News
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Data Centre Compliance: Standards, Risk & Governance
Data Centre Regulations & UK Compliance Updates
News
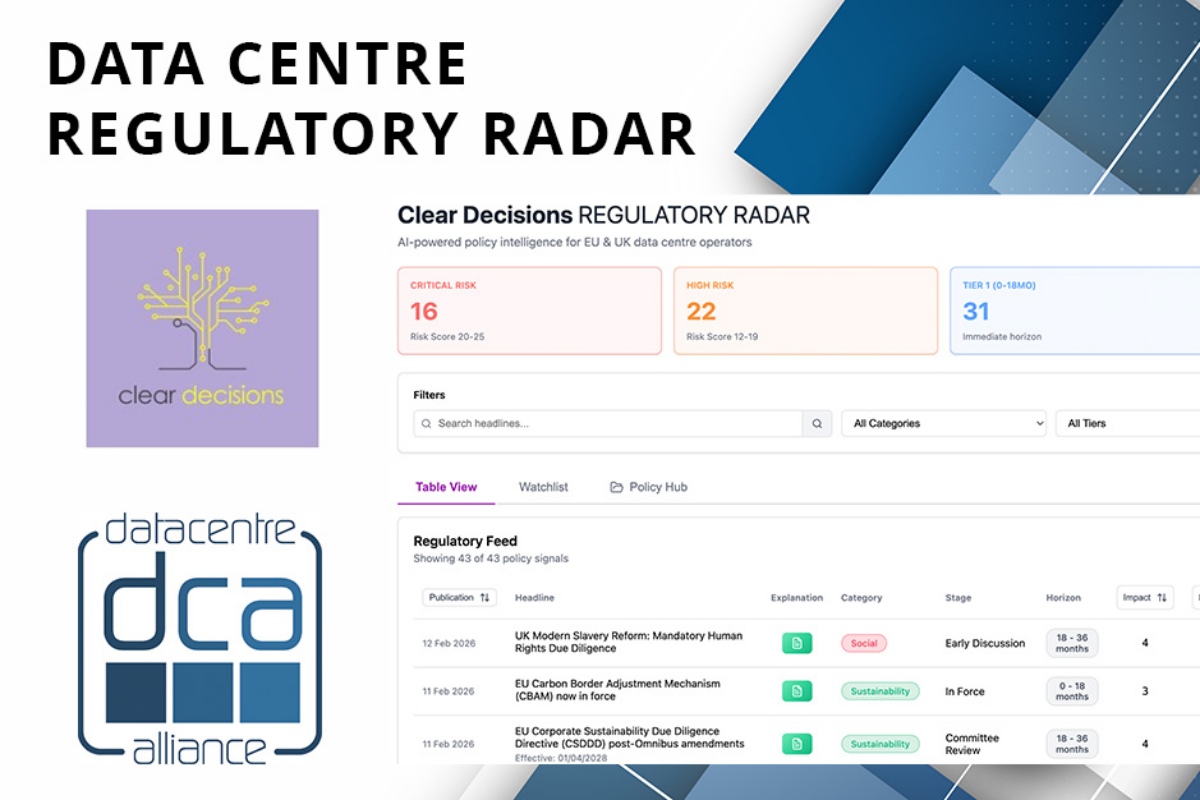
Data Centre Alliance, Clear Decisions launch Regulatory Radar
The Data Centre Alliance (DCA), a UK trade association for the data centre sector, and Clear Decisions, a regulatory compliance and sustainability reporting platform for data centre operators, have launched Regulatory Radar, a regulatory intelligence platform developed specifically for the data centre sector.
The platform is designed to provide structured, real-time updates on policy and regulatory developments across the UK and EU, including energy reform, planning policy, sustainability regulation, and AI infrastructure strategy.
Regulatory Radar combines AI-based analysis with expert review. The organisations state this approach is intended to ensure updates are interpreted in context and linked to potential operational and commercial impact.
Tracking policy change across UK and EU
The platform includes forward-looking analysis of planning, energy, and sustainability reform, alongside monitoring of digital and AI policy developments. It also identifies emerging compliance and reporting requirements.
According to the DCA and Clear Decisions, the aim is to consolidate regulatory developments into a single source and provide greater visibility of potential risks and strategic considerations for data centre operators and investors.
