Data Centre Build News & Insights
Commercial Real Estate: Property Developments, Trends & Infrastructure
Data Centre Architecture Insights & Best Practices
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
InfraPartners, JLL partner to accelerate AI DC delivery
InfraPartners, a designer and builder of prefabricated AI data centres, and JLL, a global commercial real estate and investment management company, have formed a strategic agreement to accelerate the development and operation of AI data centres.
The partnership brings together InfraPartners’ prefabricated AI data centre designs and JLL’s capabilities in site selection, project management, construction oversight, financial structuring, and facilities management.
The companies state that the combined model is intended to address persistent challenges in data centre development, particularly the period between site identification and operational readiness.
As investment in AI infrastructure grows, operators increasingly require deployment models that offer predictable schedules, reduced risk, and scalable designs suitable for GPU-heavy environments.
Data centre construction continues to face risks associated with labour shortages, schedule delays, and complex financing.
InfraPartners and JLL say they aim to manage these issues jointly by integrating design, prefabrication, delivery, and long-term operations into a single framework.
Prefabrication and integrated delivery for AI infrastructure
“Our clients are asking for faster, lower-risk routes to delivering AI infrastructure,” says Michalis Grigoratos, CEO at InfraPartners. “Our prefabricated, upgradeable digital infrastructure integrates seamlessly with JLL’s expertise across the full project lifecycle, so, together, we’re focused on providing a superior product that keeps pace with AI infrastructure changes and market growth.
"Our globally scalable, repeatable approach includes site selection, prefabrication, and long-term operations, reducing time-to-first-token and maximising performance across the lifecycle.”
Matt Landek, JLL Division President, Data Centers and Critical Environments, adds, “AI infrastructure demands a new approach - one that’s as dynamic and high-performing as the workloads it supports.
“With InfraPartners, we are delivering a unique blueprint that brings real estate, engineering, and operational precision into a unified model.”
Kristen Vosmaer, Managing Director at JLL, oversees global programme management, including JLL White Space and facilities management solutions, and supports delivery of the partnership.
He comments, “This is one of the first collaborations to fully integrate data centre design, manufacturing, construction, commissioning, computer deployment, and lifecycle management for institutional-grade real estate delivery, marking a significant shift in shortening the time to monetisation for how mission-critical infrastructure assets are developed and maintained.”
The companies plan to offer end-to-end capabilities intended to accelerate the delivery of AI-ready facilities for enterprise, government, and cloud operators.
Initial deployment efforts will focus on high-growth AI markets in EMEA and the United States from Q1 2026, with plans to expand into additional regions.
For more from InfraPartners, click here.
Joe Peck - 21 November 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
Renewables and Energy: Infrastructure Builds Driving Sustainable Power
Terra Innovatum, Uvation agree micro-modular nuclear pilot
Terra Innovatum Global, a developer of micro-modular nuclear reactors, and Uvation, an integrated technology provider, have signed a Letter of Intent (LOI) to launch a 1MWe pilot programme of Terra Innovatum’s micro-modular nuclear technology, with an option to scale up to 100MWe.
The pilot is intended to support Uvation’s growing requirements for high-density AI and modular data centre infrastructure.
Terra Innovatum develops micro-modular nuclear reactors, while Uvation focuses on technology platforms designed for large-scale, performance-intensive AI workloads.
The companies state that behind-the-meter nuclear generation could provide a resilient and scalable alternative to grid-dependent power for data centre development.
Alessandro Petruzzi, co-founder and CEO at Terra Innovatum, comments, “Uvation’s data centre expansion requires infrastructure that is not only scalable, but fundamentally resilient.
"By integrating Terra Innovatum’s SOLO micro-modular reactor, we will offer a behind-the-meter energy source capable of delivering safe, stable, high-density power that traditional grids cannot guarantee.
"SOLO adds built-in safety and provides redundancy - important for data centres, de-risking energy deployment during maintenance or shutdowns, ensuring continuity independent of power shortages, and enhancing cybersecurity protection.
