16 February 2026
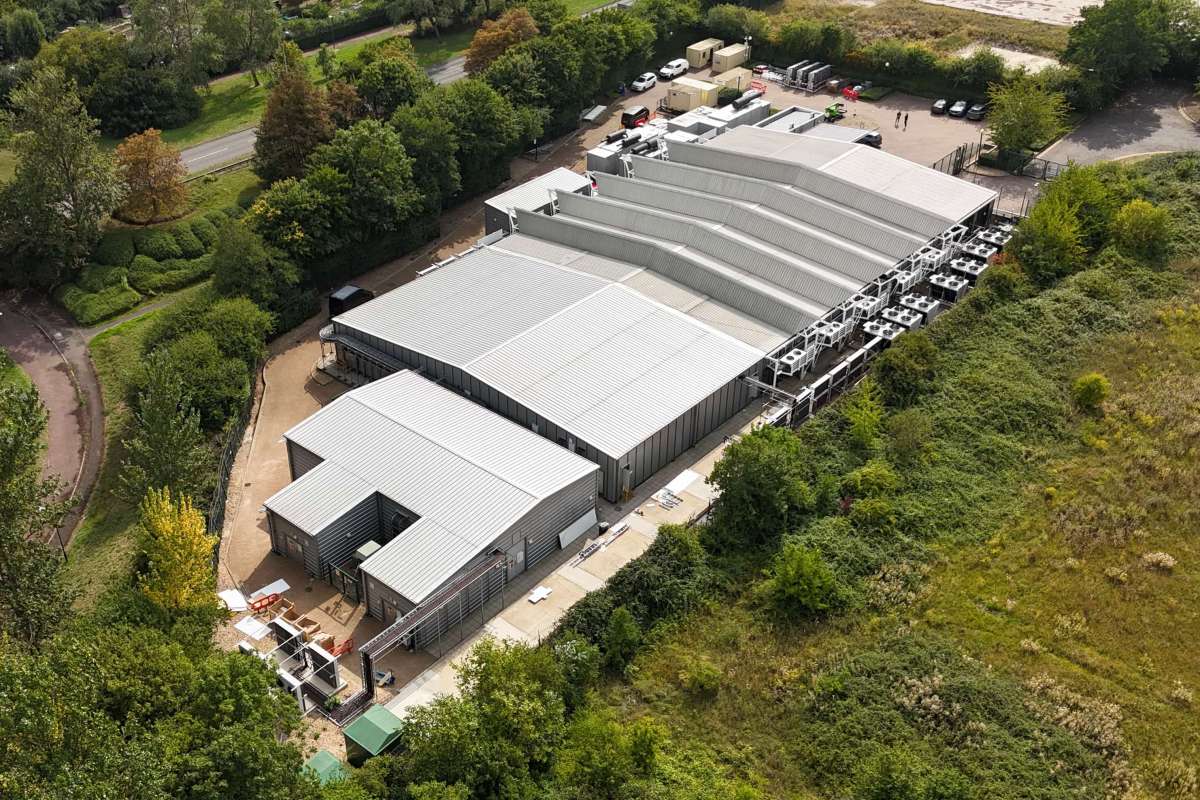
LINX to upgrade Lunar Digital data centre into fully resilient PoP
LINX to upgrade Lunar Digital data centre into fully resilient PoP
13 February 2026
Infosys, ExxonMobil collaborate on immersion cooling
Infosys, ExxonMobil collaborate on immersion cooling
12 February 2026
nLighten's Stuttgart data centre to reuse heat
nLighten's Stuttgart data centre to reuse heat
12 February 2026
ERIKS to showcase valves expertise at Data Centre World 2026
ERIKS to showcase valves expertise at Data Centre World 2026
11 February 2026
Mistral AI and EcoDataCenter to build data centre in Sweden
Mistral AI and EcoDataCenter to build data centre in Sweden
Latest News
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
Insights into Data Centre Investment & Market Growth
Liquid Cooling Technologies Driving Data Centre Efficiency
Trane to acquire LiquidStack
Trane Technologies, a US manufacturer of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire LiquidStack, a US-based provider of liquid cooling technology for data centres.
LiquidStack, headquartered in Carrollton, Texas, develops direct-to-chip and immersion cooling systems for high-density and hyperscale computing environments. The company’s technology is used to support generative AI and other compute-intensive workloads.
Trane Technologies made a minority investment in LiquidStack in 2023. The proposed acquisition expands its data centre thermal management portfolio, which includes chillers, heat rejection systems, controls, liquid distribution, and on-chip cooling.
Expanding liquid cooling capabilities
The deal includes LiquidStack’s manufacturing, engineering, and research and development operations in Texas and Hong Kong. Following completion, the business will operate within the Commercial HVAC unit of Trane Technologies’ Americas segment.