Steve Hone, Chief Executive of the Data Centre Alliance, says, “The regulatory landscape for digital infrastructure is evolving faster than ever. Our sector cannot afford to operate on partial information or delayed insight.
"Regulatory Radar combines AI-driven intelligence with expert oversight to give operators and investors the foresight required to anticipate change, shape engagement, and protect long-term value. This collaboration sets a new benchmark for industry intelligence.”
Regulatory Radar is available to DCA corporate members and Clear Decisions subscribers.
For more from the DCA, click here.
Joe Peck - 23 February 2026
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Events
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
Sponsored
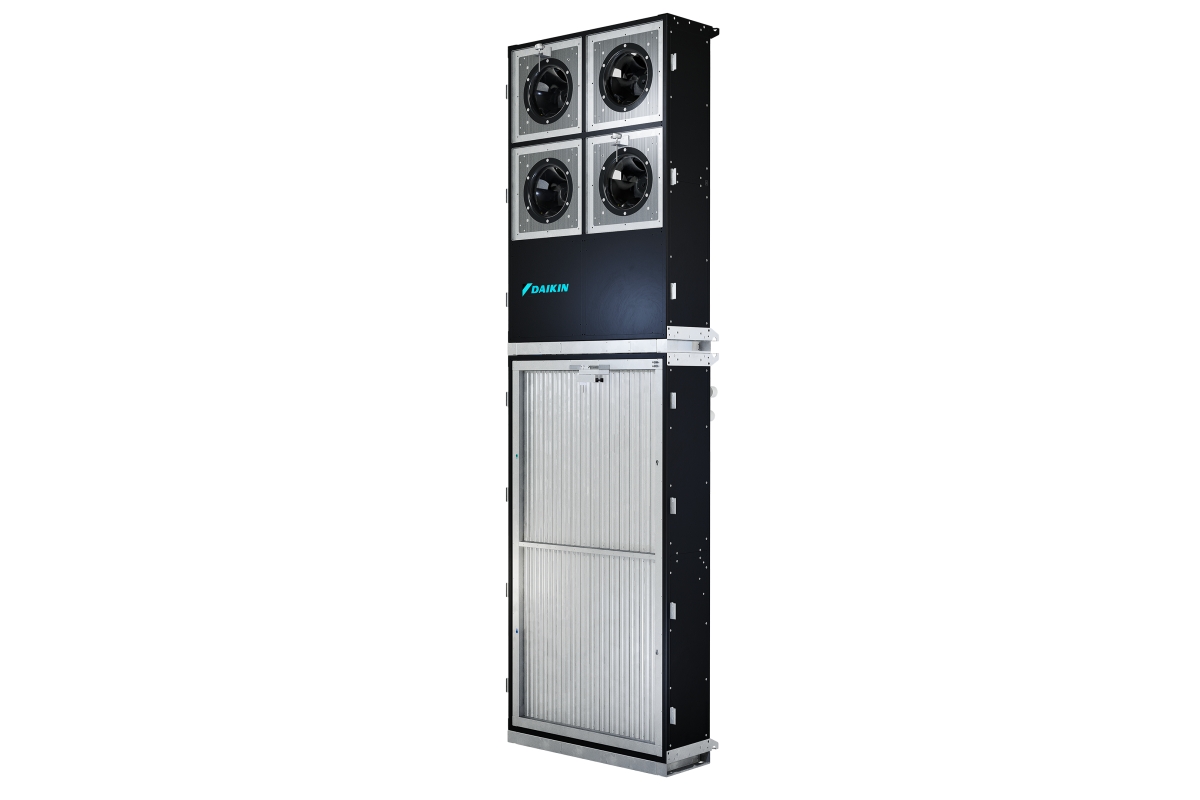
Daikin to showcase data centre solutions at DCW 2026
Daikin, a Japanese manufacturer of air conditioning and refrigeration systems, will participate in Data Centre World London 2026, where it will exhibit at Stand B140. The company says it will use the event to demonstrate how advanced cooling technologies and specialist expertise can support the sustainable growth of Europe’s rapidly expanding data centre sector.
Building on its strong market track record, Daikin Applied will showcase solutions designed to meet the evolving needs of colocation providers and hyperscalers. Visitors to the stand will be able to engage directly with Daikin’s data centre specialists and explore how the company supports projects from early design and engineering through to commissioning, operation and long-term service.
