Quantum Computing: Infrastructure Builds, Deployment & Innovation
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
Quantum Computing: Infrastructure Builds, Deployment & Innovation
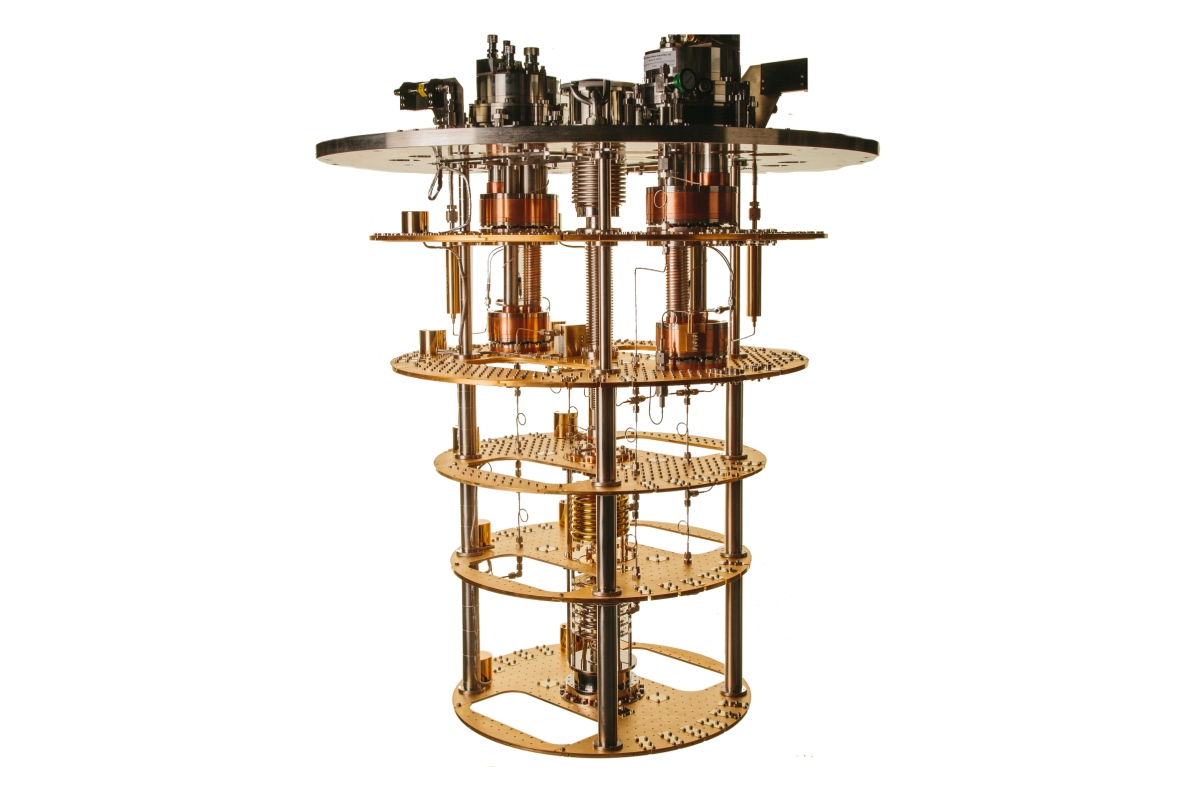
Oxford technology supplied to quantum-AI data centre
Oxford Instruments NanoScience, a UK provider of cryogenic systems for quantum computing and materials research, has supplied one of its advanced Cryofree dilution refrigerators, the ProteoxLX, to Oxford Quantum Circuits’ (OQC) newly launched Quantum-AI data centre in New York.
As the first facility designed to co-locate quantum computing and classical AI infrastructure at scale, the centre will use the ProteoxLX’s cryogenic capabilities to support OQC’s next-generation quantum processors, helping to advance the development of quantum-enabled AI applications.
Supporting quantum and AI integration
The announcement follows the opening of OQC’s New York-based Quantum-AI data centre, powered by NVIDIA CPU and GPU Superchips. The facility represents a major step towards practical, scalable quantum computing.
Within OQC’s logical-era quantum computer, OQC GENESIS, the ProteoxLX provides the ultra-low temperature environment needed to operate its 16 logical qubits, enabling over 1,000 quantum operations.
This capability aims to drive innovation across finance, security, and data-intensive sectors ranging from faster financial modelling and optimisation to quantum-assisted machine learning.
Oxford Instruments NanoScience says the collaboration highlights its expanding role in the global quantum computing landscape.
