News
Data Centres
Events
News
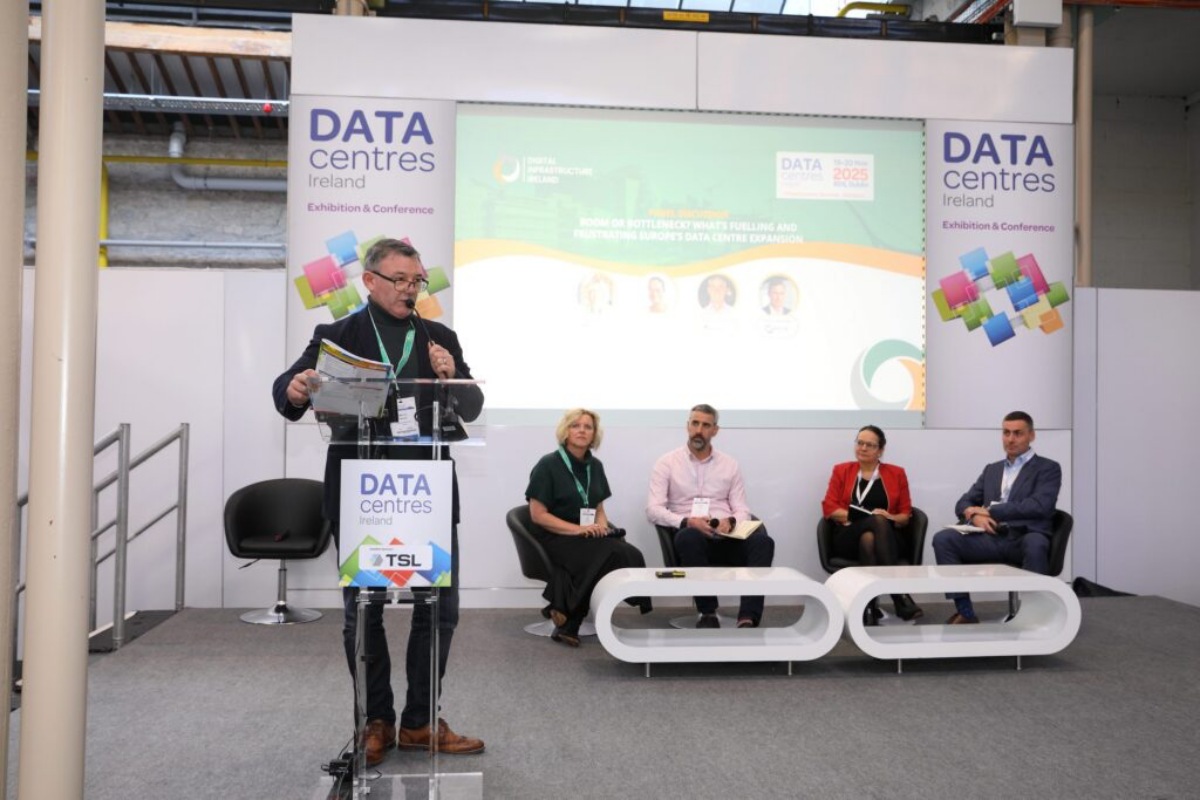
A round-up of DataCentres Ireland 2025
DataCentres Ireland was again heralded as a success by the exhibitors, alongside many of the visitors and speakers, as it delivered more attendees, more content, and more delegates than ever before.
The total attendance was up 23.0% YoY over the two days of the event, delivering to over 3000 people interested in the sector.
Louisa Cilenti, Chief Legal Officer at Clear Decisions, notes, “DataCentres Ireland was an outstanding forum to get underneath the strategic issues shaping Ireland’s future as a global data centre hub.
"From Minister Dooley’s address to the highly practical breakout sessions, the day struck the perfect balance between policy depth and real-world innovation.
"The relaxed venue made meaningful networking effortless and, as a startup, Clear Decisions really valued the genuine peer environment. A fantastic event that brings the whole ecosystem into one conversation.”
Day 1 was busy from the outset. Starting with a keynote address from Minister of State Timmy Dooley TD detailing the Irish Government recognising the essential nature of data centres in modern society and its wish to work with the data centre community both for the leveraging of AI as well as recognising the impact of data centres in attracting foreign direct investment.
Day 1 saw a massive 34.7% growth on attendance YoY, with exhibitors and attendees commenting on the buzz in the exhibition hall.