Data Centre World London is a key meeting point for operators and suppliers seeking practical, future-proof approaches to balancing performance, reliability, and sustainability. Daikin’s presence underscores its commitment to helping customers meet rising capacity demands, tighter energy efficiency targets, and increasingly complex data centre designs.
A trusted partner for mission-critical environments
At the show, Daikin will present an overview of its data centre portfolio, covering cooling solutions for a wide range of applications and design philosophies. A key feature of the stand will be a mock-up of the new Pro-W Slim fan array unit, designed to deliver high efficiency, scalability, and operational flexibility. The unit supports modular design concepts and is optimised for reliability, ease of maintenance, and precise airflow control.
The company will also showcase its new coolant distribution unit (CDU), designed to support liquid-cooled architectures and high-density applications.
Alongside these innovations, Daikin’s portfolio includes air- and water-cooled chillers, heat pumps, air handling units, CRAH systems, and integrated control solutions. Combined with specialist engineering support and lifecycle services, the company delivers tailored, end-to-end cooling solutions for data centres of all sizes and complexity levels.
For more from Daikin, click here.
Joe Peck - 23 February 2026
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
Events
Products
Sponsored
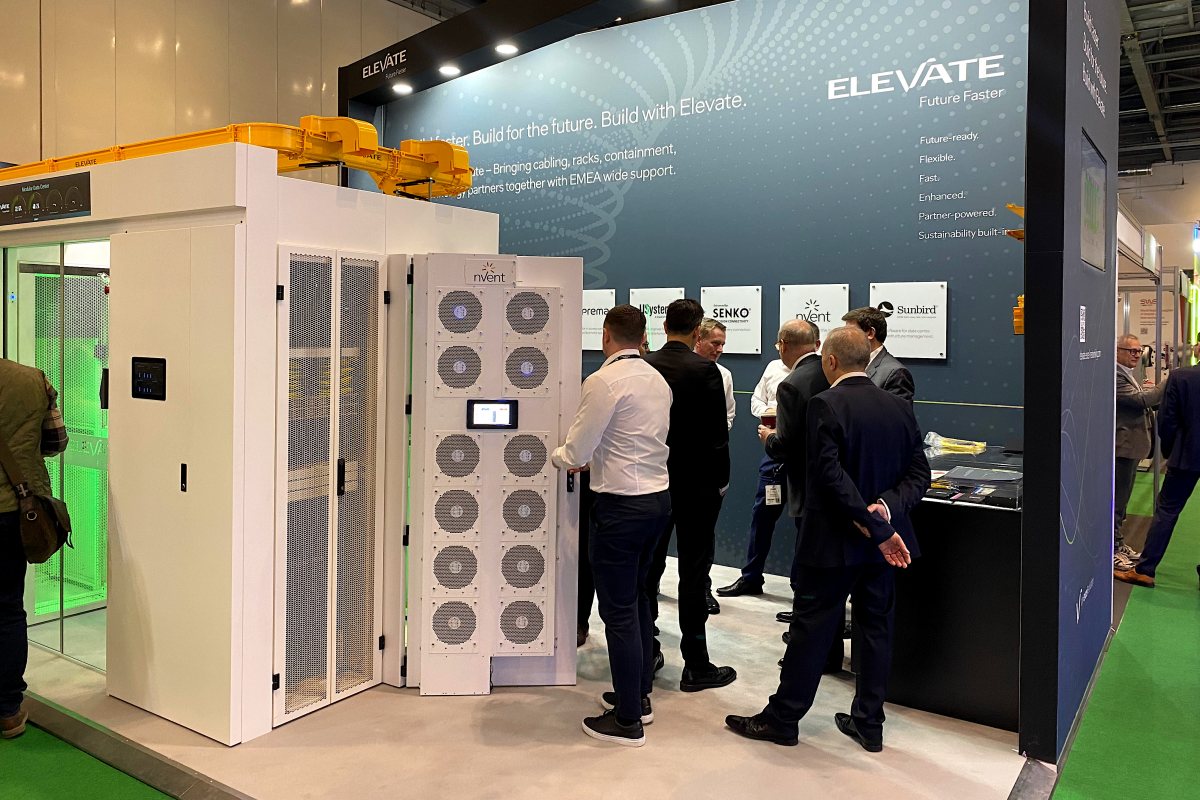
How Elevate is redefining data centre infrastructure
It feels like yesterday that Elevate – Future Faster launched at Data Centre World 2025. Since then, the team have been working closely with operators, integrators, and partners to understand where white space designs struggle under pressure, namely: how density is increasing, how airflow and power must evolve, and how programmes need to accelerate without increasing operational risk.