OQC’s data centre installations across Europe, North America, and Asia contribute to a distributed quantum infrastructure, accelerating the application of superconducting qubit technologies for industries such as pharmaceuticals.
Matthew Martin, Managing Director at Oxford Instruments NanoScience, comments, “We’re proud to support OQC in building the infrastructure that will define the next generation of computing, and it is a privilege to collaborate with our longstanding partner on this project.
“Our ProteoxLX is designed to allow users to scale, enabling them to maximise qubit counts with a large sample space and capacity for coaxial lines, so we’re excited to see how OQC will harness this platform to accelerate breakthroughs in real-world application performance.”
Simon Phillips, CTO at OQC, adds, “Oxford Instruments NanoScience’s contribution supports the centre’s goal of creating a hybrid quantum-classical computing capability, without modifying the data centre environment or generating the need for additional cooling.”
About ProteoxLX
Designed for quantum computing applications, the ProteoxLX forms part of Oxford Instruments NanoScience’s latest dilution refrigerator range, all built on a modular framework for cross-compatibility and adaptable cryogenic setups.
It offers a large sample space, extensive coaxial wiring capacity, low-vibration operation, and integrated signal conditioning for longer qubit coherence times.
The system delivers over 25 µW of cooling power at 20 mK, a base temperature below 7 mK, and several watts of cooling capacity at 4 K via twin pulse tubes.
Two fully customisable secondary inserts enable optimised cold-electronics layouts and high-capacity I/O lines, interchangeable across the Proteox family.
Joe Peck - 7 November 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centres
News
Quantum Computing: Infrastructure Builds, Deployment & Innovation
Quantum-AI data centre opens in New York City
Oxford Quantum Circuits (OQC) and Digital Realty today announced the launch of the first Quantum-AI Data Centre in New York City, located at Digital Realty’s JFK10 facility and built with NVIDIA GH200 Grace Hopper Superchips.
- Quantum-AI Data Centre: OQC and Digital Realty are working with NVIDIA to integrate superconducting quantum computers and AI supercomputing under one roof, creating a data centre built for the Quantum-AI era.
- Landmark deployment and integration: OQC’s GENESIS quantum computer will integrate NVIDIA Grace Hopper Superchips to become the first-ever quantum computing system deployed in New York City. OQC plans to integrate its quantum hardware with NVIDIA accelerated computing to support the scalability of future systems.
- Quantum-AI at scale: Embedded within Digital Realty’s global platform, PlatformDIGITAL, OQC is delivering secure, interconnected Quantum-AI infrastructure to power breakthroughs from Wall Street to Security – a central pillar of the UK–US tech trade Partnership to be announced.The Quantum-AI Data Centre brings together OQC’s quantum computing, NVIDIA accelerated AI hardware, and Digital Realty’s cutting-edge global infrastructure, eliminating geographical and infrastructure barriers to enable businesses to harness the power of quantum compute and AI. This initiative allows enterprises to access an integrated environment where quantum computing powers the AI revolution: enabling faster model training, more efficient data generation, and transformative applications in finance and security.
The system features OQC GENESIS, a logical-era quantum computer, installed within Digital Realty’s secure JFK10 site – the first-ever quantum computer installed within a New York City data centre. Integrated with NVIDIA Grace Hopper Superchips, the platform provides a launchpad for hybrid workloads and enterprise adoption at scale. OQC expects that future GENESIS systems will ship with NVIDIA accelerated computing as standard, building on its earlier collaboration integrating the NVIDIA CUDA-Q platform and providing developers seamless tools to build hybrid quantum-AI applications.
“This Quantum-AI Data Centre demonstrates how quantum can drive the AI revolution - securely, practically, and at scale - while strengthening the UK–US technology alliance.” says Gerald Mullally, CEO of OQC. “Leveraging Digital Realty’s infrastructure and NVIDIA supercomputing, we are redefining enterprise computing for finance and security.”
“Digital Realty’s mission has always been to enable the world’s most innovative technologies by providing secure, interconnected infrastructure at global scale,” adds Andy Power, President & CEO of Digital Realty. “By working with OQC, we’re using NVIDIA supercomputing to make Quantum-AI directly accessible in one of the world’s most important data hubs - empowering enterprises and governments to unlock new levels of performance and resilience.”
