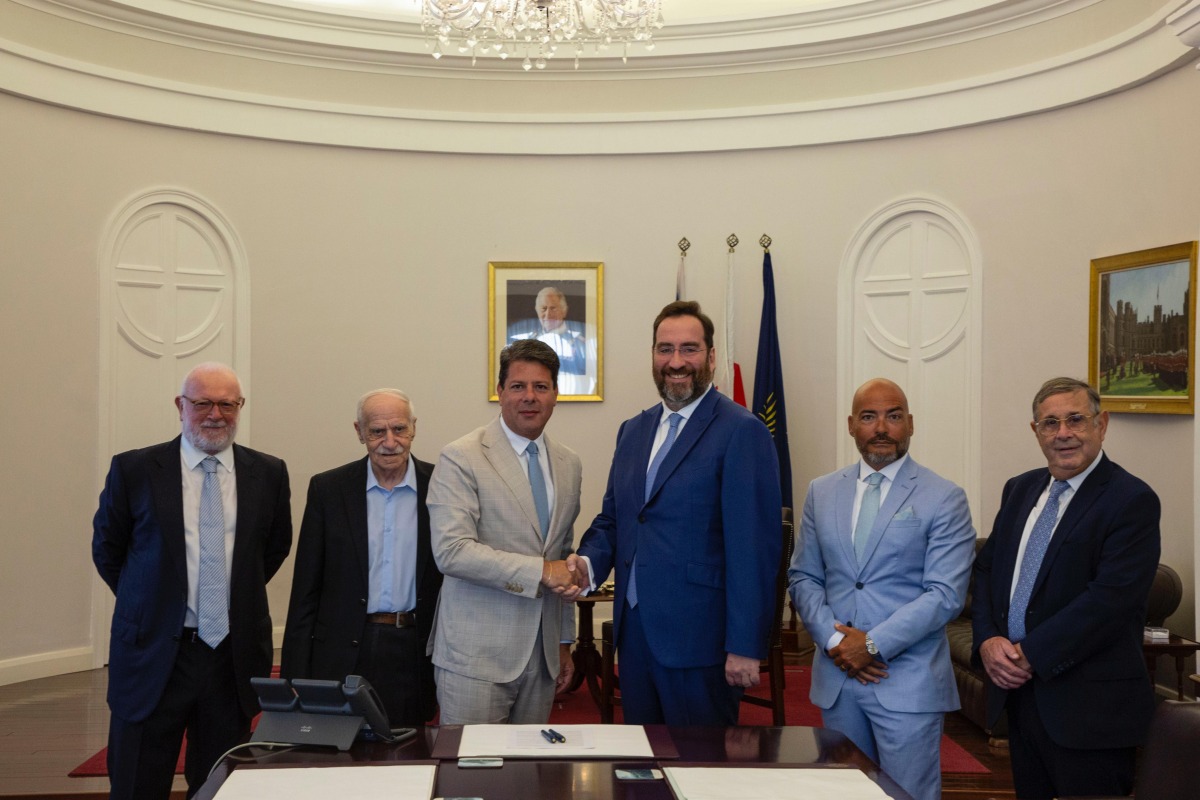
Pelagos planning ambitious 250MW facility in Gibraltar
Pelagos Data Centres, a developer of large-scale data centre infrastructure, has announced plans to build a major new data centre near the Port of Gibraltar, with capacity of up to 250MW by 2033.
Unveiled at a launch event at the offices of Gibraltar’s Chief Minister, Fabian Picardo, the project represents an investment of around £1.8 billion. It is the largest development currently planned in the territory by value, and among the largest in its history.
The facility will be built in five phases on a 20,000m² site. The first stage is scheduled to be operational in late 2027, with later phases delivered at intervals of around 18 months.
Transforming Gibraltar’s digital landscape
Funded entirely by private investment and backed by the Government of Gibraltar, the project is positioned as a step forward for the territory’s digital and economic development. It is intended to help meet Europe’s growing demand for data centre capacity, particularly as AI adoption accelerates across industries.
The site will operate independently of Gibraltar’s existing power grid and include a public leisure facility as part of the development.
Konstantin Sokolov, Chairman of Pelagos Data Centres, comments, "The scale of this project marks a new chapter for Gibraltar and for Europe's digital capabilities.
"Just as electricity and the internet transformed society in the past, AI is now emerging as the defining technology of our time with the power to redefine entire industries, economies, and communities.
"With our new facility, Pelagos Data Centres is laying the foundation for the next era of AI-driven innovation, positioning Gibraltar as a strategic hub and enabling Europe's brightest minds to unlock the full potential of this revolutionary technology."