Day 2 had a slower start, though footfall built with a good feeling in the hall. The event delivered over 600 new individuals for exhibitors to network and do business with, which were similar numbers to those achieved on Day 2 in 2024.
This was the largest visitor and total attendance in the event's 15-year history, delivering over 3000 attendees across the two days.
The number of exhibitors also grew, with the exhibition featuring over 140 individual stands and showcasing more than 180 companies and thousands of brands.
An event of opportunities
Exhibitors and attendees acknowledged that DataCentres Ireland provided a professional business environment where people were able to network with colleagues; see the latest in products, services, technology, and equipment; and listen to industry leaders and experts discussing the latest issues, approaches, and ideas affecting data centres and critical environments.
Paul Flanagan, EMEA Regional Director West, Camfil, comments, “As usual, a well-organised event by Stepex. Great variety of exhibitors and visitors, so plenty of networking opportunities along with being able to see all the latest and greatest technologies and services available on the market today.
"The data centre segment is getting smarter and more collaborative, and this event guarantees any visitor the opportunity to appreciate that in many ways.
Exhibitors commented on the quality of attendees present at DataCentres Ireland and lack of 'time wasters' at the show, giving them more time to engage with buyers, discuss their needs, and forge lasting business contacts and relationships.
The conference programme featured 90 international and local experts and industry leaders. The conference addressed a wide range of issues from data centre development, regionalisation, training and staff retention, the impact of AI on data centres, as well as decarbonisation, energy reduction, and heat re-use.
One of the many highlights was an insightful presentation by Mark Foley, CEO of Mark Foley Strategic Solutions, on the state of the Irish grid network and what could be actioned to make this grid more flexible for data centres. All presentations were broadly supportive of data centres and their continued development in Ireland.
Mark comments, “An excellent conference at a challenging time for the sector in Ireland. The key issues were discussed and practical and innovative solutions are now emerging if Government and regulators make the right decisions.”
For more from DataCentres Ireland, click here.
Joe Peck - 3 December 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
News
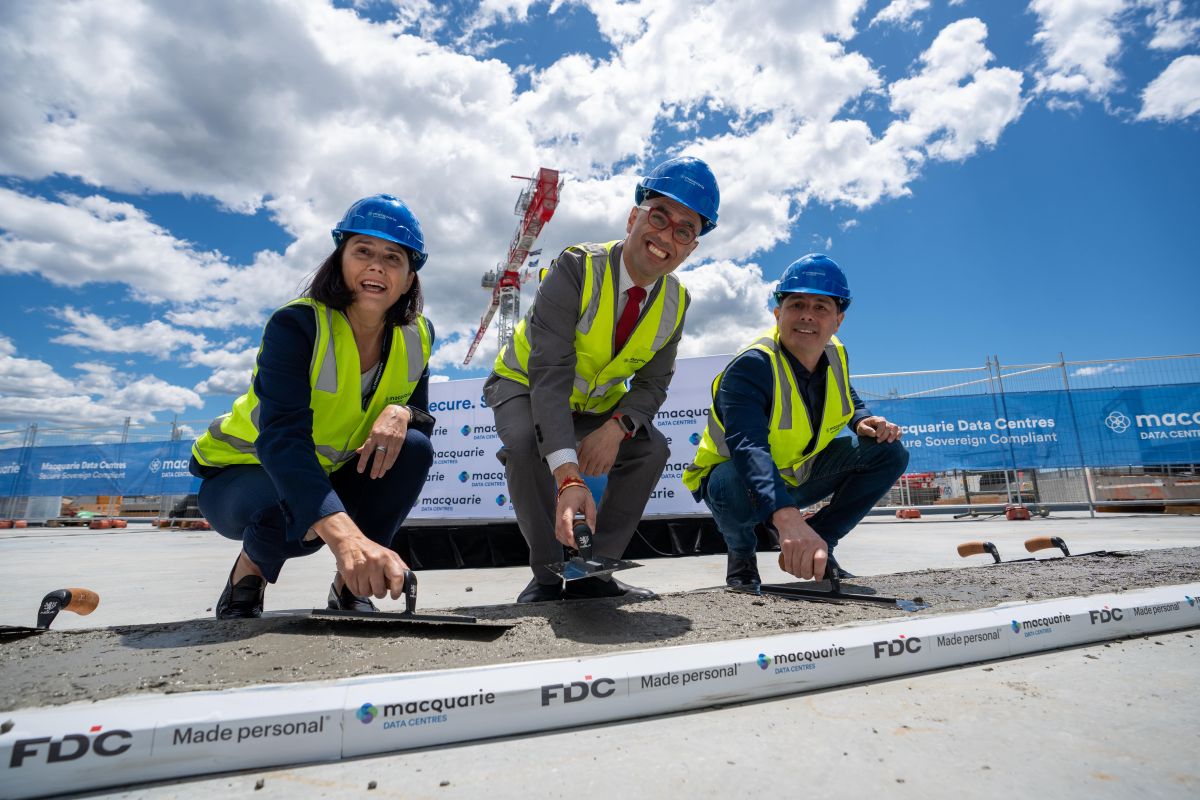
Macquarie tops out $350M, 47MW AI data centre
The New South Wales Treasurer, Hon. Daniel Mookhey MP, today poured the final concrete on Macquarie Data Centres’ newest 47 megawatt (MW) facility, IC3 Super West. The ceremony marks the completion of the building’s external structure and a major milestone toward its scheduled opening in September 2026.