Science Minister Patrick Vallance comments, “Quantum computing could transform everything - from speeding up drug discovery to supercharging clean energy so we can cut bills. The economic prize is enormous, with £212 billion expected to flow into the UK economy by 2045 and tens of thousands of high-skilled jobs on offer. OQC’s launch of the first quantum computer in New York City showcases British tech excellence and strengthens our transatlantic ties. And the industry’s first quantum-AI data centre will put British innovation at the heart of next-gen computing - delivering speed, scale and security to tackle problems today’s tech is yet to grasp."
Applications and impact
By integrating quantum computing with NVIDIA AI supercomputing inside a secure enterprise-grade data centre, OQC and Digital Realty are creating a platform that will unlock new possibilities across critical sectors:
Finance: Faster and more accurate risk modelling, portfolio optimisation, fraud detection, and derivatives pricing, delivering competitive advantage in the world’s most data-intensive markets.
Security: Advanced material simulation, logistics optimisation, and decision-making under uncertainty, strengthening resilience in mission-critical domains.
Quantum for AI: Quantum computing will unlock new frontiers for AI itself, from accelerating model training and efficient data generation to emerging quantum machine learning applications with transformative impact across industries.
“This milestone shows the strength of a British tech leader scaling globally through international collaboration,” says Jack Boyer, Chair of OQC. “Working with Digital Realty and using NVIDIA supercomputing here in the United States, OQC demonstrates how the UK and US can lead together in the responsible deployment of frontier technologies for finance and security”
“The UK–US technology alliance is vital to ensuring that powerful new capabilities like quantum computing protect our nations, improve our prosperity, and are developed securely and in line with democratic values,” remarks Sir Jeremy Fleming, OQC Board member and former Director of GCHQ. “This deployment combines British innovation and American infrastructure, and brings NVIDIA’s AI leadership to deliver trusted computing power for the most critical applications.”
Proven technology and roadmap
OQC is reportedly the only quantum computing company with live deployments into colocated data centres: OQC already has systems operating in London and Tokyo, and now in New York. Its patented dual-rail Dimon qubit technology represents a breakthrough in error suppression, reducing the hardware overheads needed for error-corrected qubits and accelerating the path to fault-tolerant quantum computing. OQC has set a market leading roadmap – in collaboration with Digital Realty – to deliver scalable, commercially viable systems, with near-term impact in finance, defence, and AI. As a British champion of quantum computing, OQC is committed to building systems that drive both commercial advantage and national resilience.
For more from Digital Realty, click here.
Simon Rowley - 16 September 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
News
Quantum Computing: Infrastructure Builds, Deployment & Innovation
Quantum-ready FN-DSA (FIPS 206) nears draft approval
NIST has submitted the draft standard for FN-DSA (FIPS 206), the FALCON-based digital signature scheme, moving it closer to formal adoption as part of the post-quantum cryptography (PQC) standardisation process.
FN-DSA was selected alongside ML-DSA and SLH-DSA for PQC standardisation, but its approval has taken longer due to mathematical complexity and refinements to its components. With the draft now submitted, the first release is imminent.
The draft will be published as an Initial Public Draft (IPD) for open review. While the timeline has not been finalised, it may coincide with the NIST PQC Standardisation Conference in September 2025.
Based on past schedules, the review period is expected to last around one year, with a final standard likely in late 2026 or early 2027.
Industry preparations
Companies such as DigiCert, a US-based digital security company, are preparing for FN-DSA’s rollout. To avoid confusion around naming and identifiers, DigiCert has stated it will not implement FN-DSA in production until the standard is finalised.
In the meantime, the company will make the IPD version available for experimentation through DigiCert Labs, which already hosts FALCON for testing. This will enable the wider community to trial the draft standard before formal approval.
Role in post-quantum cryptography
FN-DSA is seen as a special purpose scheme rather than a replacement for ML-DSA. Its smaller signature sizes could reduce certificate chain lengths, which is valuable in environments where efficiency is a priority.
However, due to the complexity of FALCON’s signing process, FN-DSA is less suited for frequently signed leaf certificates. Instead, it is expected to be more useful for root and intermediate certificates.
NIST has also signalled potential adjustments to signing and sampling methods, which could broaden FN-DSA’s applications once the draft specification is published.
The progress of FN-DSA marks another milestone in the move towards quantum-safe standards. Organisations are being encouraged to begin preparation now by testing draft algorithms, trialling implementations, and developing crypto-agility strategies to ensure a smooth transition as PQC standards are finalised.
For more from DigiCert, click here.