"This enables next-generation, high-performance modular data centres powered by a clean, uninterrupted energy backbone - unlocking new possibilities for AI, HPC, and mission-critical workloads.”
Nuclear as an alternative pathway for energy-constrained AI projects
Giordano Morichi, Founding Partner, Chief Business Development Officer and Investor Relations, adds, “As AI infrastructure outpaces today’s grid, the constraint is no longer processing power; it’s reliable, cost-effective power. Uvation’s future commitment to behind-the-meter nuclear reflects a broader market reality: energy security now defines the speed at which AI can scale.
"SOLO fast-tracks AI commercialisation by providing near-instant, CO₂-free, revenue-generating power while sidestepping the delays and CapEx overruns inherent to traditional grid-dependent solutions.
"This agreement also strengthens our commercial deployment and positions nuclear as the most viable path to support Uvation’s planned multi-gigawatt growth in the AI and data centre sector.”
Reen Singh, CEO of Uvation, notes, “Global demand for AI, driven by the US, and the need for sovereign cloud infrastructure is accelerating far faster than the available power to support it. Some of our off-takers forecast demand exceeding 1GW, yet current infrastructure and lack of readily available access to energy limit the scale of deployments.
“Power shortages have been major forces in this industry’s project delays. By integrating Terra Innovatum’s SOLO reactor into our future roadmap, we will look to secure immediate power along with a reliable, behind-the-meter energy source that enables scalable AI, inference, and edge deployments.
"Our future 1MWe SOLO pilot program represents a critical first step, with a path to expand to 100 MWe across multiple sites and potentially several megawatt-scale installations throughout the US.”
The companies intend the pilot to act as a foundation for potential multi-site expansion, citing accelerating power demand and increasing constraints on conventional grid-connected data centre projects.
Joe Peck - 21 November 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Hyperscale Data Centres: Scale, Speed & Strategy
CleanArc breaks ground on 900MW Virginia hyperscale campus
CleanArc Data Centers, a developer and operator of hyperscale data centre campuses, has just announced the groundbreaking of its flagship campus in Caroline County, Virginia.
Offering 900MW of grid capacity, the new data centre campus will aim to support the growing demand for scalable, sustainability-focused, and hyperscale-ready digital infrastructure.
Governor Glenn Youngkin joined local officials, community partners, and CleanArc leadership at the ceremony, celebrating the official start of construction on the project.
“Today marks an important milestone for CleanArc Data Centers and Northern Virginia,” says James Trout, founder and CEO of CleanArc Data Centers. “This new, leading-edge campus reflects our commitment to delivering reliable, efficient, and sustainable data centre solutions while supporting the local economy and workforce.”
Features of the VA1 campus
The VA1 campus is designed to meet growing hyperscale demand, featuring:
• Nearly 1GW of grid power — With the first 300MW coming online in Q1 2027, the second 300MW currently projected for 2030, and another 300MW in the 2033–2035 timeframe, the campus seeks to ensure robust redundancy and resilience, supporting both current demand and future scalability.
• Sustainability and efficiency focus — The VA1 campus incorporates land conservation initiatives, minimal water usage with closed-loop systems, and design features to reduce noise and light pollution. At VA1, customers have the option to leverage CleanArc’s approach to energy structuring - what it calls “True Additionality” - where clean energy is added onto electric grids in the region where the energy is being consumed.
• Design focused on scalability and speed — Using advanced modular data centre design and off-site manufacturing, CleanArc intends to deliver pre-engineered, factory-tested systems to the construction site to reduce complexity, shorten deployment timelines, and help customers capture market opportunities faster.
The future potential
The project is backed by majority investor Snowhawk and minority investors Nuveen and Townsend Group, who all say they are committed to "driving the next wave of AI and cloud innovation while prioritising responsible growth and community impact."
VA1 is expected to generate approximately $13 million (£9.9 million) in new annual tax revenue for Caroline County, equivalent to 17% of the county’s current general fund.