Chief Minister Fabian Picardo adds, "I am delighted that Pelagos Data Centres have decided that Gibraltar is the place to establish their first facility and that the whole community will benefit from their massive investment and its huge economic impact.
"I look forward to this project becoming a reality as soon as possible."
Jobs, efficiency, and sustainability
The development is expected to create up to 500 jobs during construction and around 100 permanent positions once operational. Pelagos currently employs 50 full-time staff across London and Gibraltar, and plans to expand its local workforce significantly.
The facility will be built to Tier III standards, carrier-neutral, and designed to serve both public and private sector clients. It will pursue international certifications covering information security, quality, sustainability, and energy management, with a targeted Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) of 1.2 or better.
The project’s sustainability strategy includes powering operations with a combination of renewable energy and liquefied natural gas (LNG), with the aim of achieving net-zero operational emissions by 2030.
Cooling systems will be designed to minimise water use, and the company is exploring heat recovery options to support community projects.
Sir Joe Bossano, Minister for Economic Development and Inward Investment, says, "This is the most significant infrastructure investment in Gibraltar since the early 1990s, when the GSLP Government brought state-of-the-art telecommunications as inward investment from the United States and made possible the creation of a centre for online services. Then, we future-proofed Gibraltar's economy. Today, we are doing so again.
"The technology of the future - on which every advanced economy will depend - will be artificial intelligence. AI requires data, processing power, and energy resources on a scale never before seen.
"The Ministry for Economic Development will put all its resources at the service of this initiative to ensure that it is delivered in the shortest possible time. In this field, speed of delivery is everything. Gibraltar should be the fastest jurisdiction on the planet when it comes to delivery."
A further technical briefing and press conference is planned for the first quarter of 2026, ahead of construction beginning later that year.
Joe Peck - 5 September 2025
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
Modular Data Centres in the UK: Scalable, Smart Infrastructure
News
Duos Edge AI awarded patent for modular DC entryway
The US Patent and Trademark Office has granted Duos Edge AI, a provider of edge data centre (EDC) systems, a patent for a new entryway design for modular data centres.
The system aims to improve security and protect mission-critical equipment by combining a two-door access configuration with filtration to reduce the intrusion of dust, dirt, and moisture.
Duos Edge AI, a subsidiary of Duos Technologies Group, develops modular edge data centres intended to provide reliable, low-latency data access in areas where traditional infrastructure is limited.
The patented entryway is designed to support these facilities in remote or rural locations by improving equipment resilience and service uptime.
Supporting communities
The company’s edge data centres are used by schools, hospitals, warehouses, carriers, and first responders. By enhancing environmental protection for infrastructure, the new design is expected to strengthen operational continuity in sectors that depend on constant access to digital services.
Doug Recker, President and founder of Duos Edge AI, says, "This patent demonstrates our commitment to delivering ruggedised, field-ready edge data centres that meet the unique needs of rural and underserved markets.
"By addressing critical challenges like environmental intrusion, we are setting a higher standard for reliability and long-term value for our customers."
The modular approach aligns with Duos Edge AI’s wider focus on delivering scalable, rapidly deployable facilities that move data processing closer to users. This can help reduce latency, support real-time applications, and expand digital access in regions with growing demand.
For more from Duos Edge AI, click here.