IC3 Super West will be the only data centre to add new AI capacity to Sydney’s north zone in 2026, Macquarie states. With all the end-state power already secured, the facility is being purpose-built to meet the growing demands from hyperscalers, enterprise and neoclouds for GPU and high-performance computing capacity in the Tier 1 hub. The facility is part of Macquarie Data Centres’ 200MW development pipeline adding more AI and cloud capacity to the market.
NSW Treasurer, Hon. Daniel Mookhey MP, says, “Companies like Macquarie Data Centres keep investing, keep expanding, and keep believing that NSW can be a global home for high-tech infrastructure. And it happens because the government has chosen to take planning and investment delivery seriously.
“In the years ahead, thousands of businesses will run smarter because this building exists. Research will accelerate because this building exists. AI capability will expand because this building exists. And NSW will be more competitive – globally competitive – because this building exists.”
Sydney is seeking to cement its position as a leading hub for AI, cloud and digital innovation, supported by new initiatives such as the NSW Government’s new Investment Delivery Authority - which aims to accelerate future technology infrastructure projects like Macquarie Data Centres’ recently announced 150MW planned site.
Macquarie Data Centres Group Executive, David Hirst, comments, “IC3 Super West is the next data centre in our pipeline of sites planned to add circa 200MW of AI and cloud capacity in Sydney. Demand for high-density AI infrastructure is the most significant megatrend we’ve seen in over 25 years in the data centre industry. IC3 Super West, opening in Q3 2026, is purpose-built for the high-density power and liquid cooling demands of new AI technology. Sovereign data centres keep Australia competitive in the global market and are the foundation of our AI future.”
IC3 Super West is the third facility to be built at the leading provider’s 65MW Macquarie Park Data Centre Campus in Sydney’s north zone and is designed to support a hybrid mix of air and liquid cooling for direct-to-chip, high-density AI and cloud workloads. Phase 1 of the build is a circa $350 million investment and will deliver the complete core and shell with 6MW IT load fitted out.
For more from Macquarie, click here.