Joe Peck - 8 September 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
News
Quantum Computing: Infrastructure Builds, Deployment & Innovation
Fujitsu developing 10,000+ qubit quantum computer
Japanese multinational ICT company Fujitsu today announced it has started research and development towards a superconducting quantum computer with a capacity exceeding 10,000 qubits.
Construction is slated for completion in fiscal 2030.
The new superconducting quantum computer will operate with 250 logical qubits and will utilise Fujitsu's 'STAR architecture,' an early-stage fault-tolerant quantum computing (early-FTQC) architecture also developed by the company.
Fujitsu aims to make practical quantum computing possible - particularly in areas like materials science, where complex simulations could unlock ground breaking discoveries - and, to this end, will focus on advancing key scaling technologies across various technical domains.
As part of this effort, Fujitsu has been selected as an implementing party for the 'Research and Development Project of the Enhanced Infrastructures for Post-5G Information and Communication Systems,' publicly solicited by the NEDO (New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organisation).
The company will be contributing to the thematic area of advancing the development of quantum computers towards industrialisation.
The project will be promoted through joint research with Japan’s National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) and RIKEN, and will run until fiscal year 2027.
After this 10,000-qubit machine is built, the company says it will further pursue advanced research initiatives targeting the integration of superconducting and diamond spin-based qubits from fiscal 2030, aiming to realise a 1,000 logical qubit machine in fiscal 2035, while considering the possibility of multiple interconnected quantum bit-chips.
Comments
Vivek Mahajan, Corporate Executive Officer, Corporate Vice President, CTO, in charge of System Platform, Fujitsu, claims, "Fujitsu is already recognised as a world leader in quantum computing across a broad spectrum, from software to hardware.
"This project, led by NEDO, will contribute significantly to Fujitsu’s goal of further developing a 'Made in Japan' fault tolerant superconducting quantum computer.
"We would also be aiming to combine superconducting quantum computing with diamond spin technology as part of our roadmap.
"By realising 250 logical qubits in fiscal 2030 and 1,000 logical qubits in fiscal 2035, Fujitsu is committed to leading the path forward globally in the field of quantum computing.
"Additionally, Fujitsu will be developing the next generation of its HPC platform, using its FUJITSU-MONAKA processor line, which will also power FugakuNEXT. Fujitsu will further integrate its platforms for high-performance and quantum computing to offer a comprehensive computing platform to our customers."
Focus areas for technological development
Fujitsu says its research efforts will focus on developing the following scaling technologies:
• High-throughput, high-precision qubit manufacturing technology — Improvement of the manufacturing precision of Josephson Junctions, critical components of superconducting qubits which minimise frequency variations.
• Chip-to-chip interconnect technology — Development of wiring and packaging technologies to enable the interconnection of multiple qubit chips, facilitating the creation of larger quantum processors.
• High-density packaging and low-cost qubit control — Addressing the challenges associated with cryogenic cooling and control systems, including the development of techniques to reduce component count and heat dissipation.
• Decoding technology for quantum error correction — Development of algorithms and system designs for decoding measurement data and correcting errors in quantum computations.
Background
The world faces increasingly complex challenges that demand computational power beyond the reach of traditional computers. Quantum computers offer the promise of tackling these previously intractable problems, driving advancements across numerous fields.
While a fully fault-tolerant quantum computer with 1 million qubits of processing power is considered the ultimate goal, Fujitsu states it is focused on delivering practical solutions in the near term.
In August 2024, in collaboration with the University of Osaka, Fujitsu unveiled its 'STAR architecture,' an efficient quantum computing architecture based on phase rotation gates.
This architecture could pave the way for early-FTQC systems capable of outperforming conventional computers with only 60,000 qubits.
On the hardware front, the RIKEN RQC-Fujitsu Collaboration Center, established in 2021 with RIKEN, has already yielded a 64-qubit superconducting quantum computer in October 2023, followed by a 256-qubit system in April 2025.
Scaling to even larger systems requires overcoming challenges such as maintaining high fidelity across multiple interconnected qubit chips and achieving greater integration of components and wiring within dilution refrigerators.
In addition to its superconducting approach, Fujitsu is reportedly also exploring the potential of diamond spin-based qubits, which use light for qubit connectivity.
The company is conducting research in this area in collaboration with Delft University of Technology and QuTech, a quantum technology research institute, which has resulted in the successful creation of accurate and controllable qubits.
For more from Fujitsu, click here.