Holly Paeper, President, Commercial HVAC Americas, Trane Technologies, says, “Rising chip-level power and heat densities, combined with increasingly variable workloads, are redefining thermal management requirements inside modern data centres.
"Customers need integrated cooling solutions that scale from the central plant to the chip and can adapt as performance demands continue to evolve.
"LiquidStack’s direct-to-chip and immersion cooling capabilities and talent, combined with Trane’s systems expertise and global footprint, strengthen our ability to deliver end-to-end, future-ready thermal management across the entire data centre ecosystem.”
LiquidStack co-founder and CEO Joe Capes will join Trane Technologies in a leadership role and will continue to lead the business.
Joe says, “LiquidStack has been on a mission to innovate and deliver the most advanced, powerful, and sustainable liquid cooling solutions.
"Joining Trane Technologies enables us to accelerate that mission with the resources, scale, and global reach needed to power next-generation AI workloads in the most demanding compute environments."
The transaction is expected to close in early 2026, subject to customary conditions. Financial terms have not been disclosed.
Trane Technologies also recently announced the acquisition of Stellar Energy, which is expected to complete in the first quarter of 2026.
For more from Trane Technologies, click here.
Joe Peck - 11 February 2026
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Exploring Modern Data Centre Design
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
TES Power to deliver modular power for Spanish DC
TES Power, a provider of power distribution equipment and modular electrical rooms for data centres, has been selected to deliver 48 MW of modular power infrastructure for a new greenfield data centre development in Northern Spain, designed to support artificial intelligence workloads.
The facility is intended for high-density compute environments, where power resilience, scalability, and deployment speed are key considerations.
Growing demand from AI training and inference continues to place pressure on operators to deliver robust electrical infrastructure without compromising availability or reliability.
Modular power skids for high-density AI environments
As part of the project, TES Power will design and manufacture 25 fully integrated 2.5MW IT power skids.
Each skid is a self-contained module incorporating cast resin transformers, LV switchgear, parallel UPS systems, end-of-life battery autonomy, CRAH-based cooling, and high-capacity busbar interconnections.
The skids are designed to provide continuous power to critical IT loads, with automatic transfer from mains supply to battery and generator systems in the event of a supply disruption, a requirement increasingly associated with AI-driven data centre operations.
Michael Beagan, Managing Director at TES Power, says, “AI is fundamentally changing the scale, speed, and resilience requirements of data centre power infrastructure. This project reflects exactly where the market is heading: larger, higher-density facilities that cannot tolerate risk or delay.
"By delivering fully integrated, factory-tested power skids, we’re helping our client accelerate deployment while maintaining the absolute reliability that AI workloads demand.”
The project uses off-site manufacture to reduce programme risk and enable parallel delivery, allowing electrical systems to be progressed while civil and building works continue on-site.
Each skid will undergo full Factory Acceptance Testing prior to shipment, reducing commissioning risk and limiting on-site installation time.
Building Information Modelling is being used to digitally coordinate each skid with wider site services, supporting installation sequencing, clash detection, and longer-term operational planning.
TES Power’s scope also includes project management, site services, and final commissioning.
Joe Peck - 10 February 2026
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
Insights into Data Centre Investment & Market Growth
Liquid Cooling Technologies Driving Data Centre Efficiency
Direct-to-chip liquid cooling market to reach $7.9bn by 2033
Rising computational intensity has placed unprecedented pressure on traditional air-based cooling systems. High-performance computing (HPC), artificial intelligence (AI), cloud data centres, and advanced semiconductor architectures generate dense heat loads that are increasingly difficult to manage using conventional thermal management approaches.
According to Research Intelo, a global market research and consulting firm, the global direct-to-chip liquid cooling market was valued at $1.3 billion (£951 million) in 2024 and is projected to reach $7.9 billion (£5.7 billion) by 2033, expanding at a CAGR of 22.3%. This strong growth trajectory underscores the growing reliance on liquid-based cooling technologies to support next-generation digital infrastructure.
Direct-to-chip liquid cooling has emerged as a practical and scalable response to these challenges, offering targeted heat removal directly from processors and other high-power components. By reducing thermal resistance and improving heat transfer efficiency, this approach supports higher rack densities while aligning with broader energy efficiency and sustainability objectives.
What exactly is direct-to-chip liquid cooling?
Direct-to-chip liquid cooling is a thermal management method in which a liquid coolant flows through cold plates mounted directly onto heat-generating components such as CPUs, GPUs, and accelerators. Heat is absorbed at the source and transported away through a closed-loop liquid system, minimising reliance on air circulation.
Compared to immersion cooling, which involves submerging entire systems in dielectric fluids, direct-to-chip solutions integrate more easily with existing data centre architectures. This balance between high cooling efficiency and operational compatibility has positioned the technology as a preferred option for gradual infrastructure upgrades and hybrid cooling deployments.
