26 February 2026
STL, Mynet deliver fibre in mountainous Italy
STL, Mynet deliver fibre in mountainous Italy
26 February 2026
McLaren appointed for 70MW London data centre phase
McLaren appointed for 70MW London data centre phase
25 February 2026
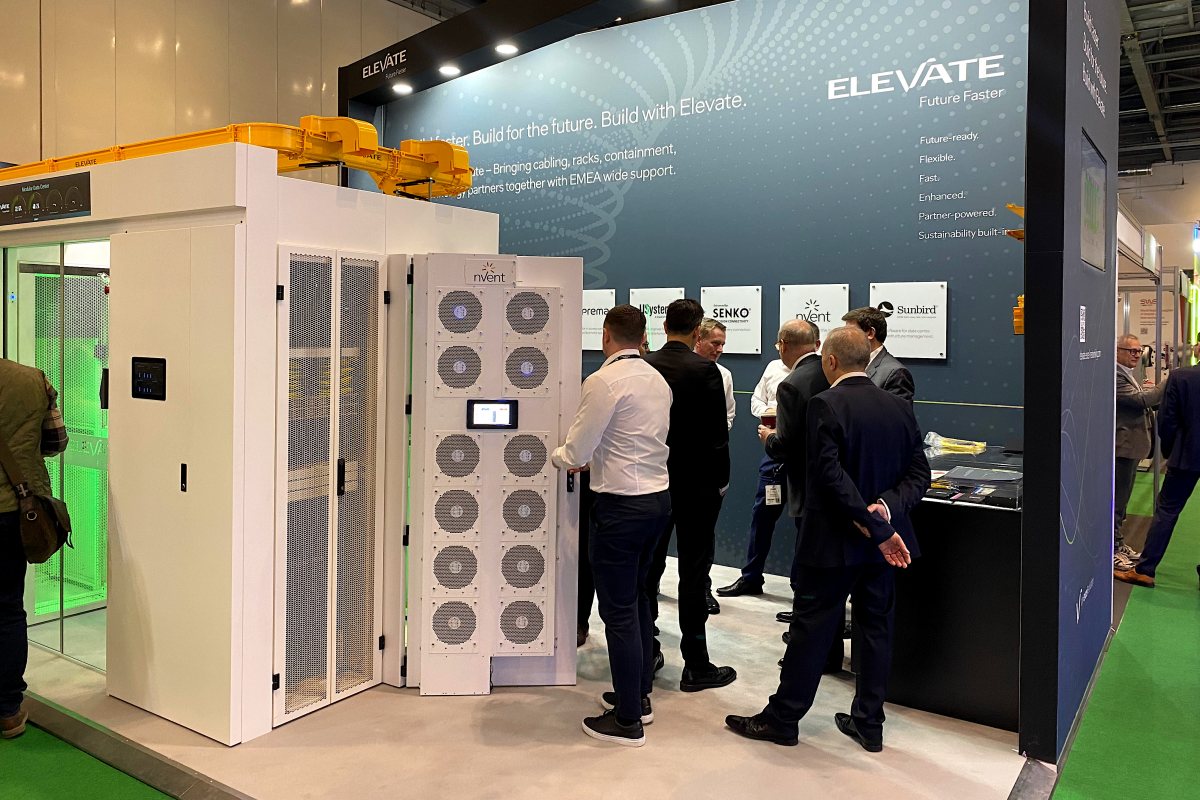
Mayflex to highlight Elevate at Data Centre World 2026
Mayflex to highlight Elevate at Data Centre World 2026
25 February 2026
Norton advises on €210m data centre financing for Berlin
Norton advises on €210m data centre financing for Berlin
Latest News
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Insights into Data Centre Investment & Market Growth
Echelon secures €1.7bn loan financing for European expansion
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Data Centre Compliance: Standards, Risk & Governance
Data Centre Regulations & UK Compliance Updates
AECOM calls for sovereign UK data centre framework
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Renewables and Energy: Infrastructure Builds Driving Sustainable Power
Sustainable Infrastructure: Building Resilient, Low-Carbon Projects
atNorth confirms 'mega' 300MW data centre in Sweden