Now, as Elevate returns for year two at Data Centre World on Stand B180, it isn’t “new for the sake of new”; it’s a platform that closes the gap between what modern data centres demand and what infrastructure can realistically deliver – more density, more control, and more scale, without complexity creeping in through the back door.
Elevate was built as an integrated ecosystem: fibre, racks, aisle containment, power, and security engineered to work together with clean installation, clear labelling, and predictable operation. In its second year, that ecosystem has expanded significantly, with wider choices for high density fibre, more robust airflow strategies, and smarter power and physical security options designed to make scaling easier.
Addressing today’s data centre challenges
Modern data centres face a familiar set of pressures: rising density, faster change cycles, and tighter operational guardrails. Elevate is designed to help teams keep pace.
Densification is no longer optional. Port counts rise, but physical space doesn’t. Elevate’s high-density fibre solutions – VSFF, MPO, and modular ODF architectures – deliver more ports in the same rack unit space while maintaining front access, bend radius control, and clear labelling. The goal isn’t only to fit more, but to manage more.
Thermal performance is another sticking point. As loads increase, improvised airflow tactics break down. Elevate’s hot and cold aisle containment is engineered to integrate properly with racks, cable pathways, and power routes. The result is stable airflow separation and higher cooling efficiency across mixed hardware environments.
Power, too, needs to evolve. It is no longer enough to energise a rack; operators need visibility, telemetry, and control. Elevate’s high-density intelligent power provides meaningful insight – usage, load, switching – so day two operations become more predictable and less prone to surprises.
Deployment speed matters as much as performance. To avoid delays and rework, Elevate prioritises pre-connectorised designs and engineered pathways. Pre-configured fibre assemblies and pre-populated ODF trays reduce on site variability, shorten install windows, and improve “first time right” outcomes.
Moreover, as estates grow, clarity becomes critical. Structured labelling, clean patch presentation, and tray level guidance help maintain consistency long after the initial build and far beyond the day one installation.
Fast, reliable availability rounds out the approach. Predictable supply chains and standardised configurations help teams maintain design intent and execute programmes without interruption.
Advancing the Elevate Platform for 2026
This year, Elevate introduces a number of key additions designed to meet the demands of increasingly dense, increasingly dynamic data centres:
1. VSFF ultra high density pre-connectorised fibre optics deliver far higher port density within standard 1U and 2U panel formats, reducing splicing, test cycles, and deployment time.
2. Hot aisle containment supports facilities optimised around hot air capture and reuse, improving thermal stability as densities rise.
3. High density intelligent power adds the visibility and control required to balance loads, automate switching, and support safe change windows.
4. Intelligent rack locking delivers scalable, auditable access control.
5. High-density ODFs with pre-connectorised trays provide structured, repeatable patching fields with predictable routing and clear documentation.
Alongside these additions, the DCR Rack Series, cold aisle containment, and MPO high-density, pre-connectorised solutions return with refinements that make dense builds easier to construct, cool, and maintain.
These aren’t isolated features; they’re responses to real operator pressures, helping teams design once, scale confidently, and maintain operational clarity.
Experience the Elevate platform at DCW London
The most reliable way to evaluate infrastructure is to see the engineering up close. At DCW London, Stand B180, you can explore ODF trays, routing paths, containment interfaces, intelligent power options, and rack level access control, as well as discuss how Elevate can support your growth, densification, or refresh plans for 2026. And while you’re there, enter Elevate’s on-stand competition for a chance to win a pair of Apple AirPods.
For more from Elevate, click here.