Which factors are driving market growth?
1. Technological innovation and automation
As processing power and server densities continue to rise, traditional air-cooling solutions are approaching their practical limits, increasing the risk of thermal throttling and hardware degradation. Direct-to-chip liquid cooling technologies provide a highly efficient alternative by enabling precise and consistent heat removal from critical components.
Ongoing innovation in cold plate design, advanced coolants, and system integration is further enhancing performance and reliability. The incorporation of smart sensors, real-time monitoring tools, and automated flow controls enables predictive maintenance and dynamic thermal optimisation. These advancements are making direct-to-chip liquid cooling more scalable and accessible across a wide range of computing environments, from hyperscale data centres to edge deployments.
2. Shifts in end-user accelerating market expansion
The rapid expansion of data-intensive applications, including AI, machine learning, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT), has led to unprecedented heat generation within servers and computing clusters. Enterprises and data centre operators face increasing pressure to maintain high performance and uptime while controlling operational costs and energy consumption.
Direct-to-chip liquid cooling addresses these demands by delivering superior thermal efficiency and reducing dependence on energy-intensive air conditioning systems. The ability to support higher rack densities is particularly valuable in urban data centres and edge locations where space and power constraints are significant. As organisations prioritise sustainability and long-term infrastructure resilience, adoption of liquid cooling technologies is expected to expand across multiple industry verticals.
3. Regulatory support and government incentives
Regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in data centres are creating favourable conditions for advanced cooling technologies. In regions such as Europe and North America, government incentives - including tax benefits, grants, and energy efficiency programs - are encouraging the adoption of low-impact thermal management solutions.
In parallel, international standards for green data centre operations are pushing organisations to modernise their infrastructure and improve environmental performance. These regulatory and policy-driven factors are fostering innovation, reducing adoption barriers, and supporting sustained market growth.
What challenges are limiting wider adoption?
Despite strong growth prospects, the market faces several challenges that could impact adoption rates. Regulatory uncertainty related to safety standards, environmental compliance, and fluid handling requirements can complicate deployment decisions. Volatility in raw material prices, particularly for copper and specialised cooling fluids, may also influence production costs and pricing strategies.
Additionally, standardisation gaps and interoperability issues can pose challenges in complex or legacy IT environments. Addressing these constraints will require continued collaboration among technology providers, regulators, and end-users to establish clear guidelines, improve compatibility, and build confidence in long-term system reliability.
Which technologies are shaping product innovation?
Manufacturers are continually refining cold plate designs to improve heat transfer efficiency and compatibility with next-generation processors. Innovations such as microchannel architectures, optimised flow paths, and advanced alloys enable higher thermal performance while minimising pressure drop and energy consumption.
Customisation tailored to specific processor architectures and workload requirements has become increasingly common. This flexibility supports diverse applications across AI, HPC, cloud computing, and enterprise data centres, further strengthening the market’s value proposition.
What regional trends are emerging?
• North America dominates the global market, accounting for over 38% of total market share in 2024. This leadership is driven by a mature data centre ecosystem, advanced IT infrastructure, and early adoption of innovative cooling technologies. The strong presence of hyperscale data centre operators and cloud service providers, particularly in the US, has accelerated deployment across the region.
• Asia Pacific is projected to register the fastest growth, with a CAGR of 27.1% from 2025 to 2033. Rapid digital transformation, expanding cloud infrastructure, and increasing investments in hyperscale and edge data centres are fuelling demand. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and Singapore are witnessing rising adoption of AI and HPC across sectors including fintech, healthcare, and smart cities, further driving the need for advanced cooling solutions.
• Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are experiencing gradual adoption of direct-to-chip liquid cooling technologies. While infrastructural limitations, budget constraints, and skills gaps have slowed deployment, growing awareness of long-term cost savings and sustainability benefits is steadily improving market outlook in these regions.
What does the competitive landscape look like?
The market features a combination of established thermal management companies and specialised liquid cooling solution providers. Competition is primarily based on cooling efficiency, system reliability, ease of integration, and total cost of ownership.
Strategic partnerships between hardware manufacturers, data centre operators, and cooling technology providers are becoming increasingly common. Continuous investment in research and development remains critical, as cooling requirements evolve alongside processor design and workload intensity.
What is the future outlook for the direct-to-chip liquid cooling market?
The transition towards high-density computing shows no signs of slowing. Market forecasts indicate strong expansion, with the direct-to-chip liquid cooling market expected to grow from $1.3 billion (£951 million) in 2024 to $7.9 billion (£5.7 billion) by 2033, reflecting sustained demand across data centre, enterprise, and research environments.