Joe Peck - 4 September 2025
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
News
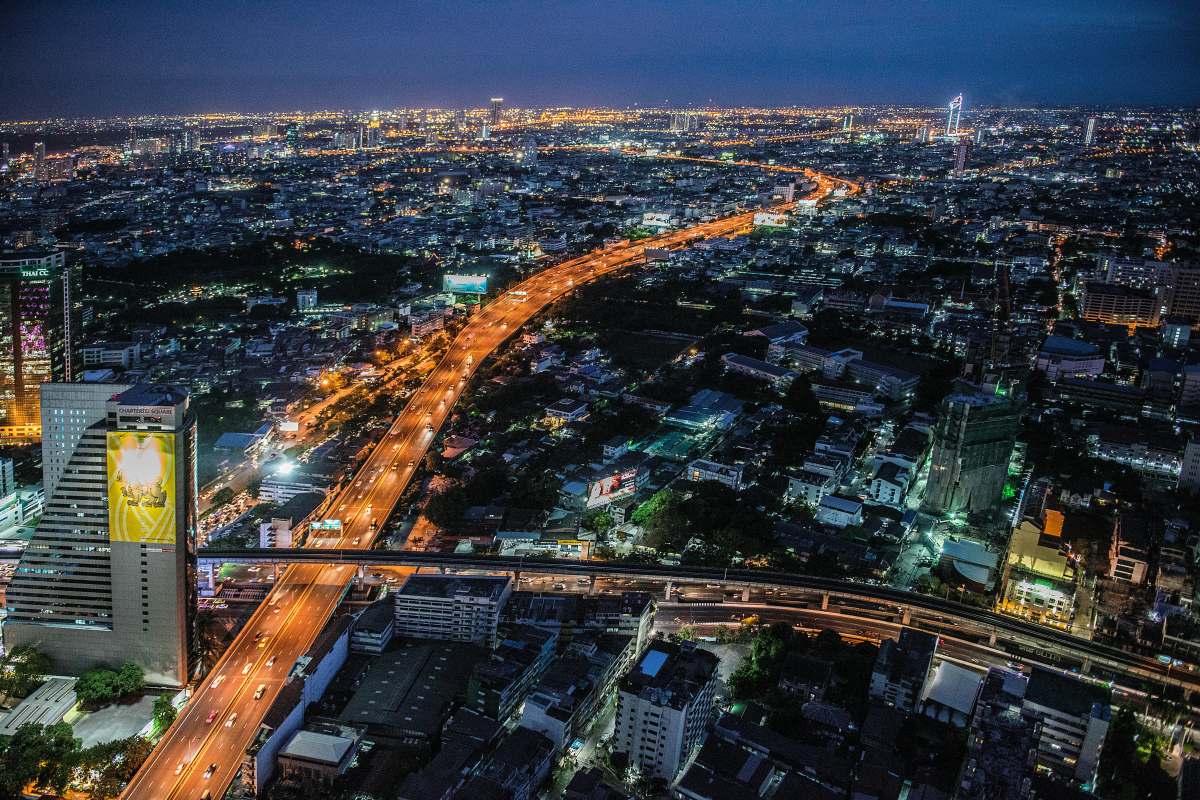
Telehouse Thailand & NT to enhance ASEAN connectivity
Telehouse Thailand, a provider of data centre colocation services, has partnered with National Telecom (NT) to enhance international data transmission via submarine cable systems.
The collaboration aims to reinforce the country’s telecommunications backbone and support digital transformation across both public and private sectors.
The agreement links NT’s international submarine cable network directly to the Telehouse Bangkok data centre, which is now fully operational. This connection allows Telehouse Thailand to provide domestic content providers and internet service providers (ISPs) from neighbouring countries with access to the Asia Direct Cable (ADC) and Asia America Gateway (AAG) systems.
The ADC network connects China, Hong Kong, Japan, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam, while the AAG network extends from Asia to the United States. Together, these systems link key data centre locations hosting major cloud and content providers, and establish direct connections with global markets.
NT’s domestic submarine cable system offers alternative routing through Thailand’s Gulf coast to its international landing stations in Songkhla and Satun, supporting reliable connectivity across multiple regions.
Strengthening Thailand’s digital infrastructure
Alongside benefits for private companies and public organisations, the partnership supports the Thai government’s aim of positioning the country as an ASEAN Digital Hub, encouraging investment and enabling regional digital growth.
Colonel Sanpachai Huvanandana, President of NT, says, "This collaboration expands Thailand’s business potential and telecommunications readiness in the AI era.
"With terabit-scale capacity and high-reliability network design, our international connectivity infrastructure addresses the critical requirements of global cloud and content providers when considering investment in Thai data centre facilities."
Ken Miyashita, Managing Director of Telehouse Thailand, adds, "Leveraging NT’s submarine cable network, a core element of Thailand’s telecommunications infrastructure, enables our customers to efficiently handle the huge volumes of data traffic from Gen AI and cloud services, which are expected to significantly grow.
"As Bangkok’s leading carrier-neutral interconnection data centre, Telehouse further strengthens this submarine connectivity and high service availability with the four diverse incoming fibre routes."
For more from Telehouse, click here.