Joe Peck - 20 February 2026
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
Products
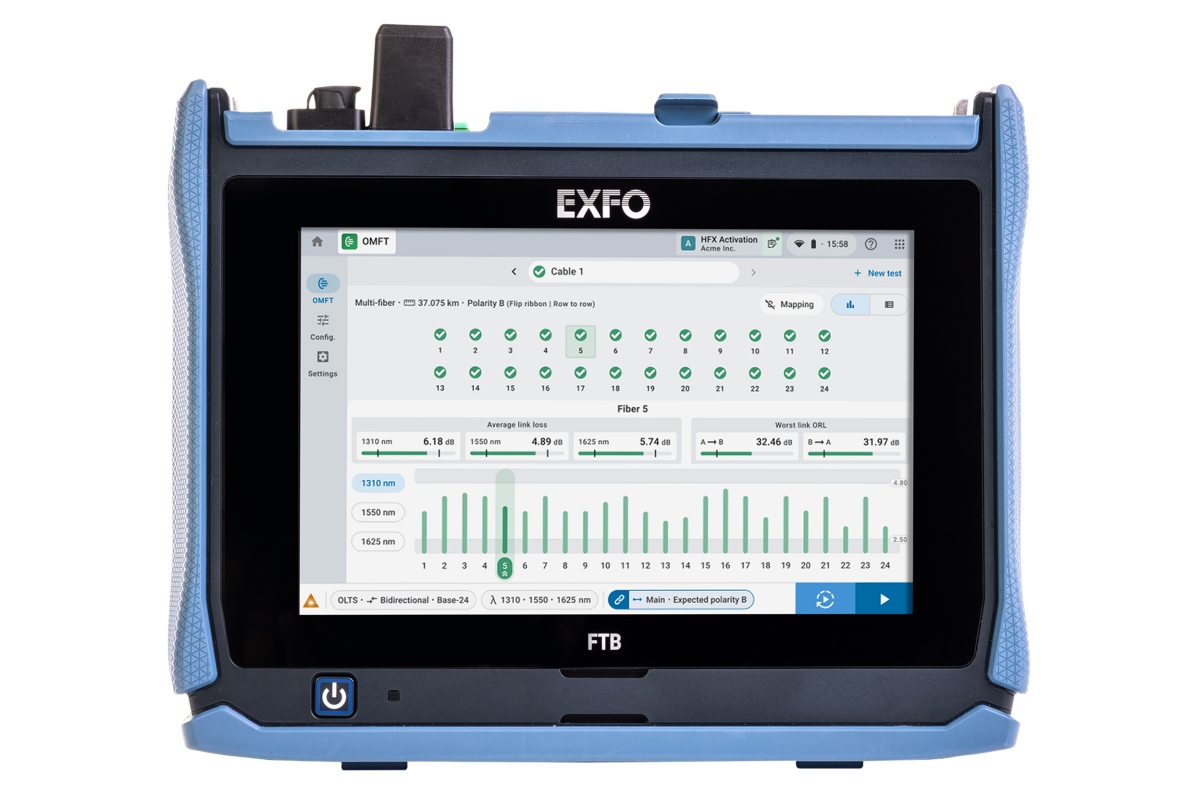
EXFO launches high fibre count data centre testers
EXFO, a Canadian provider of test, monitoring, and analytics equipment for data centres and telecommunications networks, has introduced a high fibre count data centre testing platform with two new instruments designed for hyperscale and AI infrastructure deployments.
The testers will be demonstrated at Data Centre World London 2026 on 4–6 March (Stand B202), alongside a separate showcase at OFC 2026 in Los Angeles on 17–19 March (Booth 523).
The release includes two native 24-fibre capable instruments: the FTB-Lite simplex, duplex, and multi-fibre bidirectional certifier, and the PXM/LXM duplex and multi-fibre optical loss test set (OLTS).
The equipment is intended to support certification and troubleshooting across large fibre installations in and around data centres.
Etienne Gagnon, General Manager Test & Measurement at EXFO, says, “EXFO is trusted by all major hyperscalers to support the accelerated pace of data centre and network builds happening today.
“Our high fibre count solution, now reinforced with the only native 24-fibre testers on the market, simplifies testing and enables scaling-up faster to give our customers a competitive advantage as they respond to exponential growth in AI-driven demand.”
Testing, certification, and diagnostics
The platform supports Tier 1 certification, optical return loss measurement, and Tier 2 troubleshooting across fibre counts up to 24 fibres. Features include automated bidirectional testing, referencing tools, and connector end-face analysis.
EXFO says the system is designed to address the increased number of links, connectors, and handling requirements associated with high-density fibre deployments, while reducing the risk of testing errors during large-scale construction projects.
For more from EXFO, click here.
Joe Peck - 20 February 2026
Commercial Real Estate: Property Developments, Trends & Infrastructure
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Insights into Data Centre Investment & Market Growth
News
New hyperscaler capacity to outpace colocation in Europe
Data centre capacity owned and operated exclusively by hyperscalers, also known as 'self-builds', in Europe is expected to outpace the growth of colocation supply in 2026, according to new research from real estate services company CBRE.