Joe Peck - 1 August 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
News
Quantum Computing: Infrastructure Builds, Deployment & Innovation
Sitehop, Red Helix testing quantum-ready encryption
Sitehop, a UK startup focused on quantum encryption, has announced its partnership with Red Helix, a network and security testing company, to bring advanced testing in-house and to "supercharge" the critical speed-testing of its encrypted data transmission, utilising a Teledyne LeCroy Xena system.
With support from a five-figure 'productivity grant' from South Yorkshire Mayoral Authority, Sitehop has invested in a Teledyne LeCroy Xena Loki 100G traffic-generation and testing platform, which enables bi-directional testing of sub-microsecond latency in 100Gbps networks.
Bringing testing in-house has also reportedly eliminated delays and risks in export and customs, which included a minimum two-week turnaround at more than £18,000 per testing cycle.
Previously, Sitehop relied on an outsourced facility in France, but the new UK-based set up enables them to complete testing in a single day, freeing the time of Sitehop’s engineering teams and boosting their productivity.
Sitehop uses the Xena Loki device to test and validate its Sitehop SAFEcore platform, capable of 835 nanoseconds latency at 100Gbps encryption.
The platform can support 4,000 concurrent connections, deploying "crypto-agile" encryption for use in sectors such as telecoms, financial services, government, and critical national infrastructure.
Testing with the Xena Loki device covers peak load conditions, burst traffic, error injection and fault recovery, and end-to-end encrypted traffic flows. Multi-stream stress tests, mixed protocol environments, and real-time encrypted traffic benchmarking are part of the processes.
According to the company, the "speed and accuracy" of the Xena Loki platform enables Sitehop to validate latency, throughput, packet-loss, and error-handling across different profiles.
This is important to prove the Sitehop SAFEcore platform has the necessary performance and resilience in high-bandwidth, low-latency environments and is ready for new use cases such as 5G backhaul, wearable security technology, and the evolution of post-quantum cryptography.
“Testing in this way is a strategic enabler for us, accelerating product release cycles and reducing the risk of field failure while providing clients with higher levels of confidence during procurement,” says Melissa Chambers, co-founder and CEO of Sitehop.
“This is a major selling-point for enterprise and critical infrastructure environments.”
“We are incredibly proud to be at the forefront of the next generation of British tech manufacturing and believe we are part of a resurgence of innovation in the UK. We are proving that deep tech, hardware innovation, and cyber resilience can thrive here.
"As we expand globally and target high-assurance sectors, our ability to validate performance independently and rapidly becomes a cornerstone of our growth model. The grant we received has been hugely important, enabling us to bring a critical capability in-house that has accelerated our growth momentum.”
Baseline validation using the Xena Loki device is in line with the benchmarks RFC 2544 and Y.1564. In practice, however, the Sitehop SAFEcore system - the company claims - "frequently outperforms the scope of traditional methodologies, requiring custom profiles including simulated threat-scenarios, multi-session encrypted traffic under dynamic key exchange, and adaptive stream-shaping."
Liam Jackson, Director of Technology Solutions at Red Helix, comments, “We are thrilled to work with Sitehop, an exciting start-up company demonstrating that hardware-based security innovation is alive and well in the UK.
"Testing quantum-ready security platforms requires precise accuracy, reliability, and sustained high-speed throughput, which software-only traffic-generation tools can struggle to deliver.
"Sitehop understands this, and by harnessing the hardware-based Teledyne LeCroy Xena Loki platform, it hugely accelerates essential testing, gaining the speed, precision, and confidence to bring its cutting-edge solutions to market faster without impacting quality.”
Joe Peck - 30 July 2025
Cyber Security Insights for Resilient Digital Defence
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Security: Protecting Infrastructure from Physical and Cyber Threats
Events
Quantum Computing: Infrastructure Builds, Deployment & Innovation
DigiCert opens registration for World Quantum Readiness Day
DigiCert, a US-based digital security company, today announced open registration for its annual World Quantum Readiness Day virtual event, which takes place on Wednesday, 10 September 2025. The company is also accepting submissions for its Quantum Readiness Awards. Both initiatives intend to spotlight the critical need for current security infrastructures to adapt to the imminent reality of quantum computing.
World Quantum Readiness Day is, according to DigiCert, a "catalyst for action, urging enterprises and governments worldwide to evaluate their preparedness for the emerging quantum era." It seeks to highlight the growing urgency to adopt post-quantum cryptography (PQC) standards and provide a "playbook" to help organisations defend against future quantum-enabled threats.