As processors become more powerful and energy efficiency expectations rise, direct-to-chip liquid cooling is expected to shift from selective adoption to broader implementation. Continued standardisation, declining component costs, and increased operational familiarity are likely to accelerate this transition.
Conclusion: Is direct-to-chip liquid cooling becoming a standard rather than an option?
Direct-to-chip liquid cooling addresses some of the most critical challenges facing modern computing infrastructure. By enabling efficient heat management, supporting high-performance workloads, and aligning with sustainability and energy efficiency goals, the technology is redefining thermal management strategies.
As digital workloads intensify and infrastructure demands evolve, the market’s trajectory raises a defining question: Will direct-to-chip liquid cooling soon be regarded as a baseline requirement for advanced computing environments rather than a specialised enhancement?
Joe Peck - 10 February 2026
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
Features
News in Cloud Computing & Data Storage
OpenNebula validated with NVIDIA Spectrum-X
OpenNebula Systems has today announced that its cloud management and virtualisation platform, OpenNebula, has been validated by NVIDIA as an orchestration platform integrated with NVIDIA Spectrum-X Ethernet networking.
OpenNebula is used as a multi-tenant platform for AI factories, providing isolation, governance, and lifecycle management for accelerated infrastructure. The company says the validation supports the deployment of AI-ready cloud infrastructure using Spectrum-X Ethernet.
Spectrum-X Ethernet is designed for AI networking environments, where latency, congestion, and jitter can affect large-scale training and multi-tenant inference workloads.
OpenNebula now integrates with the networking platform to provide a software-defined cloud environment for AI applications, with multi-tenancy across compute, GPU, and network layers on a shared Spectrum-X Ethernet fabric.
Automated orchestration for AI workloads
The integration allows OpenNebula to orchestrate tenant provisioning, network configuration, and device attachment through Spectrum-X Ethernet.
The OpenNebula control plane also runs on NVIDIA Air, which provides a platform for testing, integration, and validation.
Customers can use the environment to evaluate the integration, run simulations, and test automation workflows for AI factory deployments.
Ignacio M. Llorente, CEO of OpenNebula Systems, says, “Through our collaboration with NVIDIA, we are extending OpenNebula to support the networking and performance requirements of modern AI infrastructures.
"This integration allows customers to manage multi-tenant AI environments where NVIDIA Grace Blackwell and NVIDIA Grace Blackwell Ultra compute and Spectrum-X Ethernet networking are tightly orchestrated and optimised as a single platform.”
Amit Katz, VP of Networking at NVIDIA, adds, “OpenNebula’s integration with NVIDIA Spectrum-X Ethernet brings cloud-native agility to the AI Factory, enabling customers to orchestrate multi-tenant accelerated infrastructure with maximum performance and predictability.
"NVIDIA Air enables OpenNebula and our ecosystem partners to validate and simulate large-scale AI Factory deployments, giving customers a powerful environment to evaluate and accelerate their AI cloud strategies.”