The latest research shows that hyperscaler self-build capacity across Europe is expected to reach 4.2GW this year, representing 24% year-on-year growth compared to 2025. This new supply will be delivered across nine European countries, marking the seventeenth consecutive year of double-digit expansion for the segment.
Hyperscalers are set to deliver a record level of self-build capacity this year as they expand cloud regions and support increasing volumes of equipment dedicated to artificial intelligence workloads. As of Q4 2025, approximately 60% of Europe's operational hyperscaler self-build capacity is located in Ireland, the Netherlands, Sweden, and Belgium.
By comparison, the top 15 European colocation data centre markets are expected to grow 19% year-on-year. Despite slower growth relative to new hyperscaler self-builds, the European colocation segment will remain significantly larger.
Strong demand endures
CBRE notes that demand for colocation facilities remains robust across Europe. Hyperscalers and neocloud providers continue to rely on developer-operators for rapid delivery, flexible design options, and the ability to secure capacity on shorter timelines.
Andrew Jay, Head of Data Centre Solutions, Europe at CBRE, says, "The hyperscaler self-build segment is growing as hyperscalers are looking to build facilities at scale and control more of the supply chain, the design of the facility, and ensure they have the power necessary."
Kevin Restivo, Director, European Data Centre Research at CBRE, adds, "Traditionally, the fastest route to market for hyperscalers in need of data centre capacity delivered are the developer-operators. We expect this to remain true for the foreseeable future. Hyperscalers will, in some instances, build their own facilities though."
For more from CBRE, click here.
Joe Peck - 19 February 2026
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Events
Liquid Cooling Technologies Driving Data Centre Efficiency
Products
Geberit to highlight piping systems at DCW 2026
Swiss manufacturer Geberit will present two supply systems for data centre environments - the Geberit Mapress Stainless Steel and Geberit FlowFit - at Data Centre World 2026 in London, 4–5 March 2026.
Geberit Mapress Stainless Steel is designed for long-term operation in demanding conditions. The material’s molybdenum content provides corrosion resistance intended to support continuous operation in critical facilities where downtime must be avoided.
Geberit FlowFit focuses on installation efficiency. Its lateral pressing method covers pipe dimensions from d16 to d75 using two pressing jaws, reducing tool changes during installation.
Inspection windows and pressing indicators allow installers to verify connections, while fitting geometry maintains flow performance and enables smaller pipe diameters to be used.
The company says the two systems are intended to support reliability and consistent performance across modern data centre infrastructure.
Joe Peck - 19 February 2026
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Exclusive
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
Renewables and Energy: Infrastructure Builds Driving Sustainable Power
Power supply options for data centres
In this exclusive article for DCNN, Tania Arora and James Wyatt, Partners at Baker McKenzie (London), examine the evolving landscape of data centre power supply, highlighting why a tailored approach - blending grid connections, on-site generation, microgrids, and emerging technologies such as SMRs and battery energy storage - is increasingly essential for resilience, sustainability, and commercial optimisation:
No universal solution
Data centres presently require considerable energy resources, with projections indicating a marked increase in their consumption in the coming years. Securing a steady, sufficient, reliable, and scalable power supply is crucial for the financing, operational success, and long-term resilience of any data centre.
A universal strategy does not exist for procuring power for data centres; each project requires a tailored approach. The market offers a wide range of power supply options and these are frequently combined to address the specific requirements of each project. The exact power procurement strategy for each project is determined by several factors, most notably the location of the data centre, local regulatory frameworks, its current and future operational needs, and the strategy of the developer (particularly considering other assets / other electricity supply arrangements they own). This article considers power procurement options available in the market and how these could be combined to achieve a successful power supply strategy.
The key power supply options available at present include grid power, on-site or adjacent-site power generation, and microgrids (renewable or conventional), supported by backup generators, battery energy storage systems (BESS), and fuel cells. On-site or adjacent-site nuclear power is increasingly viewed as a panacea solution for data centre energy needs, although there are still considerable political, technological, and risk-allocation problems to solve.
Data centres usually connect to public electricity grids, but most grids were not designed for their high load. Upgrades and expansions are often needed, which can be time-consuming and expensive. Sometimes, users must pay for these improvements, and further upgrades may be required if the data centre expands. Furthermore, securing a grid connection is rarely guaranteed; capacity reservations may be needed and are often subject to legal conditions.