Simon Rowley - 2 December 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
News
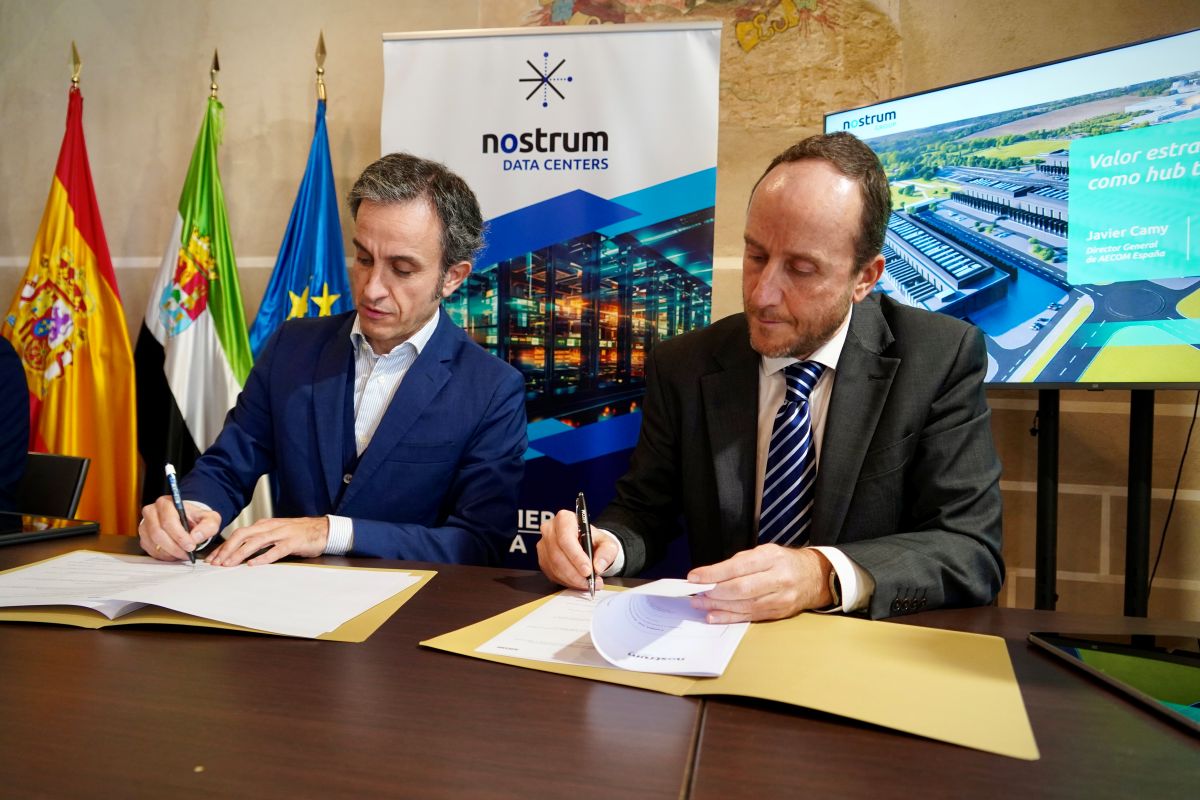
AECOM appointed to deliver data centre in Spain
AECOM, a global infrastructure specialist, today announced it has been selected by Nostrum Data Centers (an affiliate of Nostrum Group) to lead the design and construction management of a new data centre in Badajoz, Spain. With an investment exceeding €1.9 billion, ‘Nostrum Evergreen’ is reportedly one of Spain’s most ambitious digital infrastructures projects, with capacity expected to reach 500 megawatts, supporting the rapid growth of AI across Europe.
The first phase includes the design and construction of data halls and the critical operational infrastructure, with an initial capacity of 150 million watts of electric capacity (MWe). The second phase, which will allow the site to reach 300 MWe, is scheduled to begin in early 2029. The complex’s design will enable scalability up to 500 MWe, making it one of the most ambitious facilities in southern Europe. A ‘next-generation’ campus, Nostrum Evergreen will also integrate advanced cooling systems and intelligent power consumption management.
"This data centre in Badajoz will have a total capacity similar to the combined capacity of all current operational data centres in Spain,” says Gabriel Nebreda, CEO of Nostrum Group. “Furthermore, we have set ourselves a very demanding deadline to start construction of this mega campus next year. Achieving this ambition is only possible through strategic partnerships with leading global players in the data centre sector. We are very pleased to announce this agreement with AECOM, one of the most prestigious engineering firms, who have extensive experience in AI gigafactories worldwide."
"We are delighted to collaborate with Nostrum Group on this project, which will become an international benchmark in data centres,” adds Javier Camy, Managing Director, Spain, AECOM. “At AECOM, we leverage our global capability in highly complex technical projects and our strong position in the sector to apply a transformative approach that ensures a sustainable, forward-thinking solution. This partnership reflects our ability to co-lead initiatives that redefine regions and enhance the global competitiveness of our clients."
“This is very positive news for the city and for the region as a whole. It represents a decisive opportunity for the development of Badajoz and highlights the dedication and strong commitment to our city, something we deeply value and appreciate,” notes Ignacio Gragera, Mayor of Badajoz.
The project, which expects to obtain its building permit by mid-2026, has already secured electrical capacity, without relying on the future Spanish Electrical Grid Development Plan 2025–2030. In addition, it boasts more than 200,000 square metres of ready-to-build industrial land in one of the region’s most advanced industrial parks. The site aims to position the Extremadura region as an emerging hub in the European data centre ecosystem.