“Quantum computing has the potential to unlock transformative advancements across industries, but it also requires a fundamental rethink of our cybersecurity foundations,” argues Deepika Chauhan, Chief Product Officer at DigiCert. “World Quantum Readiness Day isn’t just a date on the calendar, it’s a starting point for a global conversation about the urgent need for collective action to secure our quantum future.”
The Quantum Readiness Awards were created to celebrate organisations that are leading the charge in quantum preparedness.
Judges for the Quantum Readiness Awards include:
· Bill Newhouse, Cybersecurity Engineer & Project Lead, National Cybersecurity Center of Excellence, NIST· Dr Ali El Kaafarani, CEO, PQShield· Alan Shimel, CEO, TechStrong Group· Blair Canavan, Director, Alliances PQC Portfolio, Thales· Tim Hollebeek, Industry Technology Strategist, DigiCert
For more from DigiCert, click here.
Joe Peck - 14 July 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
News
Quantum Computing: Infrastructure Builds, Deployment & Innovation
IBM, RIKEN unveil first Quantum System Two outside of the US
IBM, an American multinational technology corporation, and RIKEN, a national research laboratory in Japan, have unveiled the first IBM Quantum System Two ever to be deployed outside of the United States and beyond an IBM quantum data centre. The availability of this system also marks a milestone as the first quantum computer to be co-located with RIKEN's supercomputer, Fugaku — one of the most powerful classical systems on Earth. This effort is supported by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organisation (NEDO), an organisation under the jurisdiction of Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI)'s 'Development of Integrated Utilisation Technology for Quantum and Supercomputers' as part of the 'Project for Research and Development of Enhanced Infrastructures for Post 5G Information and Communications Systems.'
IBM Quantum System Two at RIKEN is powered by IBM's 156-qubit IBM Quantum Heron, one of the company's quantum processors. IBM Heron's quality as measured by the two-qubit error rate, across a 100-qubit layered circuit, is 3x10-3 — which, the company claims, is 10 times better than the previous generation 127-qubit IBM Quantum Eagle. IBM Heron's speed, as measured by the CLOPS (circuit layer operations per second) metric, is 250,000, which would reflect another 10 times improvement in the past year over IBM Eagle.
At a scale of 156 qubits, with these quality and speed metrics, Heron is the most performant quantum processor in the world. This latest Heron is capable of running quantum circuits that are beyond brute-force simulations on classical computers, and its connection to Fugaku will enable RIKEN teams to use quantum-centric supercomputing approaches to push forward research on advanced algorithms, such as fundamental chemistry problems.
The new IBM Quantum System Two is co-located with Fugaku within the RIKEN Center for Computational Science (R-CCS), one of Japan's high-performance computing (HPC) centres. The computers are linked through a high-speed network at the fundamental instruction level to form a proving ground for quantum-centric supercomputing. This low-level integration aims to allow RIKEN and IBM engineers to develop parallelised workloads, low-latency classical-quantum communication protocols, and advanced compilation passes and libraries. Because quantum and classical systems will ultimately offer different computational strengths, this hopes to allow each paradigm to perform the parts of an algorithm for which it is best suited.
This new development expands IBM's global fleet of quantum computers and was officially launched during a ribbon-cutting ceremony today (24 June 2025) in Kobe, Japan. The event featured opening remarks from RIKEN President Makoto Gonokami; Jay Gambetta, IBM Fellow and Vice President of IBM Quantum; Akio Yamaguchi, General Manager of IBM Japan; as well as local parliament members and representatives from the Kobe Prefecture and City, METI, NEDO, and MEXT.
"The future of computing is quantum-centric and with our partners at RIKEN we are taking a big step forward to make this vision a reality," claims Jay Gambetta, VP, IBM Quantum. "The new IBM Quantum System Two, powered by our latest Heron processor and connected to Fugaku, will allow scientists and engineers to push the limits of what is possible."
"By combining Fugaku and the IBM Quantum System Two, RIKEN aims to lead Japan into a new era of high-performance computing," says Mitsuhisa Sato, Division Director of the Quantum-HPC Hybrid Platform Division, RIKEN Center for Computational Science. "Our mission is to develop and demonstrate practical quantum-HPC hybrid workflows that can be explored by both the scientific community and industry. The connection of these two systems enables us to take critical steps toward realising this vision."