In some cases, installing on-site generation and microgrids can help address grid challenges. This could involve constructing solar and wind power plants (supported by BESS), gas-fired power stations, and/or combined heat and power (CHP) units adjacent to the data centre and supplying electricity directly without relying on the public grid.
Furthermore, fuel cell and linear generator systems - as well as small modular reactors (SMRs) - are emerging as low-carbon, scalable power solutions for data centres. While the ongoing costs for self-generated energy are generally much lower, building such a dedicated energy infrastructure typically entails significantly higher upfront costs compared to connecting to the public grid. Furthermore, on-site projects are often constrained by space and planning restrictions, particularly in urban or suburban markets where demand is highest.
Sustainable options
Sustainability is a key consideration for a number of data centre market participants. Even if on-site wind or solar energy is economically viable for a project, these renewables alone cannot provide a stable base load due to their intermittency. To ensure base-load coverage, additional infrastructure such as energy storage systems, fuel cells, and conventional backup generators are required.
SMRs and advanced nuclear technologies are emerging as promising solutions for the rising power needs of data centres. They offer reliable, consistent base-load power, load-following capability, scalable output, low carbon emissions, and a small physical footprint. They can operate independently of the grid or alongside renewables and are designed to be more cost-effective and quicker to deploy than traditional large-scale nuclear plants due to modular construction and established supply chains.
SMRs are becoming a tangible reality for data centres. For example, the UK Government recently provided a considerable amount of support for SMRs for data centres through planning reforms, regulatory acceleration, funding, and explicit policy direction encouraging SMR–data‑centre colocation. However, SMRs face challenges: they are largely unproven and most jurisdictions still lack regulatory frameworks tailored to their unique characteristics. Key considerations for deploying SMRs include understanding local nuclear regulations, licensing and approval processes, decommissioning requirements, nuclear waste management, fuel supply security, and site suitability. Addressing these legal and regulatory issues is essential before SMRs can be widely adopted for data centres.
BESS has become a key part of data centre power strategies, serving not only as resilience infrastructure but also helping to unlock commercial opportunities. It provides load shifting and peak shaving, thus reducing exposure to volatile wholesale prices and network charges by charging during low-cost or high-renewable periods and discharging power at peak demand. BESS also delivers instant backup power during outages and enables participation in grid services for additional revenue. Key issues include permitting and safety (especially for large-scale systems near nuclear or high-voltage facilities), complex grid connection agreements, and risk allocation where BESS is delivered via third-party energy-as-a-service contracts.
Final considerations
The near to mid-term future of data centre power lies in combined strategies. Every option in the combination presents its own distinct legal and commercial considerations. Consequently, as strategies become more complex, market participants should anticipate navigating a greater number of legal issues within the context of rapidly evolving regulatory frameworks.
Joe Peck - 18 February 2026
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Events
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
Liquid Cooling Technologies Driving Data Centre Efficiency
Products
Carrier to showcase AI cooling at DCW London 2026
Carrier, a manufacturer of HVAC, refrigeration, and fire and security equipment, will present its QuantumLeap portfolio at Data Centre World London 2026, taking place on 4–5 March.
As a Platinum Sponsor, the company will host a panel discussion, a keynote session, and a solo presentation focused on cooling, building management, and lifecycle services for AI-driven data centres.
Carrier, part of Carrier Global Corporation, will outline how increasing AI workloads are affecting thermal density and energy consumption across data centre environments.
The company says the rapid growth of AI is creating pressure to manage higher heat loads while reducing overall energy use. Its QuantumLeap portfolio includes liquid cooling systems and high-efficiency chillers designed to support next-generation processors and higher rack densities.
Integrated management and lifecycle focus
Carrier will also highlight its building automation and data centre infrastructure management capabilities. By linking cooling, power, and IT systems through building automation systems and DCIM platforms, the company aims to give operators clearer operational oversight and improved energy control.
In addition, Carrier will address lifecycle management, including waste heat reuse and grid participation, as part of broader sustainability strategies within AI data centres.
Bertrand Rotagnon, Executive Director Commercial Business Line & Data Centres Europe, says, “Data centres can’t choose between growth, resilience, and energy performance; they need all three.