For more from AECOM, click here.
Simon Rowley - 1 December 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
News
Sustainable Infrastructure: Building Resilient, Low-Carbon Projects
atNorth's DEN01 to supply district heating in Copenhagen
atNorth, an Icelandic operator of sustainable Nordic data centres, has agreed a partnership with Vestforbrænding, Denmark’s largest waste-to-energy company, to supply excess heat from its forthcoming DEN01 data centre campus into the district heating network serving Greater Copenhagen.
DEN01, a 22.5MW site in Ballerup, is scheduled to open in early 2026. Through the collaboration, warm water generated as a by-product of direct liquid cooling will be transferred into Vestforbrænding’s network from 2028.
The recovered heat is expected to support the heating of more than 8,000 homes, reducing energy consumption for local central heating and lowering emissions for both organisations.
Denmark has pursued decarbonisation for several years and has set a national target to become net zero by 2045, with a 110% emissions reduction target by 2050. Coal is being phased out of the district heating sector, and heat-reuse projects form part of the country’s circular economy strategy.
atNorth highlights that the initiative aligns with its wider approach to sustainable construction, energy efficiency, and community-focused development.
Vestforbrænding is expanding its network as part of its 2030 District Heating Plan, replacing oil and gas boilers across thousands of households and integrating new heat sources such as surplus heat from data centres.
Heat-reuse initiatives across the Nordics
Steen Neuchs Vedel, CEO of Vestforbrænding, says, “For many years, we have talked about surplus heat from data centres being part of the future. Now, the future is here.
“With today’s contract signing, we are showing the way forward for how surplus heat from data centres can reach people’s homes. There has also been talk about sector coupling in the district heating sector: today, we demonstrate how this can happen in practice, to the benefit of consumers.”
Eyjólfur Magnús Kristinsson, CEO at atNorth, adds, “As the demand for AI-ready digital infrastructure continues to increase, it is imperative that data centre companies scale in a responsible way.
“By actively seeking heat-reuse partnerships for our data centres, we can mitigate our environmental impact, benefit the communities in which we operate, and help clients decarbonise their IT workloads.”
The announcement follows atNorth’s partnership with Wa3rm, which plans to use waste heat from the company’s DEN02 site to support local vegetable production.
atNorth has also agreed a heat-reuse initiative with Kesko Corporation to supply recovered heat from its FIN02 site to a neighbouring store.
For more from atNorth, click here.
Joe Peck - 1 December 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
News
Subzero Engineering opens new Vietnam facility
Subzero Engineering, a provider of data centre containment systems, has expanded its global operations with a new facility in Ho Chi Minh City, strengthening its position in the Asia-Pacific market and supporting growing regional demand for data centre infrastructure.
The site will act as a central hub for APAC activities, reinforcing the company’s long-term presence in the region and improving proximity to partners and supply chains.
Midge Pan, General Manager, APAC, Subzero Engineering, comments, “This expansion is about more than infrastructure; it’s about proximity to our partners, agility in the supply chain, and speed to market.
“Vietnam offers a unique combination of talent, resilience, and strategic location that enables us to meet APAC’s growing demand for cutting-edge digital infrastructure.”
'Centre of excellence' for design and manufacturing
The Ho Chi Minh City facility will serve as a "centre of excellence" supporting global engineering teams. It will accommodate manufacturing, design, and research and development functions, and will produce Subzero’s containment systems, modular enclosures, aisle frames, and airflow management equipment.
Dedicated research and development space will also support the creation of technologies tailored to APAC’s fast-changing data centre market, including approaches aimed at AI, high-density computing, and sustainability.
Shane Kilfoil, President of Subzero Engineering, explains, “This new facility is a strategic cornerstone in Subzero’s global vision, designed to integrate localised innovation with global scale.
“By establishing a centre of excellence in Vietnam, we’re not just expanding our footprint; we’re embedding agility, resilience, and sustainability into the core of our operations.”
The company expects the site to create more than 50 skilled roles across engineering and technical disciplines. Subzero also plans to form partnerships with local universities and technical institutions to support training and internship programmes.
The facility has been developed within a building designed with sustainability features, including on-site solar generation, energy-efficient systems, and low-carbon construction methods.
Subzero says these measures reflect its wider environmental commitments and its focus on reducing operational impact.