Joe Peck - 4 September 2025
Data Centres
Events
News
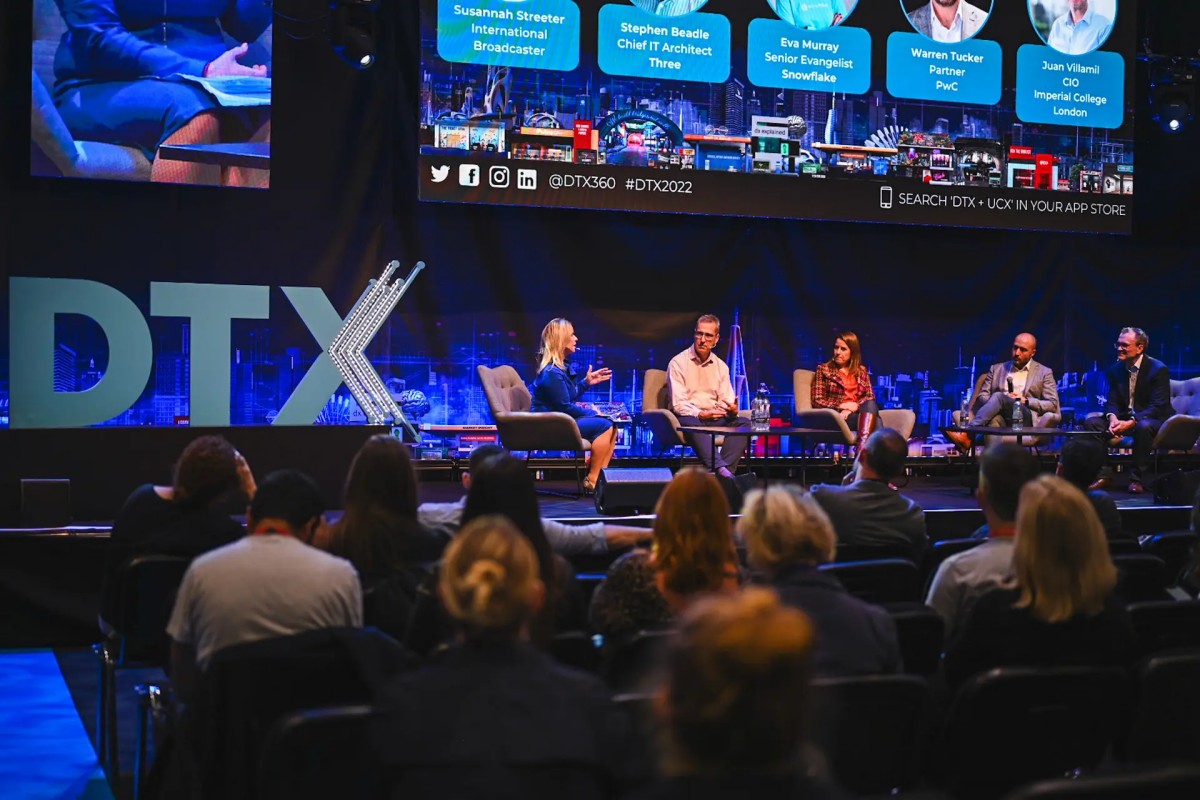
DTX London 2025 returns
DTX London, a UK event dedicated to business transformation, will open its doors at ExCeL on 1-2 October 2025 for its 20th anniversary.
Dedicated to ‘Innovation with integrity; driving value, delivering purpose’, this year’s event will showcase a lineup of prominent speakers, including Olympic Champion Mo Farah, who will "help technology teams establish the skills, mindsets, and tools to tackle transformation challenges, enhance experiences, and fuel growth."
The operators say DTX 2025 has been "reimagined to unite the people, technologies, and strategies that drive purposeful, long-term business change." Every stage is built around the real-world challenges facing organisations today, while offering an educational programme which highlights the importance of people in achieving successful business transformation.
The Main Stage will host technology experts from the newly formed DTX Advisory Board. These senior leaders - from organisations including Segro, Apollo, Santander, Vanquis, the NFL, and RSA - are driving digital and business transformation across the UK. They will share practical insights and first-hand experience on delivering projects designed for long-term success.
Highlight speakers include athlete Mo Farah, who will open the event on day one, discussing how business leaders can turn their aspirations into groundbreaking realities; Jason Hardy, CTO for AI at Hitachi Vantara, who will speak on the Data & AI Stage, discussing why AI’s future depends on data integrity; and Alan Reed, Head of Platform Innovation at bet365, who will discuss why most AI initiatives fail and how to beat the odds.
While cyber has traditionally had its own dedicated part of the show, this year’s event will see the topic weaved across all stages with a big focus on human-cyber risk. This reflects the real-world reality that cyber is not solely the responsibility of security teams; it's a business-wide priority that affects every department and technology initiative, carrying serious consequences if overlooked.
One of many panels on the Holistic Cyber Strategies Stage will feature experts from Deliveroo and Citi, discussing how AI can be implemented responsibly without neglecting security, and Moona Ederveen, Principal Consultant at Information Security Forum, who will also present on how organisations cut through the hype around quantum threats and build a realistic roadmap for readiness.