The project will also create at least 50 new full-time jobs in the county and hundreds of additional jobs during the project’s construction over the next several years.
Additionally, CleanArc is reportedly partnering with local vendors and workforce programs to support economic growth in the county
Brian McMullen, Managing Partner and co-founder of Snowhawk Partners, comments, “We are thrilled to support this project, which represents a significant investment in the future of digital infrastructure and underscores our commitment to building advanced, sustainable facilities that empower businesses and communities.”
For more from CleanArc Data Centers, click here.
Joe Peck - 21 November 2025
Artificial Intelligence in Data Centre Operations
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
XYZ Reality, Applied Digital partner on 400MW campus
XYZ Reality, a provider of augmented reality (AR) and real-time project controls, is supporting high-performance data centre operator Applied Digital’s delivery of an AI factory in Ellendale, North Dakota.
The 400-megawatt (MW) Ellendale AI Factory Campus leverages North Dakota’s cool climate and renewable energy to create a sustainable foundation for advanced computing.
XYZ Reality’s construction delivery platform, supported by its team of site engineers, is helping Applied Digital’s project teams track progress in real time, validate installations, and maintain quality standards throughout the build.
As part of the partnership, XYZ Reality’s site engineers are embedded on-site to provide verified build progress, installation accuracy, and proactive quality assurance aligned with project plans.
Construction of an AI factory
David Mitchell, Founder & CEO of XYZ Reality, comments, “Applied Digital is redefining what’s possible in AI infrastructure and it’s exciting to be part of that journey.
"From day one, our teams have clicked through a shared drive to push boundaries and use technology differently. Together, we’re proving that transparency, precision, and data-led delivery can transform how these massive projects come to life.”
Waleed Zafar, CRO at XYZ Reality, adds, “Working alongside Tier 1 developers like Applied Digital, we’re demonstrating the true impact of data-led construction.
"Our platform gives project teams complete visibility and confidence from the ground up - driving precision, accountability, and measurable performance improvements across delivery.
"Having already been deployed on more than 2.5GW of data centres, we’re proud to be setting a new standard for how mission-critical infrastructure is built.”
For more from XYZ Reality, click here.
Joe Peck - 20 November 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
News
Sustainable Infrastructure: Building Resilient, Low-Carbon Projects
Verne, Nscale planning 15MW AI deployment in the Nordics
Verne, a provider of low-carbon high-performance data centres across the Nordics, has agreed a 15MW AI infrastructure deployment with hyperscaler Nscale, expanding high-density, renewable-powered computing capacity across its Icelandic campus.
The project centres on liquid-cooled GPU infrastructure and is set to run throughout 2026.
The installation will comprise around 4,600 NVIDIA Blackwell Ultra GPUs, with an 85% liquid-cooled and 15% air-cooled configuration designed to maximise efficiency within Verne’s existing facilities.
It is one of the region’s largest liquid-cooled GPU projects and is expected to support lower energy use and reduced environmental impact.
Iceland’s renewable electricity and natural free-cooling conditions position it as a suitable location for high-density AI workloads.
Nscale selected Verne based on its experience in renewable-powered data centres and its ability to support large-scale training and inference environments.
Large-scale renewable AI capacity across the region
“The pace of change in AI infrastructure is extraordinary," notes Dominic Ward, CEO of Verne. "As the demand for GPU capacity accelerates, availability of clean, renewable power has become as important as raw performance.
"Partnering with Nscale, whose expertise is redefining how AI infrastructure is delivered responsibly at scale, demonstrates how the Nordics are fast becoming a strategic hub for sustainable AI growth.”
Philippe Sachs, Chief Business Officer and President of EMEA at Nscale, adds, “As compute demand grows, we’ve worked with partners throughout the world and the Nordic region to deliver sustainable solutions to meet that demand.
"The Nordics offer a uniquely sustainable foundation: abundant renewable energy and natural cooling. With our existing operations in Norway, we’ve seen first-hand how the region powers low-carbon, sovereign-grade AI infrastructure."