With established operations across North America and Europe, the addition of the Vietnam site aims to strengthen the company’s global network. It also allows Subzero to offer more responsive support to regional customers as demand for new data centre capacity increases.
For more from Subzero Engineering, click here.
Joe Peck - 28 November 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
News
Pure DC secures approval for Madrid data centre
Pure Data Centres Group (Pure DC), a digital infrastructure organisation, has received final planning approval for the first phase of its €400 million Madrid data centre development, including a private substation.
The campus has a planned capacity of 70MW, with Phase 1 comprising a substation and a 30MW facility.
The project is expected to support digital demand across the region and strengthen local energy resilience. More than 400 construction roles will be created, with an emphasis on employing local firms.
Once operational, the site will provide more than 50 permanent technical and support positions and contribute to improvements in nearby power and telecommunications infrastructure.
Work is expected to begin this month, with early activity focused on connecting high-voltage lines from the Iberdrola power substation and constructing the new private substation.
Substation and modular data hall development
The private substation will use environmentally focused gas-insulated switchgear from Siemens. This equipment replaces traditional insulating gases with alternatives that avoid greenhouse gas emissions and toxic by-products.
Pure DC notes that the site will be among the first in Spain to use this type of switchgear.
The company anticipates completing the substation by early 2027, followed by phased construction of modular data halls. These halls will support high-density deployments and can be configured for either air or liquid cooling.
Both cooling approaches use closed-loop systems with zero operational water consumption.
Pedro L. Sanz, Mayor of Meco Municipality, comments, “This licence approval highlights the constructive dialogue and collaboration between Pure DC and our City Council.
"The project not only reinforces our city's position as a technology hub, but marks a mutual achievement that will boost employment and the digital future of our region.”
Dame Dawn Childs, CEO at Pure Data Centres, notes, “Like many major European cities, Madrid’s demand for digital infrastructure far out-strips the supply coming online.
“Pure DC’s ability to bring on new low-latency, high-quality capacity in such supply constrained locations demonstrates our capability to deliver compelling partnerships for local authorities, potential customers, and our supply chain.”
Pure DC also plans to work with nearby communities, mirroring programmes in place at its other sites.
These include partnerships with schools and universities, training and careers initiatives, community outreach, and collaborations with local organisations on environmental projects.
For more from Pure DC, click here.
Joe Peck - 27 November 2025
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
Data Centre Software for Smarter Operations
News
Schneider joins OpenUSD alliance to advance digital twins
Global energy technology company Schneider Electric, alongside AVEVA and ETAP, has joined the Alliance for OpenUSD (AOUSD) to accelerate the development of interoperable digital twins and simulation-ready 3D assets for industrial environments.
The three companies join existing contributors such as NVIDIA, Pixar, Adobe, and Autodesk.
The announcement was made during Schneider Electric’s Innovation Summit North America in Las Vegas, which brought together more than 2,500 industry leaders to discuss the future of resilient and intelligent energy systems.
OpenUSD is an extensible framework designed to improve interoperability between software tools and data formats used to build virtual environments and industrial digital twins.
By joining the alliance, the three companies aim to advance open standards that support industrial simulation, collaborative design, and large-scale AI infrastructure planning.
Supporting next-generation digital twins
The collaboration aligns the companies more closely with NVIDIA’s vision for real-time, physically accurate digital twins that can model buildings, data centres, factories, and emerging AI infrastructure.
Many organisations now use NVIDIA Omniverse libraries to develop digital twin applications that optimise design, performance, and sustainability.
By adopting OpenUSD as a shared foundation, Schneider Electric, AVEVA, and ETAP aim to support new capabilities across:
• SimReady asset development, enabling interoperable models of physical infrastructure such as power and cooling systems for use in Omniverse-based simulations.
• Digital twin collaboration, allowing integrated views of complex systems, including data centres, energy networks, and industrial facilities built on platforms such as EcoStruxure, AVEVA, and ETAP.
• AI infrastructure planning, using tools including the NVIDIA Omniverse DSX Blueprint to support the co-design of gigawatt-scale AI factories.
These capabilities are intended to support more accurate modelling of thermal behaviour, power distribution, airflow, and other operational variables within data centres and industrial sites.
Jim Simonelli, Senior Vice President and Chief Technology Officer for Data Centres at Schneider Electric, comments, “Joining the Alliance allows us to contribute to a shared digital language that empowers collaboration, simulation, and innovation across the AI ecosystem.”