The Main Stage will tackle the most pressing themes from navigating geopolitical impacts to building the future workforce, featuring a panel of C-level executives from Vanquis, the University of East London, and Lloyds Banking Group discussing how to align tech leadership for strategic impact.
Attendees will also be treated to a session from UK Editor Bryan Glick of Computer Weekly. His publication is responsible for uncovering and reporting on the Post Office scandal, spotlighting injustice while actively campaigning to overturn wrongful convictions. Bryan will take to the Main Stage for a fireside chat with Sharon Gunn, Chief Executive for BCS, on day one, discussing lessons learned from Computer Weekly’s 16-year reporting on the scandal, while also highlighting the important role of people in technology.
This year’s DTX - which is once again colocated with Unified Communications Expo (UCX) - is centred around the importance of people in business and digital evolution, exploring how people, platforms, and processes come together to accelerate real transformation. It is the place to hear about how businesses can leverage the latest technology advances for every job function, from developers to cyber teams and everyone in between, all under one roof.
DTX + UCX is designed for anyone influencing technology selection and implementation, helping them discover innovation and find solutions that drive measurable business benefits.
Why attend DTX + UCX London
• Purpose-driven technology sourcing — See the latest innovations and discover the technologies and solutions that support your business objectives. Gain insights into emerging trends and best practices for leveraging technology to drive efficiency and growth.
• Connecting teams & bridging silos — Foster collaboration and knowledge sharing by connecting with leading tech teams and experts. Forge valuable partnerships, break down internal silos, and unlock the collective potential of your organisation.
• Meaningful conversations & networking — Engage with industry leaders, peers, and technology providers. Build strategic relationships, explore innovative solutions, and gain valuable perspectives that will shape your business transformation journey.
• Driving measurable benefit — Translate technology investments into tangible business outcomes. Learn how to optimise processes, enhance customer experiences, and generate sustainable growth through strategic technology adoption.
To guarantee a front-row seat and join the game-changers and tech pioneers at this year’s event, get your free pass here.
Access the full agenda here.
For more from DTX, click here.
Joe Peck - 4 September 2025
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
News
84% of businesses report rising network outages
Nearly nine in ten organisations have experienced an increase in network outages over the past two years, with more than a quarter reporting increases of 25% to 50%, according to new research from Opengear, a developer of remote infrastructure management systems and a Digi International company.
The rise in outages has reportedly cost more than a third of businesses between $1 million (£744,000) and $5 million (£3.7 million) in the past year alone. Over half of organisations also noted a 10-24% increase in outages over the two-year timeframe.
The survey, designed to identify critical pain points affecting data centre operations, polled over 1,000 CIOs, CSOs, and network engineers across the UK, US, France, Germany, and Australia. The survey highlights how network outages are causing significant disruptions across data centre operations, affecting everything from system availability to business continuity.
What the research shows
Network engineers identified the most common causes of these outages as device configuration changes (highlighted by 27%) and server hardware failures (referenced by 26%), both of which can severely impact the stability and performance of data centres.
To mitigate these risks, nearly a third of organisations (32%) rank AI and machine learning technologies among the technologies they have primarily invested in to support data centre operations. At the same time, 30% expect to increase spending on Out-of-Band (OOB) management solutions over the next five years to meet this same goal.
Patrick Quirk, President and General Manager, Opengear, says, “Outages are no longer isolated events; they are happening more often and the cost is hitting businesses hard. Complexity, ageing infrastructure, human error, and cyberattacks are all part of the problem.
"Governments are starting to take notice too, putting policies in place to protect critical digital infrastructure. As organisations lean more heavily on data centres to power digital transformation, the stakes are higher than ever. An outage is not just downtime; it is lost revenue, lost productivity, and lost trust.
“Forward-looking businesses are not standing still; they are rethinking their strategies to build resilience into every layer of their operations. One clear shift is towards decentralisation, pushing workloads closer to where data is generated and consumed. That move reduces risk from a single point of failure, but it also demands new approaches to management and security.”
As businesses adopt decentralised data processing models, 28% of organisations view the shift to edge computing and distributed networks as a trend that will significantly impact network management within their data centres over the next five years.
This move towards edge computing further reflects the broader trend of decentralisation in network architecture, which - while offering operational efficiencies - requires more sophisticated management systems to handle the increased complexity of data centre operations.