David Hogan, Vice President Enterprise at NVIDIA, comments, “The collaboration between Verne and Nscale showcases how NVIDIA technology can enable high-performance AI factories with a focus on energy efficiency and sustainability.
"Deployments like this reflect how organisations are scaling the next generation of AI workloads responsibly, using innovative cooling and renewable-powered data centres.”
The agreement aligns with Verne’s wider European expansion, which includes new campuses planned in Finland and early-stage development activity in France.
The companies state that these projects contribute to the Nordics’ growing role as a centre for renewable-powered AI infrastructure.
For more from Verne, click here.
Joe Peck - 20 November 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
NorthC, Legrand upgrade Münchenstein (Basel) data centre
NorthC Data Centers, a Dutch provider of sustainable data centre and colocation services, has partnered with Legrand, a French multinational manufacturer of electrical and digital building infrastructure products, to upgrade its Münchenstein (Basel) site, introducing higher-density infrastructure to support AI, hybrid-cloud, and high-performance computing workloads.
The project was completed within a six-month window to meet rising regional demand for GPU-driven environments.
NorthC operates regional facilities across Switzerland, the Netherlands, and Germany. The company sought to replace low-density systems and traditional air-cooling at the Münchenstein site to accommodate higher power and thermal loads associated with modern AI deployments.
Legrand, through USystems, supplied rear-door heat exchangers for rack-level cooling. These units are mounted to the rear of server racks, absorbing heat from server exhaust and transferring it through a heat exchanger before returning cooled air to the data hall.
The closed-loop design supports higher rack densities while improving energy performance.
The cooling equipment was installed while the data centre remained live, a process described by Wolfgang Voigt, Münchenstein Data Center Site Manager at NorthC, as “like open-heart surgery.”
Focus on efficiency and future expansion
NorthC reports that energy consumption at the site has fallen by about 80% following the cooling upgrade and broader infrastructure improvements.
The facility now supports GPU-based clusters, hybrid-cloud environments, and high-density workloads, while maintaining compliance with Swiss data protection requirements.
Wolfgang says, “Adopting the energy-efficient RDHx technology has been a game-changer for us. The fact that it enables high-density computing while reducing energy consumption makes it a compelling choice to meet AI and HPC requirements.”
The upgraded design also accommodates future development, including additional rack capacity or a shift towards liquid or direct-to-chip cooling.
NorthC says it continues to pursue its long-term sustainability goals through efficiency measures and ongoing optimisation of existing sites.
Colin Rowlands, European Technical Support at USystems, notes, “Installing the basic infrastructure for our cooling solutions in a data centre, whether in the entire data centre or just part of it, makes upgrading easy.
"The joint solution, which we are very proud of, provides NorthC with future-proof and flexible infrastructure.”
For more from NorthC, click here.