"At DCW London 2026, we’re showcasing Carrier QuantumLeap solutions to help operators simplify decisions, improve efficiency, and move towards measurable energy contribution.”
Carrier will be located at Stand D70. The company’s panel discussion takes place at 12:20 on Wednesday, 4 March, with a solo presentation at 15:55 on the same day and a keynote at 14:50 on Thursday, 5 March.
For more from Carrier, click here.
Joe Peck - 18 February 2026
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Data Centre Compliance: Standards, Risk & Governance
News
Data Centre Alliance appoints new advisory board
The Data Centre Alliance (DCA), the UK trade association for the data centre sector, has appointed a new Advisory Board to lead its expanded Advisory Council.
Liam Round has been named Chair, alongside board members Jonathon Freegard, Scott Cunningham, Astrid Wynne, Phil Beale, and John Booth. The appointments reflect experience across different areas of the data centre industry.
The board will oversee the Advisory Council’s work in identifying key industry priorities and developing initiatives aimed at informing end users, policymakers, media, and the wider public.
Focus on policy, energy, and standards
Previous DCA initiatives include:
• The DCA UK Data Centre Legislation Horizon Scan report• The Drowning in Data report on data centre water usage• The Data Centre Anti Contamination, Filtration, and Cleaning guide• The Data Centre Planning Policy, Sustainability, and Resilience Initiative guide• EU Code of Conduct for data centres energy efficiency updates• DCA data centre standards whitepapers
Liam Round, Managing Director of Teksan UK and now Chair of the Advisory Council at the DCA, comments, “It is an honour to take on the role of Chair of the Advisory Board and Council at The Data Centre Alliance at such an important time for our sector.
"Digital infrastructure underpins economic growth, national resilience, and AI development. I look forward to working with the DCA’s leadership and Partners to provide clear guidance, strong governance, and strategic focus as the industry navigates rapid change.”
Over the next year, the Advisory Board and Council says it will focus on planning reform, energy market integration, grid access, sustainability, water resilience, AI infrastructure readiness, and industry standards development.
Joe Peck - 18 February 2026
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
Events
Products
Sponsored
AFL: Why data centre leaders are heading to Stand C110
AFL, a manufacturer of fibre optic cables and connectivity equipment, will be attending this year's Data Centre World in London, 4–5 March 2026, exhibiting on Stand C110. In this article, the company tells you about what you can expect:
Your AI clusters are hungry for bandwidth. GPU-to-GPU latency is make or break, and you’re being asked to scale yesterday, all while maintaining uptime, managing density, and staying within budget. AFL understands. It has engineered solutions specifically for these problems.
What you’ll experience at Stand C110:
• Hands-on demos• Industry-first technology• Solutions for your biggest bottlenecks• Modular white space infrastructure you can deploy rapidly• AI-GPU connectivity optimised for ultra-low latency compute fabrics• High-density DCI solutions that maximise available space in cable ducts• Pre-terminated, plug-and-play modules with full traceability to help you deploy faster• Fujikura’s Multi-Core, Hollow-Core, and Mass-Fusion splicers in action – the precision tools that research labs and hyperscalers trust for next-generation fibre deployment• Small-form-factor assemblies – reduce diameter, increase density, maximise airflow and cable pathways• Test with confidence – advanced inspection tools that validate performance before the first packet flows
Why AFL for hyperscale data centres?
• Globally available — consistent supply chain, wherever you build• Proven reliability — supporting the world’s largest hyperscale networks• Modular and scalable — grow your infrastructure without forklift upgrades• Built for AI workloads — engineered for the bandwidth and latency demands of dense GPU clusters
Who should visit the stand?
• Network engineers deploying or upgrading DCI links• Data centre architects planning next-generation AI infrastructure• Infrastructure leaders evaluating fibre solutions for hyperscale growth• Operations teams seeking faster commissioning and maintenance workflows
Ready to enhance hyperscale efficiency?
Bring your toughest connectivity challenges to Stand C110 and see how AFL’s team is already solving the real-world problems you face with innovative solutions ready for immediate global deployment.
Find out how its optical fibre experts can help you scale seamlessly across growing hyperscale deployments for AI and cloud.
For more from AFL, click here.
Joe Peck - 17 February 2026

Head office & Accounts:
Suite 14, 6-8 Revenge Road, Lordswood
Kent ME5 8UD
T: +44 (0)1634 673163
F: +44 (0)1634 673173