The installation of IBM Quantum System Two at RIKEN is poised to expand previous efforts by RIKEN and IBM researchers as they seek to discover algorithms that offer quantum advantage: the point at which a quantum computer can solve a problem faster, cheaper, or more accurately than any known classical method. This includes work recently featured on the cover of Science Advances, based on sample-based quantum diagonalisation (SQD) techniques to accurately model the electronic structure of iron sulphides, a compound present widely in nature and organic systems. The ability to realistically model such a complex system is essential for many problems in chemistry, and was historically believed to require fault-tolerant quantum computers. SQD workflows are among the first demonstrations of how the near-term quantum computers of today can provide scientific value when integrated with powerful classical infrastructure.
For more from IBM, click here.
Joe Peck - 24 June 2025
Cyber Security Insights for Resilient Digital Defence
Data Centre Security: Protecting Infrastructure from Physical and Cyber Threats
News
Quantum Computing: Infrastructure Builds, Deployment & Innovation
KETS Quantum Security reacts to Salt Typhoon cyber attacks
On the back of the Salt Typhoon cyber attacks, Chris Erven, CEO & Co-Founder of KETS Quantum Security, comments on the potential threat of China developing a quantum computer and the danger for telecommunications companies.
Chris takes up the story: “This is a fully global threat. Every single telco should be considering their cyber defences in the wake of the Salt Typhoon attacks.
“China is making some of the largest investments in quantum computing, pumping in billions of dollars into research and development in the hope of being the first to create a large-scale, cryptographically relevant machine. And although they may be a few years away from being fully operational, we know a quantum computer will be capable of breaking all traditional cyber defences we currently use. So they, and others, are actively harvesting now, to decrypt later.
“Telcos are particularly vulnerable since they provide the communication services for major enterprises and many governments, so these organisations should be the first to upgrade to quantum-safe methods, including a defence in depth approach with quantum key distribution and post quantum algorithms.
“Adding to the danger, many telcos are moving to software-defined networks which use software-based controllers to manage the underlying network infrastructure rather than dedicated and more restricted hardware devices. This makes them particularly vulnerable because if an adversary gets into the management plane of a telco's SDN, they will have complete control of that network; whereas in the past, the access would have been much more limited. We really are talking about taking down the UK’s national telecommunications network.
“Despite warning bells being raised for the last decade, Q Day is rapidly approaching, and telcos have to prepare now to avoid a catastrophic data breach. Thankfully, telcos - like BT and SK Telecom - are actively working to upgrade their systems to make them quantum-safe in the future. However, this transition needs to happen even quicker, and the Salt Typhoon attacks serve as a timely reminder that robust cyber defences are not a ‘nice to have’ - they are essential to protecting our way of living.”
Simon Rowley - 10 January 2025
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
News
News in Cloud Computing & Data Storage
Quantum Computing: Infrastructure Builds, Deployment & Innovation
Amidata implements Quantum ActiveScale to launch new cloud storage service
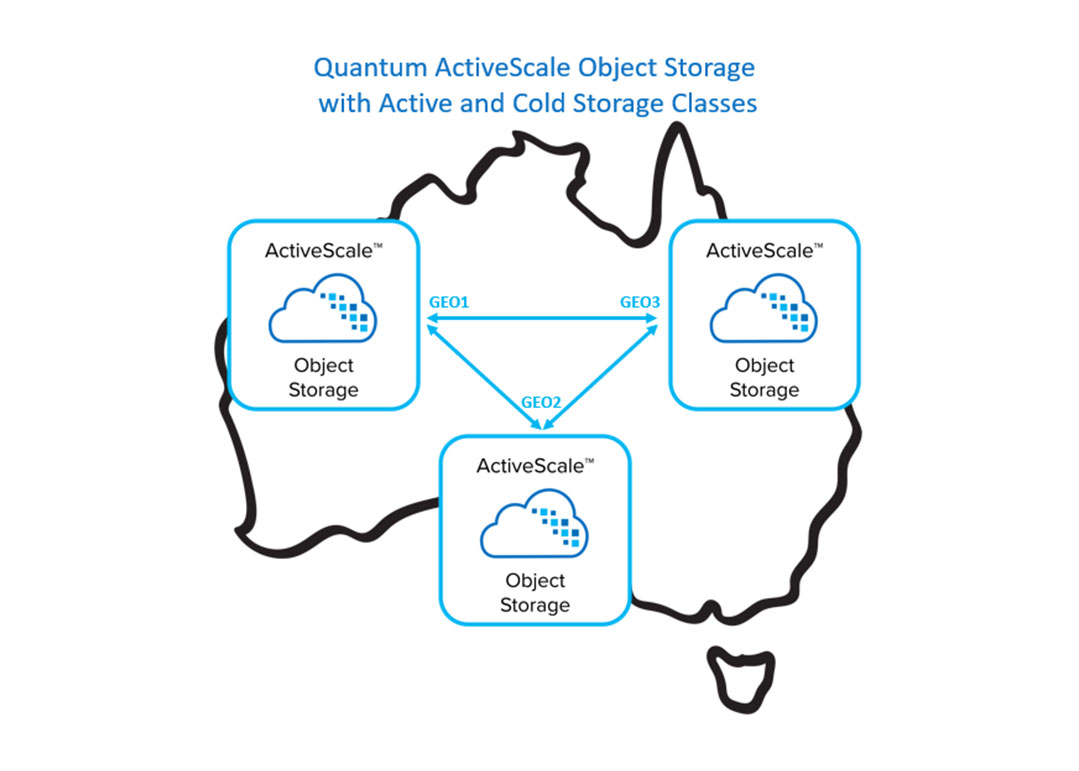
Quantum Corporation has announced that Amidata has implemented Quantum ActiveScale Object Storage as the foundation for its new Amidata Secure Cloud Storage service. Amidata has deployed ActiveScale object storage to build a secure, resilient set of cloud storage services accessible from across all of Australia, where the company is based. This way the company achieves simple operational efficiency, seamless scalability, and the ability to address customer needs across a wide range of use cases, workflows, and price points.