Joe Peck - 19 November 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
News
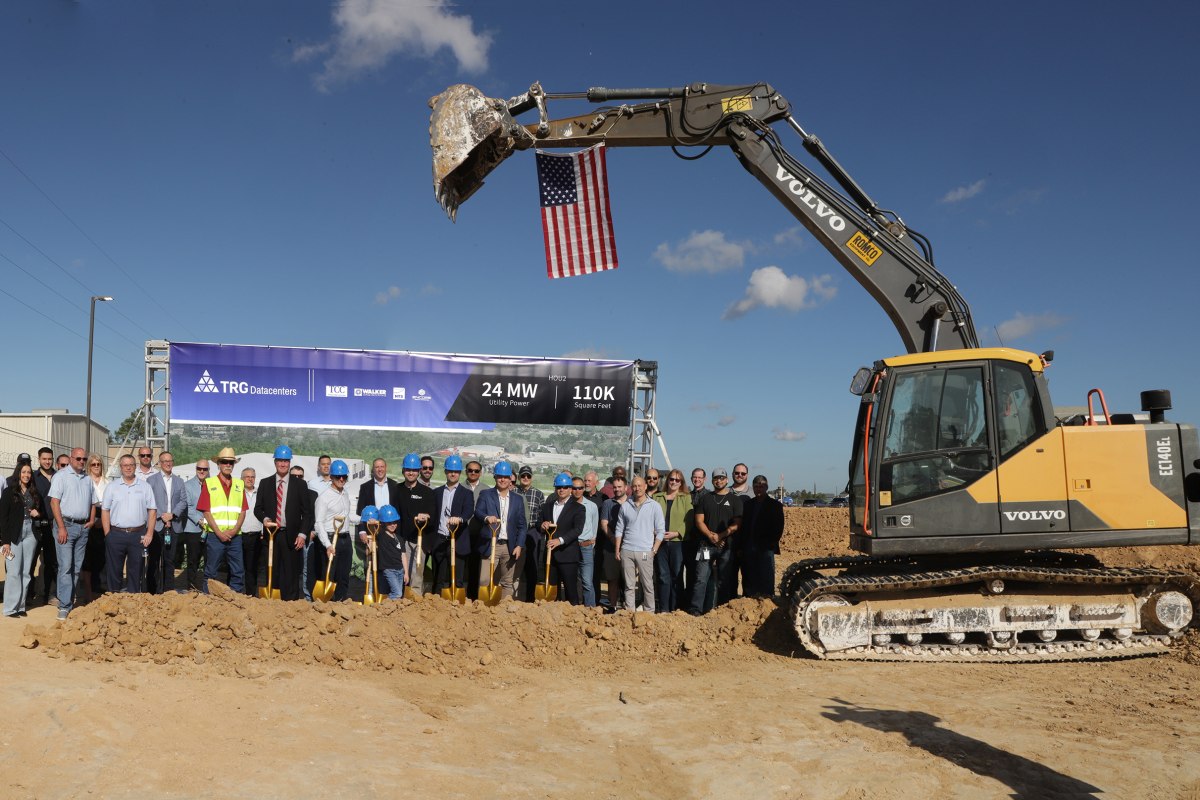
TRG Datacenters breaks ground on 24 MW Houston DC
TRG Datacenters, a developer and operator of digital infrastructure, has begun construction of HOU2, the second facility on its Spring, Texas campus.
Backed by Tallvine Partners, the developer aims to add 24MW of utility capacity to address continued demand from existing and new customers.
The purpose-built 110,000ft² (10,219m²) site is expected to offer ready-to-occupy IT capacity from Q4 2026.
HOU1, delivered in 2018, has reportedly recorded 100% uptime and now supports more than 160 customers, including several Fortune 500 organisations.
TRG states that HOU2 follows the same design principles, with distributed-redundant infrastructure and flexible data halls to accommodate enterprise, hosting, cloud, and AI deployments.
Focus on capacity growth in a constrained market
Christopher Hinkle, CEO of TRG Datacenters, comments, “TRG’s strong track record of delivering high-quality infrastructure and customer service has brought us to an inflection point, with HOU1 nearly fully subscribed and HOU2 construction underway.
“With secured power capacity on an entitled, operational site that hosts 16 carriers and more than 160 existing clients, the HOU2 expansion provides a level of certainty our existing and prospective customers can rely on in an otherwise supply-constrained US data centre market.”
The groundbreaking took place on 14 November 2025, attended by industry partners including CenterPoint Energy, Walker Engineering, HTS, Thomas Craig Construction, and Encore Concrete Construction.
Mark Clark, Partner at Tallvine Partners, says, “This expansion is fully aligned with Tallvine’s organic growth strategy for the TRG platform and follows accelerating customer demand across the business.
“We look forward to supporting TRG’s continued growth in both existing and new markets in the years ahead.”
Bob West, Head of Revenue at TRG Datacenters, adds, “TRG Datacenters thanks the sponsors, speakers, and local leaders who joined us in celebrating this important milestone.
“We also extend our appreciation to our customers, vendors, CenterPoint, and Tallvine, and we remain committed to delivering exceptional service and partnership with HOU2.”