According to Patrick, “Edge computing brings clear advantages in speed, security, and efficiency, but it does not make the job easier. Distributed environments create more moving parts, and that means more opportunity for failure if they are not managed properly.
"The answer is a resilient foundation and secure remote management that keeps infrastructure reachable and under control, no matter where it is deployed.”
Joe Peck - 3 September 2025
Artificial Intelligence in Data Centre Operations
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
News
World's first AI internet exchange launched by DE-CIX
DE-CIX, an internet exchange (IX) operator, has announced the launch of what it calls the world’s first AI Internet Exchange (AI-IX), making its global network of internet exchanges “AI-ready.”
The company has completed the first phase of the rollout, connecting more than 50 AI-related networks – including providers of AI inference and GPU services, alongside a range of cloud platforms – to its ecosystem.
DE-CIX says it now operates over 160 cloud on-ramps globally, supported by its proprietary multi-AI routing system. The new exchange capabilities are available across all DE-CIX locations worldwide, including its flagship site in Frankfurt.
Two-phase rollout
The second phase of deployment will see DE-CIX AI-IX made Ultra Ethernet-ready, designed to support geographically distributed AI training as workloads move away from large centralised data centres. Once complete, the operator says it will be the first to offer an exchange capable of supporting both AI inference and AI training.
AI inference – where trained models are applied in real-world use cases – depends on low-latency, high-security connections. According to DE-CIX CEO Ivo Ivanov, the growth of AI agents and AI-enabled devices is creating new demand for direct interconnection.
“This is the core benefit of the DE-CIX AI-IX, which uses the unique DE-CIX AI router to enable seamless multi-agent inference for today’s complex use-cases and tomorrow’s innovation in all industry segments,” Ivo says.
Ultra ethernet and AI training
Phase two focuses on AI model training. DE-CIX CTO Thomas King says that Ultra Ethernet, a new networking protocol optimised for AI, will enable disaggregated computing across metropolitan areas. This could reduce reliance on centralised data centres and create more cost-effective, resilient private AI infrastructure.
“Until now, huge, centralised data centres have been needed to quickly process AI computing loads on parallel clusters,” Thomas explains. “Ultra Ethernet is driving the trend towards disaggregated computing, enabling AI training to be carried out in a geographically distributed manner.”
DE-CIX hardware is already compatible with Ultra Ethernet and the operator plans to introduce it once network equipment vendors make the necessary software features available.
For more from DE-CIX, click here.
Joe Peck - 3 September 2025
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
News
Products
rConfig launches Version 8 of its network configuration platform
Irish software developer rConfig has announced the release of Version 8 of its network configuration and compliance management platform.
The update introduces a new distributed architecture, enhanced security features, and broader vendor support. It has been designed to support large-scale environments, with capacity for more than 20,000 devices and faster search and compliance processes.
Key Features in Version 8
• Vector architecture — Distributed collection and multi-tenant scalability for managed service providers and large enterprises
• Security and compliance — Expanded policy frameworks, encrypted configuration storage, and reporting designed to meet regulatory requirements
• Performance — Proven capability to manage 20,000+ devices with faster compliance execution
• Vendor support — Broad compatibility without restrictions
Positioning in the Market
The company says the platform combines its open-source heritage with enterprise-level capability. Its distributed design, focus on compliance automation, and multi-vendor support aim to make it suitable for sectors including telecommunications, manufacturing, energy, and government.
rConfig is also developing AI-driven features, including automated compliance baselines, anomaly detection, and predictive analytics to support proactive network management.
Industry Collaboration
The company will be a Platinum Partner at Zabbix Summit 2025 in Riga this October, where it will demonstrate how Version 8 integrates with Zabbix for real-time configuration monitoring and compliance.
“With V8, we’ve set a new standard for the industry,” claims Stephen Stack, CTO of rConfig. “Our customers demanded speed, compliance, and distributed scale – we delivered. And with AI-driven innovation and our deepening partnership with Zabbix, we’re excited to lead the next chapter of network automation.”