Rev Lebaredian, Vice President of Omniverse and Simulation Technology at NVIDIA, notes, “To efficiently design and operate complex systems like AI factories, industries need a robust, simulation-ready foundation.
"Schneider Electric’s expertise in energy management, hardware, and software, combined with NVIDIA Omniverse libraries, will accelerate the creation of the AI factories and intelligent grids of the future.”
Expanding long-term collaboration
The three companies have an established partnership with NVIDIA across digital twin development and AI infrastructure design.
They are co-developing reference architectures and integrated hardware and software approaches to support power, cooling, and energy management for next-generation AI factories.
At the recent GTC DC event, Schneider Electric was named as a power, cooling, and energy technology partner for the NVIDIA AI Factory Research Center, which is powered by the NVIDIA Vera Rubin platform.
The facility serves as a foundation for the Omniverse DSX Blueprint and supports research in generative AI, scientific computing, and advanced manufacturing.
In March 2025, ETAP by Schneider Electric released a new digital twin tool capable of accurately modelling the power requirements of AI factories.
For more from Schneider Electric, click here.
Joe Peck - 25 November 2025
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Insights into Data Centre Investment & Market Growth
News
atNorth expands team to meet AI demand
atNorth, an Icelandic operator of sustainable Nordic data centres, has established a new director-level structure within its development organisation, appointing four country leads to support the delivery of new high-density, AI-ready data centres across the Nordics.
The roles include one internal promotion and are intended to strengthen operational development as the company expands its regional footprint and continues to grow its portfolio of high-performance facilities, driven by rising demand for AI-focused infrastructure.
The new directors will oversee project delivery in Iceland, Finland, Denmark, and Sweden, ensuring consistency across design, construction, and commissioning activities.
The appointments
Hallgrímur Örn Arngrímsson has been appointed Director of Delivery for Iceland, responsible for end-to-end project execution. He brings more than 15 years of experience in civil engineering and infrastructure, including geotechnical engineering and large-scale civil works. His previous roles include senior positions at Verkís Consulting Engineers and Sweco Norge.
Toni Germano becomes Director of Delivery for Finland. With over 25 years of experience in digital transformation and infrastructure strategy, he will manage delivery operations across the country. He previously held leadership roles at Cisco, including serving as CTO for SP EMEAR North.
Dave O’Brien has been named Director of Delivery for Denmark. He has more than a decade of experience in data centre construction and engineering, including project management and electrical systems delivery. Before joining atNorth, he worked at Mercury, leading retrofit and new-build projects in Denmark.
Daniel Kolm, promoted internally, is the new Director of Delivery for Sweden. He joined atNorth in 2022 and has a background in mechanical engineering and energy systems. His previous experience includes roles at CBRE and DigiPlex, where he led multidisciplinary projects from initial study to commissioning.
Strengthening Nordic delivery capabilities
Together, the four directors support atNorth’s pan-Nordic delivery model, combining local market knowledge with regional coordination.
Their remit spans feasibility assessments, site acquisition, design, deployment, and operational readiness, supporting customers in hyperscale, enterprise, and AI-focused sectors.
Anna Kristín Pálsdóttir, Chief Development Officer at atNorth, comments, “We are pleased to welcome such a talented group of development professionals at this crucial time of accelerated growth.
“Their combined expertise ensures we are fully equipped to meet the demands of today’s compute-intensive workloads, whilst delivering projects with the speed, scalability, and quality that our customers expect.”
For more from atNorth, click here.
Joe Peck - 24 November 2025
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Data Centre Security: Protecting Infrastructure from Physical and Cyber Threats
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
Products
Security Risk Management for Data Centre Infrastructure
SPP Pumps brings fire and cooling experience to DCs
SPP Pumps, a manufacturer of centrifugal pumps and systems, and its subsidiary, SyncroFlo, have combined their fire protection and cooling capabilities to support the expanding data centre sector.
The companies aim to offer an integrated approach to pumping, fire suppression, and liquid cooling as operators and contractors face rising demand for large-scale, high-density facilities.
The combined portfolio draws on SPP’s nearly 150 years of engineering experience and SyncroFlo’s long history in pre-packaged pump system manufacturing.