For more from TRG Datacenters, click here.
Joe Peck - 19 November 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Insights into Data Centre Investment & Market Growth
Carbon3.ai to invest £1bn in UK’s AI infrastructure network
Carbon3.ai, a UK sovereign AI infrastructure company, has announced a £1 billion commitment to develop a nationwide network of data centres that aims to transform legacy industrial and energy infrastructure into secure, fully sustainable, AI-ready hubs.
Designed, owned, and operated by Carbon3.ai, the network will seek to deliver high-performance, low-carbon compute capacity to fuel the digital readiness of UK enterprise, research, and public services.
All infrastructure and data processing will be located within the UK and fully subject to UK jurisdiction and regulatory oversight.
The company has already completed a successful proof of concept and is moving into full-scale rollout with its first 5MW site in the East Midlands, set to open in March 2026, and planning permission submitted for a second facility in Derbyshire.
New appointments for further expansion
To drive this next phase of growth, Carbon3.ai says it has strengthened its leadership with a team that "brings together deep expertise across government, finance, and national security."
Sana Khareghani, former Head of the UK Government Office for Artificial Intelligence, joins as Chief Strategy Officer, leading the company’s strategy on national AI infrastructure and seeking to ensure its network advances the UK’s digital competitiveness and long-term energy transition.
Sana is supported by advisors Richard Collier-Keywood, former Vice Chair of PwC’s Global Board, and Sir George Zambellas, former Navy Chief.
Sana comments, “If the UK is to lead in AI, we must first secure the foundations that make it possible: compute, power, and data. Carbon3 is building those foundations here at home, transforming legacy energy sites into a sovereign, renewable, AI-ready infrastructure network.
"This isn’t a vision on paper, we’re making it happen now on the ground. By putting critical infrastructure back under UK control, we’re creating sustainable capacity and national capability that will power innovation, research, and enterprise for decades to come.”
Tom Humphreys, CEO of Carbon3.ai, adds, “The UK’s competitiveness in AI depends on infrastructure that is truly sovereign, sustainable, and resilient. It’s not enough to invest in data centres; we need a national backbone for AI that’s owned, powered, and secured right here at home.
"Our goal is to ensure that British enterprise, researchers, and public institutions have access to world-class compute capacity without relying on foreign-controlled infrastructure.
"The Government recognises the urgency; that is why they have said we need 6GW of sovereign AI capacity by 2030. Together, we can get there, securing a foundation for innovation, investment, and long-term national advantage.”
Carbon3.ai asserts that these developments support the UK Government’s AI and digital infrastructure agenda of strengthening national resilience, creating regional opportunity, and ensuring the benefits of technological progress are rooted in British infrastructure and communities.
By converting brownfield and legacy energy sites into renewable-powered compute hubs, the company says it aligns directly with the Government’s priorities for AI growth zones and the designation of data centres as critical national infrastructure.
Joe Peck - 18 November 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Modular Data Centres in the UK: Scalable, Smart Infrastructure
Schneider, DataCentre UK deliver £1.4m modular DC
Schneider Electric, a global energy technology company, in partnership with its EcoXpert Partner DataCentre UK, has delivered a new modular data centre for South Warwickshire University NHS Foundation Trust (SWFT).
The £1.4 million project seeks to strengthen the Trust’s digital infrastructure, improving energy efficiency, operational resilience, and capacity to support future healthcare demands.
Supporting digital transformation and scalable healthcare infrastructure
Facing growing pressure on legacy systems, Innovate Healthcare Services required a modern, scalable, and secure data centre.
The new facility incorporates Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure Data Centre technology, including APC NetShelter racks, modular cooling units, APC power distribution units (PDUs), and Easy UPS systems.
Together, these components should provide greater resiliency and efficiency, while supporting the Trust’s sustainability goals.
Paul Almond, MD at DataCentre UK, says, “As an EcoXpert Partner to Schneider Electric, we have integrated Schneider Electric's EcoStruxure Data Centre solutions into the design.