For more from OpenNebula, click here.
Joe Peck - 10 February 2026
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
Liquid Cooling Technologies Driving Data Centre Efficiency
Products
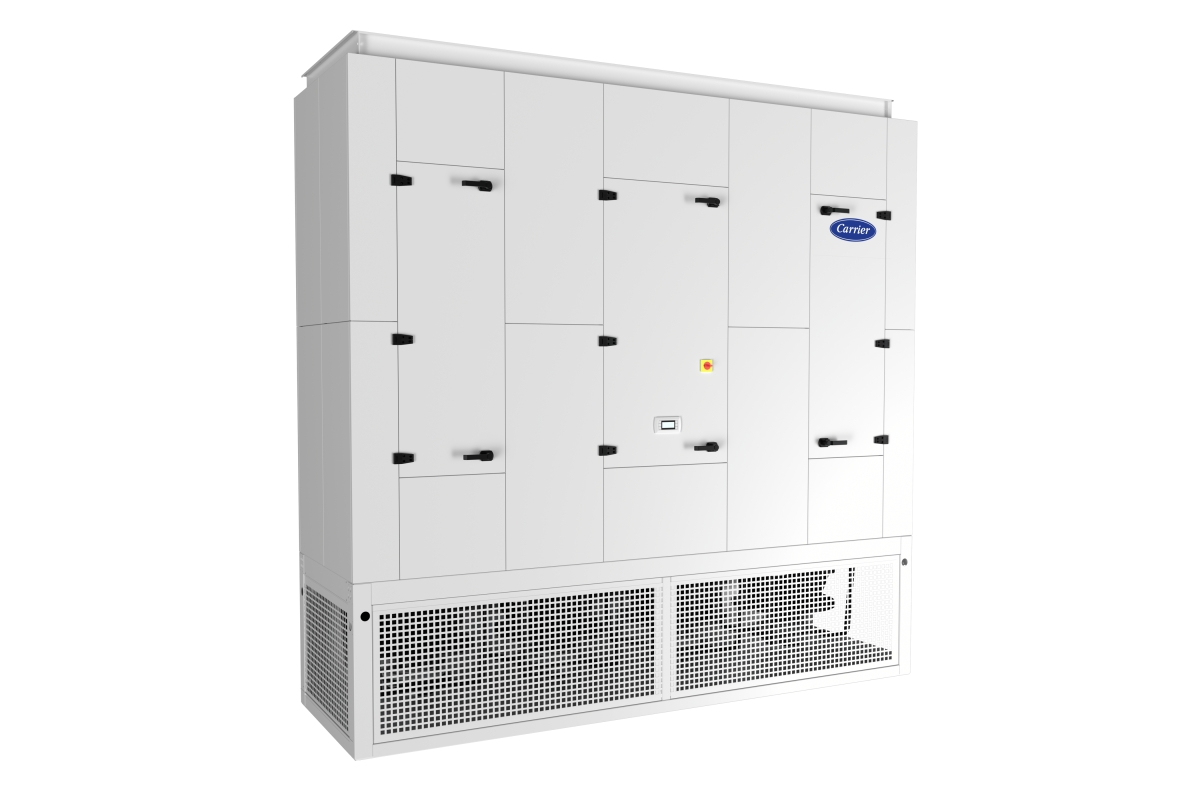
Carrier launches CRAH for data centres
Carrier, a manufacturer of HVAC, refrigeration, and fire and security equipment, has introduced the AiroVision 39CV Computer Room Air Handler (CRAH), expanding its QuantumLeap portfolio with a precision cooling system designed for medium- to large-scale data centre environments.
Developed and manufactured in Europe, the AiroVision 39CV is intended to support energy efficiency, reliability, and shorter lead times, while meeting EU regulatory requirements.
The unit offers a cooling capacity from 20kW to 250kW and is designed to operate with elevated chilled water temperatures.
Carrier states that this approach can improve energy performance and contribute to lower power usage effectiveness (PUE) by enabling more efficient chiller operation and supporting free cooling strategies.
Factory-integrated design for simplified deployment
The AiroVision 39CV features a built-in controller for real-time monitoring, adaptive operation, and integration with building management systems. The control platform can be configured to suit specific operational requirements.
All components are factory-integrated to reduce on-site installation and commissioning work. Additional features, including an auto transfer switch and ultra-capacitors, are intended to support service continuity in critical environments.
Michel Grabon, EMEA Marketing and Market Verticals Director at Carrier, says, “The 39CV is a strategic addition to our QuantumLeap Solutions portfolio, designed to help data centre operators address today’s most pressing challenges: increasing thermal loads from higher computing densities, the need to reduce energy consumption to meet sustainability targets, and the pressure to deploy solutions quickly and efficiently.
"With its high-efficiency design, intelligent control system, and factory-integrated components, the 39CV helps operators to improve energy performance, optimise installation time, and build scalable infrastructures with confidence.”
For more from Carrier, click here.
Joe Peck - 9 February 2026
Commercial Real Estate: Property Developments, Trends & Infrastructure
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
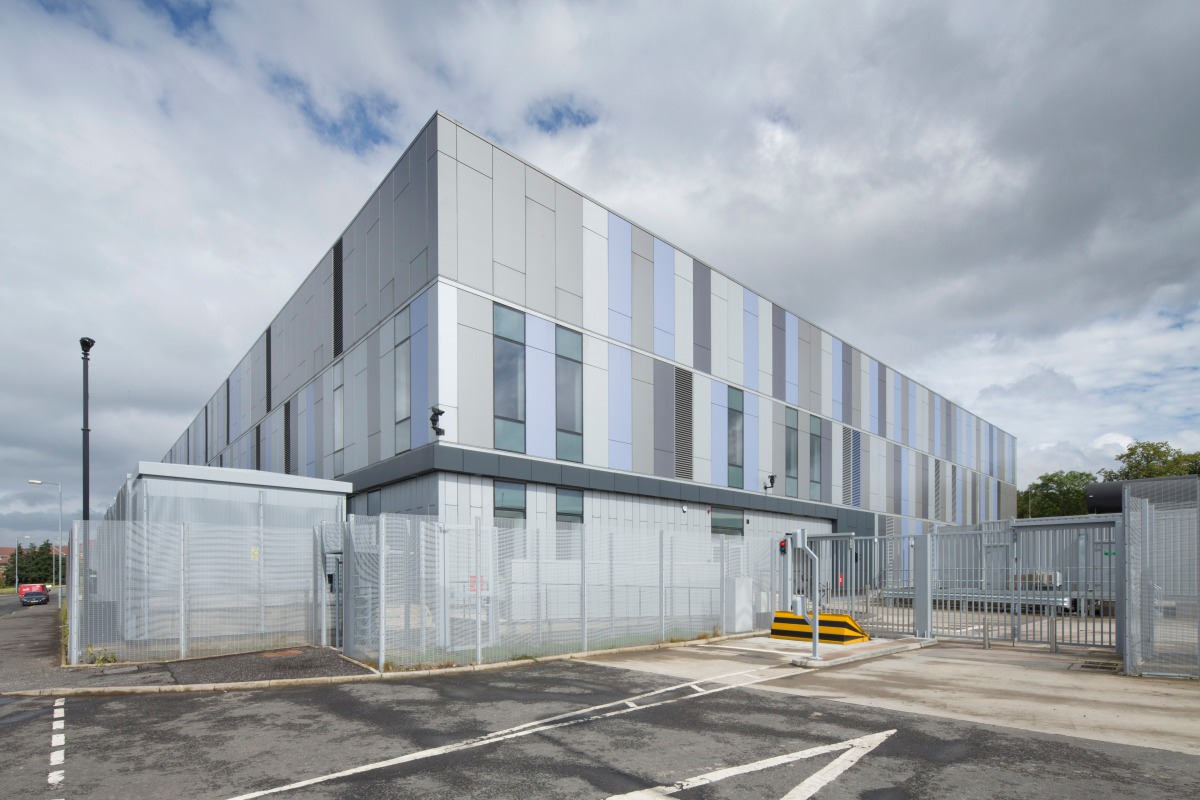
Pulsant opens high-density UK facility outside London
UK data centre operator Pulsant has completed a £10 million investment in a new high-density data hall at its Milton Keynes site, SE-1.
The facility has been developed to support increased demand for artificial intelligence and advanced computing workloads, with the expansion forming part of Pulsant’s national platformEDGE framework, extending high-performance, UK-based infrastructure outside the London market.
The 1.2MW expansion is designed for high-density computing applications, including AI, machine learning, and accelerated workloads. These use cases are commonly associated with sectors such as financial services, healthcare, biotechnology, IT, and gaming.
Regional capacity beyond the London market