With modern co-location and hyperscale facilities requiring hundreds of pumps on a single site, the companies state that the joint approach is intended to streamline procurement and project coordination for contractors, consultants, developers, and OEMs.
SPP’s offering spans pump equipment for liquid-cooled systems, cooling towers, chillers, CRAC and CRAH systems, water treatment, transformer cooling, heat recovery, and fire suppression. Its fire pump equipment is currently deployed across regulated markets, with SPP and SyncroFlo packages available to meet NFPA 20 requirements.
Integrated pump systems for construction efficiency
The company says its portfolio also includes pre-packaged pump systems that are modular and tailored to each project. These factory-tested units are designed to reduce installation time and simplify on-site coordination, helping to address construction schedules and cost pressures.
Tom Salmon, Group Business Development Manager for Data Centres at SPP and SyncroFlo, comments, “Both organisations have established strong credentials independently, with over 75 data centre projects delivered for the world’s largest operators.
"We’re now combining our group’s extensive fire suppression, HVAC, and cooling capabilities. By bringing together our complementary capabilities from SPP, SyncroFlo, and other companies in our group, we can now offer comprehensive solutions that cover an entire data centre's pumping requirements.”
John Santi, Vice President of Commercial Sales at SyncroFlo, adds, “Design consultants and contractors tell us lead time is critical. They cannot afford schedule delays. Our pre-packaged systems are factory-tested and ready for immediate commissioning.
"With our project delivery experience and expertise across fire suppression, cooling, and heat transfer combined under one roof, we eliminate the coordination headaches of managing multiple suppliers across different disciplines.”
Tom continues, “In many growth markets, data centres are now classified as critical national infrastructure, and rightly so. These facilities cannot afford downtime, and our experience with critical infrastructure positions us to best serve this market."
Joe Peck - 20 November 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
News
Sustainable Infrastructure: Building Resilient, Low-Carbon Projects
Verne, Nscale planning 15MW AI deployment in the Nordics
Verne, a provider of low-carbon high-performance data centres across the Nordics, has agreed a 15MW AI infrastructure deployment with hyperscaler Nscale, expanding high-density, renewable-powered computing capacity across its Icelandic campus.
The project centres on liquid-cooled GPU infrastructure and is set to run throughout 2026.
The installation will comprise around 4,600 NVIDIA Blackwell Ultra GPUs, with an 85% liquid-cooled and 15% air-cooled configuration designed to maximise efficiency within Verne’s existing facilities.
It is one of the region’s largest liquid-cooled GPU projects and is expected to support lower energy use and reduced environmental impact.
Iceland’s renewable electricity and natural free-cooling conditions position it as a suitable location for high-density AI workloads.
Nscale selected Verne based on its experience in renewable-powered data centres and its ability to support large-scale training and inference environments.
Large-scale renewable AI capacity across the region
“The pace of change in AI infrastructure is extraordinary," notes Dominic Ward, CEO of Verne. "As the demand for GPU capacity accelerates, availability of clean, renewable power has become as important as raw performance.
"Partnering with Nscale, whose expertise is redefining how AI infrastructure is delivered responsibly at scale, demonstrates how the Nordics are fast becoming a strategic hub for sustainable AI growth.”
Philippe Sachs, Chief Business Officer and President of EMEA at Nscale, adds, “As compute demand grows, we’ve worked with partners throughout the world and the Nordic region to deliver sustainable solutions to meet that demand.
"The Nordics offer a uniquely sustainable foundation: abundant renewable energy and natural cooling. With our existing operations in Norway, we’ve seen first-hand how the region powers low-carbon, sovereign-grade AI infrastructure."
David Hogan, Vice President Enterprise at NVIDIA, comments, “The collaboration between Verne and Nscale showcases how NVIDIA technology can enable high-performance AI factories with a focus on energy efficiency and sustainability.
"Deployments like this reflect how organisations are scaling the next generation of AI workloads responsibly, using innovative cooling and renewable-powered data centres.”
The agreement aligns with Verne’s wider European expansion, which includes new campuses planned in Finland and early-stage development activity in France.
The companies state that these projects contribute to the Nordics’ growing role as a centre for renewable-powered AI infrastructure.
For more from Verne, click here.
Joe Peck - 20 November 2025

Head office & Accounts:
Suite 14, 6-8 Revenge Road, Lordswood
Kent ME5 8UD
T: +44 (0)1634 673163
F: +44 (0)1634 673173