Joe Peck - 2 September 2025
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
News
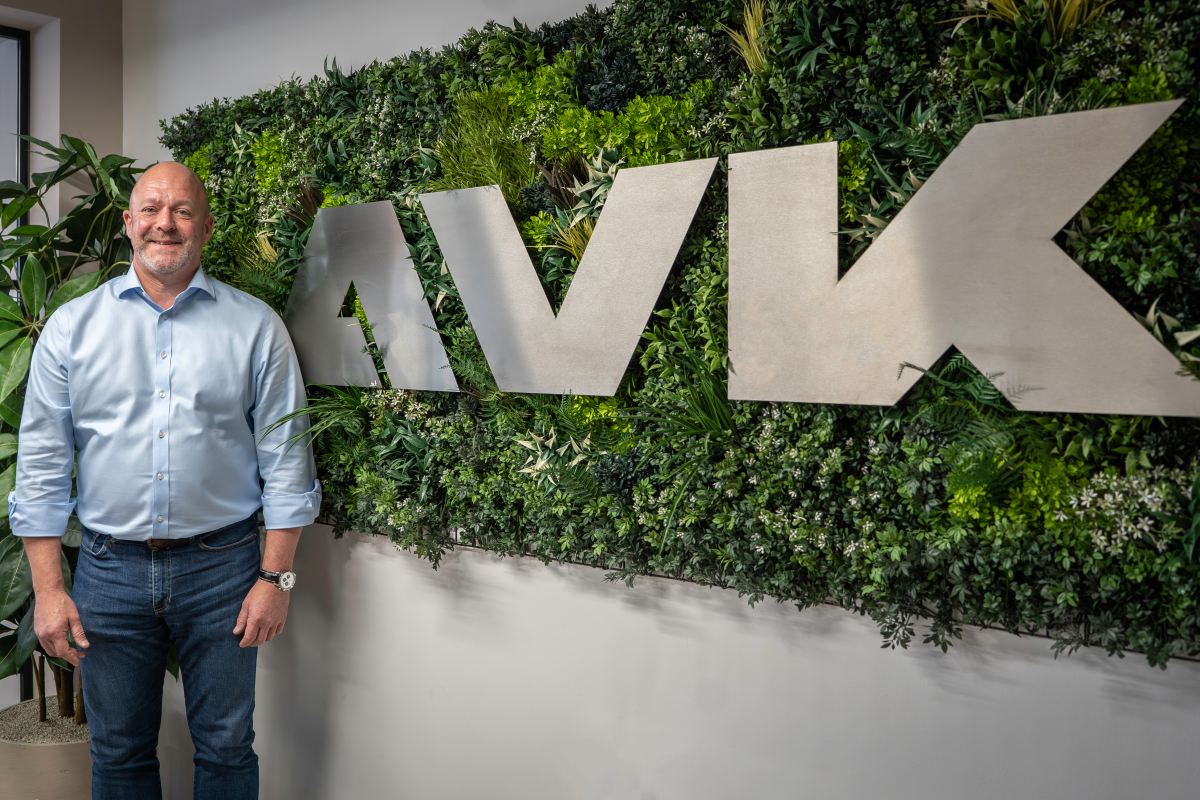
AVK appoints new Chief Operating Officer
AVK, a UK provider of power systems and electrical infrastructure for data centres, has announced the appointment of Paul Hood as its new Chief Operating Officer (COO). He brings extensive experience from senior roles in the data centre sector, including positions at Yondr Group, Pure Data Centres Group, Barclays, and JP Morgan.
Paul was formerly Managing Director and then COO of Yondr Group, and Global Operations Director and MD (Africa region) at Pure Data Centres Group. His career also includes 13 years at JP Morgan, where he oversaw the company’s entire data centre infrastructure across Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, managing an annual budget of $90 million (£67 million).
Industry experience
Paul’s background is rooted in systems and control engineering for building services, later expanding to building electrical systems management. He has also planned and administered multi-million-pound engineering budgets, conducted inspections in health, safety, and fire prevention, and co-founded the Universal Technical College network of STEM-focused schools.
Ben Pritchard, CEO of AVK, comments, “I am genuinely excited about Paul joining our team. He has a superb engineering brain, he is a very logical thinker, and he has a real passion for working hard. Essentially, he believes in what he does. Paul doesn’t just bring vast global experience to AVK; he is a leader who has done it all.”
Paul says, “I’ve known AVK for 30 years and I understand exactly where the company has come from and where it is going in this incredibly competitive industry. I am delighted to be working with some of the most committed infrastructure engineers in the world. I’m also known for investing in people, getting decisions done, and getting things over the line, and I’m truly excited about my forthcoming journey at AVK.”
Future role at AVK
Paul’s appointment comes as AVK pursues growth in integrated power infrastructure for data centres, including prime power, microgrids, standby, and modular energy systems. He is expected to play a key role in expanding service and maintenance operations, developing client relationships, and supporting long-term partnerships.
For more from AVK, click here.