Pulsant positions the Milton Keynes site as an alternative location for organisations seeking UK data centre capacity outside London. The site sits within the Oxford-Cambridge technology cluster, which is home to around 570,000 employees and generates approximately £135 billion in annual turnover.
The facility offers latency of around two milliseconds to London Docklands and Slough. It forms part of Pulsant’s network of 14 UK data centres, interconnected via a 400Gb-capable network, providing access to more than 1,600 cloud services, network providers, and business partners.
The launch follows increased focus on domestic digital infrastructure, including government funding aimed at strengthening UK AI capability. Milton Keynes has continued to attract technology businesses, supported by regional business networks and digital innovation activity.
Rob Coupland, CEO at Pulsant, says, “The £10 million expansion of our Milton Keynes data centre is another big investment in our digital platform to meet hunger for high density compute power.
"UK digital infrastructure is facing unprecedented demand. With AI-ready capacity in short supply, bringing high performance, flexibility, and choice to regional locations is critical.
“For organisations looking for ultra-low latency, international connectivity, and UK sovereign compute power, Milton Keynes is a great option compared to constrained and costly London data centres which lack the opportunity for expansion.
“Our unique platform gives local, national, and international clients the flexibility to circumvent some of the risks associated with the London cluster while maintaining high performance, resilience, and connectivity.”
Pulsant states that it plans to roll out its high-density model to additional UK regions as part of its wider national infrastructure strategy.
For more from Pulsant, click here.
Joe Peck - 9 February 2026
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
News
North East England data centre hub launched
A consortium of North East engineering and manufacturing powerhouses have joined forces to launch a new not-for-profit forum designed to help shape and propel the future of the data centre sector in the region.
The North East Data Centre Hub has been founded by major global companies including RED Engineering Design, Cleveland Cable Company, CMP Products, Durata, and RWO Associates.
Together, the founding members says they share a clear ambition to build momentum by collaborating on the development of a strong local engineering, construction, and digital supply chain to support data centre projects across the region and beyond.
Opportunities in the North East
With the North East strongly positioned as one of Europe’s largest data centre and AI infrastructure hubs - driven by government policy, energy availability, and major hyperscale investment - the launch of the hub provides an opportunity to shape the conversation locally and accelerate growth through regular engagement.
The initiative aims to unlock the region’s full potential as a leading data centre destination.
To mark its launch, the consortium will host the North East Data Centre Hub’s first networking event (which is already fully booked) on 25 February, from 5:30pm to 8:00pm, at Liberty House in Newcastle's city centre.