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
News
RETN launches Tallinn–Cēsis backbone route
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Data Centre Compliance: Standards, Risk & Governance
Data Centre Regulations & UK Compliance Updates
News
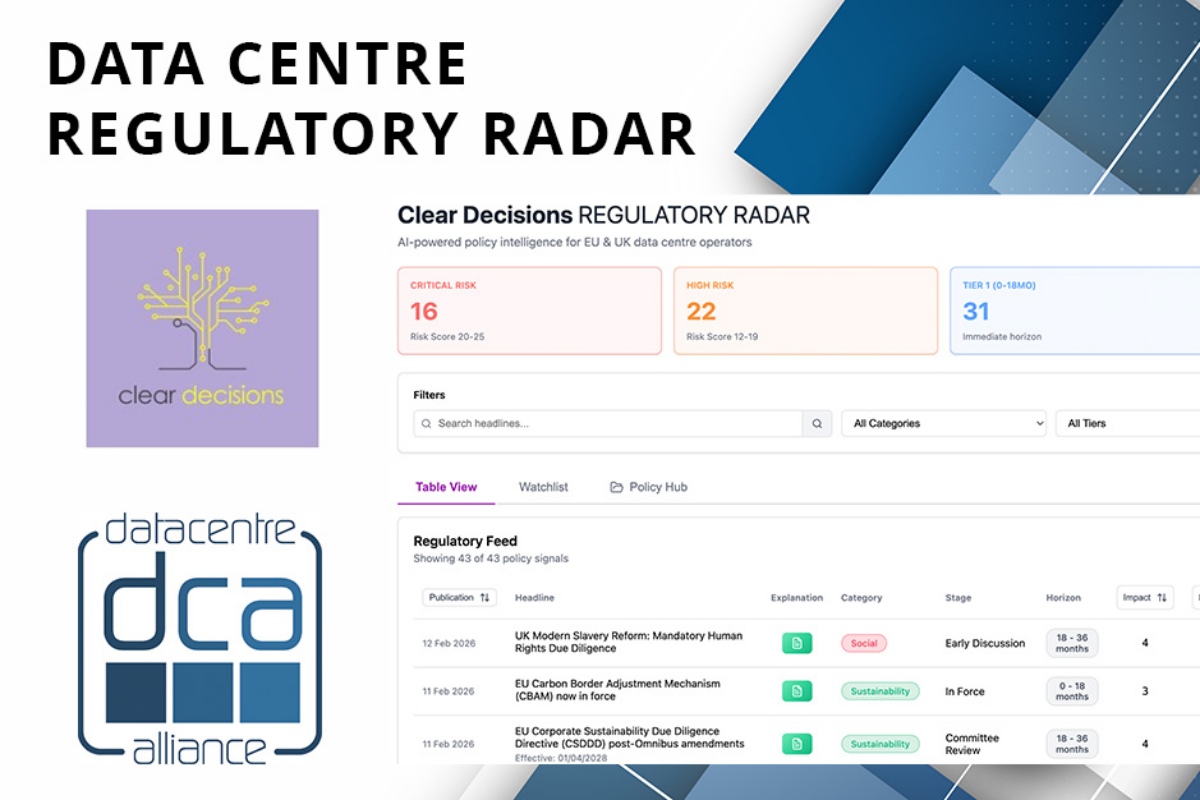
Data Centre Alliance, Clear Decisions launch Regulatory Radar
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Events
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
Sponsored
Daikin to showcase data centre solutions at DCW 2026
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Exploring Modern Data Centre Design
Secure I.T. completes Qatar financial data centre design
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Insights into Data Centre Investment & Market Growth
Liquid Cooling Technologies Driving Data Centre Efficiency
Johnson Controls to acquire Alloy Enterprises
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
Events
Products
Sponsored
How Elevate is redefining data centre infrastructure
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
Products
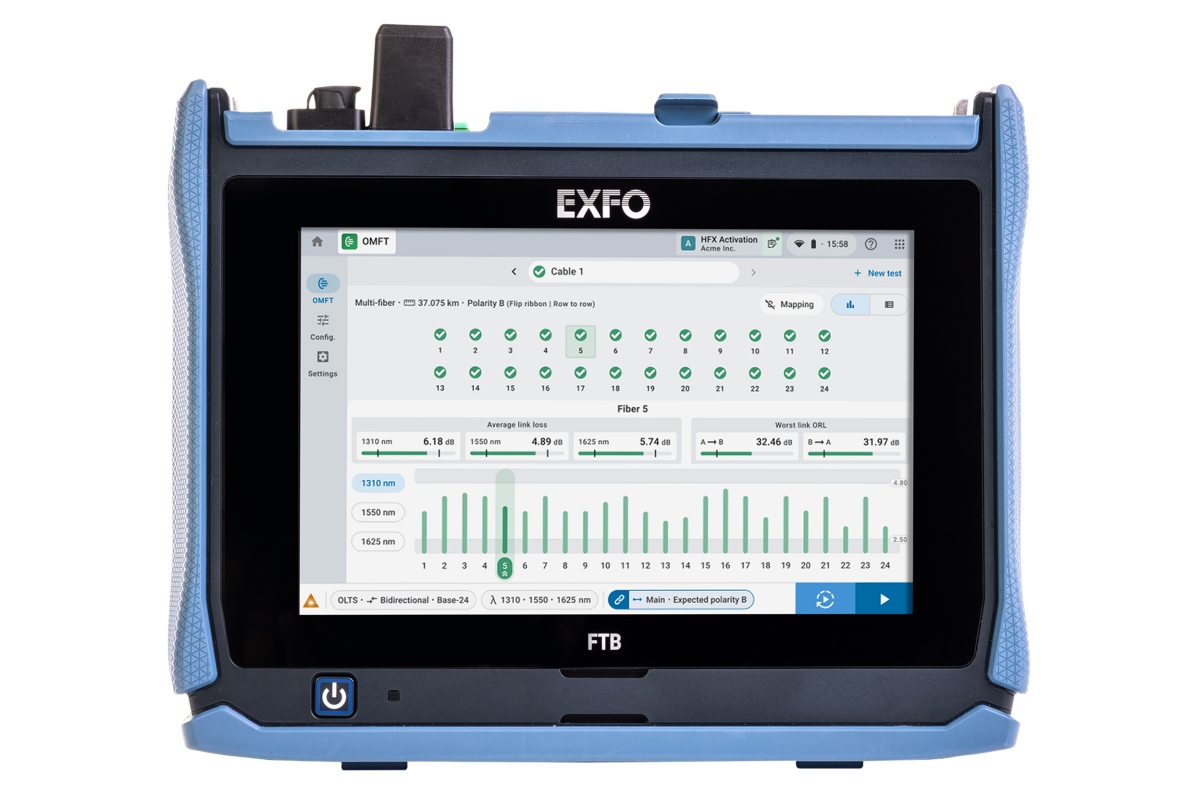
EXFO launches high fibre count data centre testers