Joe Peck - 2 September 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Insights into Data Centre Investment & Market Growth
News
Renewables and Energy: Infrastructure Builds Driving Sustainable Power
Inspired, VIRTUS sign wind-powered tri-party CPPA
Inspired, a UK commercial energy and sustainability advisory firm, has announced the signing of a tri-party corporate power purchase agreement (CPPA) with VIRTUS Data Centres, a UK data centre provider, and Lynn and Inner Dowsing (LID) windfarms.
VIRTUS has subscribed to a combined power purchase agreement (PPA) totalling 31MW of wind power, representing 16% of the total generation from Lynn and Inner Dowsing (LID) offshore windfarms, with a commencement date of 1 October 2025. This agreement seeks to ensure a long-term supply of renewable energy.
The agreement
A CPPA is a long-term energy contract between a corporate customer and a renewable power generator/developer. They are becoming an increasingly popular choice for companies wanting to reach net zero as they offer up to 100% renewable power.
Having a CPPA means the energy businesses use can be traced back to a specific renewable energy project, such as a wind or solar farm, which feeds an equivalent amount of power into the grid.
David Cockshott, Chief Commercial Officer at Inspired, says, “Inspired has been proud to partner with VIRTUS as their dedicated energy consultant. We are excited to continue supporting their sustainable journey and to commence this tri-party agreement, which allows renewable power to flow directly to their data centres.”
Helen Kinsman, SVP Commercial and Regulatory Affairs at VIRTUS, adds, “As an energy intensive user, we know it’s our responsibility to minimise the environmental impact from all our data centre facilities. Hence, since going live with our first site in 2011, we have been procuring power from 100% renewable sources.
"We are committed to delivering reliable, resilient, and responsible digital infrastructure to our customers and operate the gold standard in sustainable data centres in the UK and Europe.”
The renewable power will be delivered by Lynn and Inner Dowsing (LID) offshore windfarms, owned by funds managed by Macquarie Asset Management. Macquarie Asset Management is supported by XceCo, a UK asset management company specialising in the full project life cycle of renewable energy ventures.
The offshore wind farms are located 5km off the east coast of England, by the town of Skegness in Lincolnshire.
Bailey Bradley, Managing Director and co-founder XceCo, comments, “The successful delivery of this CPPA for one of our offshore wind farm assets under management stands as a testament to the exceptional collaboration between XceCo and all stakeholders involved in delivering this transaction.
"The commercial complexities involved in delivering this CPPA have proven to be a great experience. Through painstaking efforts, continuous multi-party engagements, a shared vision, and unwavering commitment, we turned a complex challenge into a powerful achievement, generating success together."
Inspired also provide a variety of additional services to VIRTUS as their dedicated energy and sustainability consultant.
For more from VIRTUS, click here.
Joe Peck - 2 September 2025
Commercial Real Estate: Property Developments, Trends & Infrastructure
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
News
NorthC completes acquisition of six Colt data centres
NorthC, a Dutch provider of sustainable data centre and colocation services, has finalised the acquisition of six data centres from multinational telecommunications company Colt Technology Services, taking over operations on 1 September 2025. The sites are located in Frankfurt, Berlin, Hamburg, Munich, and Düsseldorf in Germany, and in Amsterdam in the Netherlands.
The acquisition adds more than 25MW of capacity to NorthC’s platform and expands its presence in both the Benelux and DACH regions. In Germany, the deal increases the company’s footprint to seven data centres in total, while simultaneously boosting capacity in Amsterdam, a key connectivity hub.
Expansion in Germany and the Netherlands
NorthC says it plans to invest further in the newly acquired sites to expand capacity and improve efficiency and sustainability. The sites will be integrated into the company’s platform and aligned with its operational and service standards. Customers will also gain access to NorthC’s digital services, including the MyNorthC self-service portal.
Alexandra Schless, CEO of NorthC Group, comments, “Today marks a major milestone in NorthC’s mission to build the premier regional data centre platform in Northwestern Europe. The integration of these six strategic sites accelerates our expansion, particularly in Germany, enabling us to support customers across all major metropolitan regions with scalable, secure, and sustainable digital infrastructure.”
Customers and continuity
Colt Technology Services will remain a long-term customer at the acquired facilities, which NorthC says will ensure continuity of service.
The company adds that the new sites are in regions with strong connectivity and growing demand for digital infrastructure, allowing it to better serve enterprises, cloud and IT providers, and public sector organisations with cross-border operations.
For more from NorthC, click here.
Joe Peck - 1 September 2025

Head office & Accounts:
Suite 14, 6-8 Revenge Road, Lordswood
Kent ME5 8UD
T: +44 (0)1634 673163
F: +44 (0)1634 673173