Speaking about the North East Data Hub and its first event, John McGee (pictured above), Group CEO at Durata, says, “The hub provides an excellent opportunity for professionals in the sector - from developers and operators through to consultants and suppliers - to collaborate, share innovation, and exchange best practice.
"By strengthening local connections, we can amplify the North East’s contribution to the wider UK and global data centre market.
“We are delighted with the companies spearheading this initiative. Each brings extensive global experience in delivering critical infrastructure projects and, by working together - and joining forces with other local businesses - we can build a strong, resilient regional supply chain that supports long‑term growth, investment, and skills development in the North East.
“With registration already reaching full capacity for our first event, it’s clear there is strong appetite for a hub of this nature. Many delegates will be attending with a shared goal, and this is just the beginning. We have an exciting programme of events planned over the next 12 months, with much more to come from the North East Data Centre Hub.”
The North East Data Centre Hub is open to organisations across the data centre ecosystem, with plans for a programme of bi-monthly events hosted across the region, featuring speakers and with the opportunity for discussion and continued networking.
To be the first to know about upcoming events and industry news from the newly formed hub, you can sign up for alerts by clicking here.
Joe Peck - 6 February 2026
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
News
Aggreko: Power supply will decide AI winners and losers
Following the publication of a report that states up to a third of US data centres are expected to be fully off-grid by 2030, Aggreko, a British multinational temporary power generation company, is warning that the European market could follow the same trend, noting that the provision of power will be the deciding factor in the companies and markets that draw the biggest benefit from the ongoing AI boom.
Bloom Energy’s 2026 power report, which looks specifically at developments in the US data centre market, also indicates that data centres are already beginning to move from areas where the grid is strained to those that can offer more ample supply. For instance, Texas’s data centre load is set to double by 2028, while traditionally leading areas like California and Oregon are set to lose 50% of their relative market share.
Billy Durie, Global Sector Head of Data Centres at Aggreko, believes that these findings are a sign of what is to come in Europe, stating, “I am not surprised by the findings of Bloom’s latest report. Securing a reliable power supply has long been the bugbear of data centre operators across the world, though increasing power demand driven by the development of AI is now taking this challenge to new extremes in the US and Europe.
“Depending on which source you look at, AI is set to increase power demand by as much as 150% by 2035, which is why operators are either relocating or taking power provision into their own hands in an attempt to find a permanent solution.
“In my experience, these trends tend to emerge earlier in the US than in Europe, though we can certainly expect this market to follow suit. While this is a global challenge, with older grid infrastructure and more severe strain in Europe, you could even argue that we will see an even more acute response on this side of the pond very soon.”
Moving off-grid in Europe
The effects of grid strain on European data centre development have been well documented. In Scotland, a recent study has indicated that AI data centres could consume up to 75% of the nation’s electricity, while in Switzerland, there are fears that Zurich’s grid no longer has capacity to deal with additional demand.
With comparatively limited options for relocation in Europe, many data centre operators have already turned to decentralised energy, though fully off-grid facilities are yet to be realised on a wider scale.
Among the most popular solutions available on the market today are stage-V generators for short-term projects, while gas generators, microgrids, and renewables coupled with battery energy storage systems (BESS) are all in-demand options for energy provision and bridging power during upgrades.
Small modular reactors (SMRs) also hold a place in the plans of many stakeholders, though are not expected to be commercially available until the end of the next decade, requiring effective bridging solutions in the interim.
Billy concludes, “For European data centre operators who don’t have the same power of relocation that their US counterparts do, the ability to reduce dependence on the grid will be critical. Fortunately, there are already many solutions already available to help them do this, and even more exciting technologies in development.
"Whatever option they choose to deploy, one thing is certain: the ability to source a stable power supply will dictate the winners and losers of the AI boom.”
For more from Aggreko, click here.
Joe Peck - 6 February 2026
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Features
News in Cloud Computing & Data Storage
DataVita secures £44.9m contract with Glasgow City Council
DataVita, a UK data centre and cloud services provider, has announced it has secured a major contract with Glasgow City Council to provide the city’s core compute and storage services.
The initial agreement is valued at £44.9 million over five years and nine months and will see DataVita modernise the Council's digital backbone to underpin essential public services.
The partnership includes options for the Council to extend for multiple periods and, should the contract run for its maximum permitted duration of over 10 years, the total projected value is estimated to be between £80 million and £110 million.
Under the initial term, which began on 8 October 2025, DataVita will deliver a comprehensive suite of services from its Tier-III-certified Scottish data centres. These services will form the foundation of the Council's IT infrastructure, supporting over 400 applications that are critical to daily public services.
The scope includes providing resilient primary and disaster recovery environments, managing virtual and physical servers, scalable storage, and "robust backup solutions" featuring immutable copies for maximum data protection.