"These solutions are pre-engineered, configurable, and scalable, encompassing racks, power, cooling, and management systems, aimed at maximising resiliency, sustainability, and efficiency.
“Innovate and SWFT trusted our design and our selection of products and approved us to proceed with the build-out.”
Improving energy performance and sustainability
The upgraded infrastructure has reportedly reduced the Trust’s data centre energy consumption by an estimated 60% compared with its previous setup.
Enhanced monitoring and management capabilities allow continuous optimisation of performance and efficiency, in line with SWFT’s Green Plan.
“It was all built around sustainability,” notes Mike Conlon, Associate Director of Technology Services at Innovate Healthcare Services. “Conservatively, we are now using 60% less electricity on the same amount of IT load, based on the previous server room implementation, and the system has been designed with an expected annualised PUE of 1.2.”
Ongoing operation and maintenance will be provided through a year-round support agreement managed by DataCentre UK and Schneider Electric.
Strengthening healthcare resilience through infrastructure partnerships
Karlton Gray, Director of Channels, UK & Ireland, Schneider Electric, comments, “With data centres underpinning critical healthcare services, it’s essential that infrastructure delivers the highest levels of reliability, scalability, and sustainability.
"Our solutions have helped Innovate significantly improve their environmental footprint, while maintaining exceptional operational performance, and delivered a healthcare environment built for the future.”
The project demonstrates how modular and energy-efficient data centre designs can support digital transformation across the healthcare sector, helping organisations meet sustainability targets while maintaining continuity of care.
For more from Schneider Electric, click here.
Joe Peck - 12 November 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
Vertiv to supply Digital Realty's new Italy campus
Vertiv, a global provider of critical digital infrastructure, today announced it will supply infrastructure for ROM1, Digital Realty's first data centre in Italy and which has a planned capacity exceeding 3 MW.
The agreement extends the suite of Vertiv systems and existing technology implementations with Digital Realty across European locations, including Paris, Madrid, and Amsterdam.
The ROM1 facility will feature advanced cooling and power infrastructure designed specifically for high-performance computing (HPC) environments.
The technology implementation includes free-cooling systems that leverage Rome's climate conditions and energy-efficient power management systems designed to support high-density workloads.
The ROM1 project
The project will be implemented in phases, with the facility planned to begin operations in 2027.
ROM1 will serve as a carrier-neutral facility optimised for AI and machine learning workloads. Its strategic location aims to establish Rome as a key digital hub, connecting to major Mediterranean cities through fibre networks and submarine cables.
Expansion plans also include connectivity in Barcelona, launching in early 2026.
The new facility will support the company’s growth in the Mediterranean, complementing its existing data centres in Marseille, Athens, and Crete.
Alessandro Talotta, Managing Director, Italy at Digital Realty, says, "Rome is emerging as a crucial gateway for digital infrastructure between Europe and the Mediterranean.
"The cutting-edge technologies selected for ROM1 will help establish it as a strategic AI hub, setting new benchmarks for energy efficiency and performance in high-performance computing."
Karsten Winther, President for EMEA at Vertiv, adds, "The growing adoption of AI applications is driving the need for more sophisticated data centre infrastructure.
"Our cooling and power solutions are built on decades of experience in supporting the most demanding applications and are designed for projected scalability while helping customers meet their efficiency objectives."
Technical details of ROM1 include AI-ready cooling systems that, Vertiv says, adapt to varying workload demands, as well as high-efficiency power distribution designed for intensive computing.
The facility incorporates smart environmental controls that respond to real-time conditions and are integrated with alternative energy sources.
The two companies say these technological choices reflect their joint focus on supporting advanced computing needs while minimising energy consumption and environmental impact.
For more from Vertiv, click here.
Joe Peck - 11 November 2025

Head office & Accounts:
Suite 14, 6-8 Revenge Road, Lordswood
Kent ME5 8UD
T: +44 (0)1634 673163
F: +44 (0)1634 673173