As part of the contract, up to 25 new roles will also be created, including several apprenticeships, which DataVita says reflects its "commitment to skills development and job creation within Scotland’s tech sector."
Investments in Scotland's backbone
Danny Quinn, Managing Director of DataVita, comments, "We are incredibly proud to be selected as a strategic partner for Glasgow City Council. We are focused on delivering exceptional value and innovation over the initial term and see this as the start of a long-term partnership.
"Our mission is to provide a resilient, secure, and sustainable digital infrastructure that will not only meet the city's needs today, but also support its ambitions for the future. This award is a testament to our team's expertise and our commitment to investing in Scotland's technology ecosystem."
As part of Glasgow's transition to a multi-source IT delivery model, DataVita will integrate with the Council's Service Integration and Management (SIAM) function, aiming to ensure efficient and collaborative service delivery alongside other partners.
Paul Leinster, Chair of the Digital Glasgow Board from Glasgow City Council, says, “The essential services that we deliver to citizens and the value they add to people’s lives are always our first priorities.
“Increasingly, though, we rely on a complex digital estate to deliver those services, and this contract will ensure we have a secure, resilient platform to support what is an incredibly diverse range of work.
"DataVita brings proven capability here in Scotland, and their commitment to renewable, energy‑efficient operations aligns with Glasgow’s ambitions for a cleaner, greener city.”
For more from DataVita, click here.
Joe Peck - 6 February 2026
Data Centre Business News and Industry Trends
Data Centre Regulations & UK Compliance Updates
Insights into Data Centre Investment & Market Growth
News
UK parliamentarians launch Data Centres APPG
MPs and peers have launched a new All-Party Parliamentary Group (APPG) focused on data centres, examining the sector’s role in economic growth, digital infrastructure resilience, and net zero targets.
The cross-party group is chaired by Chris Curtis MP, Labour MP for Milton Keynes North and Chair of the Labour Growth Group. Other officers include:
• Lewis Cocking MP, Conservative MP for Broxbourne (as co-chair)• Alison Griffiths MP, Conservative MP for Bognor Regis and Littlehampton• Lord Philip Hunt of Kings Heath OBE, former Minister of State for Energy Security and Net Zero
The APPG aims to improve parliamentary understanding of data centre development across the UK, review challenges and opportunities facing the sector, and produce evidence-based policy recommendations.
The group will examine areas including infrastructure delivery, planning considerations, and energy demand linked to sector growth.
The APPG has opened a formal call for evidence, inviting contributions from across the digital infrastructure ecosystem. Submissions will help shape the group’s Terms of Reference and define its areas of focus for 2026.
Stakeholders invited to contribute include data centre operators and developers, energy suppliers, network operators, water providers, investors, consultancy organisations, local authorities, technology providers, trade associations, environmental groups, and academic institutions.
Consultation launched to gather industry evidence
Chris Curtis MP, Chair of the Data Centres APPG, notes, “Data centres are a vital part of the UK’s digital economy, and it is essential that we remain an attractive destination for the investment that drives growth and creates high-skilled jobs.
"As Chair of the APPG, I want to ensure Parliament has the evidence and understanding it needs to shape a balanced approach: one that supports development, delivers real economic benefits, and works for local communities, while recognising wider considerations.
"Getting this right will be critical to securing the UK’s long-term digital future.”
Lewis Cocking MP, Co-Chair of the Data Centres APPG, adds, “Data centre development must work for the communities that host them. Google's £1 billion investment at Waltham Cross is a clear sign of Broxbourne's growing importance as a hub for technology and innovation, and we must ensure this growth delivers genuine benefits for local people.
"This new APPG will focus on ensuring that local voices are heard in planning processes, that developments deliver tangible benefits (such as local jobs and waste heat utilisation), and that the highest environmental standards are met.
"Local residents need to have a real say in projects like these. We'll work to ensure developments like Google's enhance Broxbourne and other local areas while meeting our environmental commitments.”
Lord Hunt of Kings Heath OBE, Officer of the Data Centres APPG, says, “As a former Minister of State for Energy Security and Net Zero, I've seen firsthand how critical it is to align infrastructure growth with our climate commitments.
"Data centres are major energy users, but they're also driving innovation in renewable energy procurement and efficiency.
"This APPG will focus on ensuring their growth supports our net zero ambitions, exploring how these facilities can contribute to clean energy infrastructure, utilise waste heat, and support grid modernisation.
"With the right policy framework, we can build the digital capacity our economy needs while advancing our environmental goals. Data centres shouldn't be seen as a challenge to net zero, but as part of the solution.”
Joe Peck - 5 February 2026

Head office & Accounts:
Suite 14, 6-8 Revenge Road, Lordswood
Kent ME5 8UD
T: +44 (0)1634 673163
F: +44 (0)1634 673173