Amidata’s adoption of object storage also aligns with current IT trends. “More and more organisations are looking at object storage to create secure and massively scalable hybrid clouds,” says Michael Whelan, Managing Director, Amidata. “ActiveScale provides a durable, cost-effective approach for backing up and archiving fast-growing data volumes while also protecting data from ransomware attacks. Plus, by deploying the ActiveScale Cold Storage feature, we are delivering multiple storage classes as part of our service offerings, allowing us to target a wider set of customers and use cases. With our Secure Cloud cold storage option, customers can retain data longer and at a lower cost; that’s useful for offsite copies, data compliance, and increasingly, for storing the growing data sets that are fuelling AI-driven business analytics and insights.”
ActiveScale also supports multiple S3-compatible storage classes using flash, disk, and tape medias, providing a seamless environment that can flexibly grow capacity and performance to any scale. Cold Storage, a key feature, integrates Quantum Scalar tape libraries as a lower cost storage class to efficiently store cold and archived data sets. Quantum’s tape libraries are nearline storage, where customers can easily access and retrieve cold or less used data with slightly longer latency—minutes instead of seconds—but at a low cost, leveraging the same infrastructure used by the major hyperscalers. It intelligently stores and protects data across all storage resources using Quantum’s patented two-dimensional erasure coding to achieve extreme data durability, performance, availability, and storage efficiency.
For more information on Amidata’s implementation of ActiveScale, view the video case study.
Isha Jain - 1 February 2024
Data
Quantum Computing: Infrastructure Builds, Deployment & Innovation
MR Datentechnik launches a new data storage service
MR Datentechnik has implemented Quantum ActiveScale object storage along with Veeam Backup and Replication to launch a new S3-compatible storage service. By using ActiveScale, the company offers a resilient, highly scalable service that has the flexibility to support a wide range of S3-enabled apps and workflows.“Quantum ActiveScale provides the reliable, highly scalable S3-compatible object storage we needed for building our new storage service. The platform is stable even under high loads, and it offers sophisticated software that is extremely useful for multi-tenant management,” says Jochen Kraus, Managing Director, MR Datentechnik.
Solution overview
Quantum ActiveScale Object Storage
Veeam Backup and Replication
Key benefits
Built an easily scalable online data storage service to accommodate rapidly rising customer data volumes
Seamlessly integrated with software, Veeam Backup and Replication v12
Accelerated customer onboarding to under a day and achieved customer growth targets one year early
Created a resilient, always-on service that provides reliable data access for customers
Streamlined storage administration to minimise overhead and efficiently scale the managed service
Gained the flexibility for future use cases by supporting the S3 storage protocol
Headquartered in the German state of Bavaria, MR Datentechnik offers a full range of IT solutions and managed services. Organisations engage the company for everything from infrastructure deployment and systems integration to digitisation initiatives and fully outsourced IT management.
Recently, the leadership team at MR Datentechnik decided to launch a new storage service to support customers’ needs to preserve and protect fast-growing data volumes. The service, which would be designed for online storage of object data, could be used for backup and recovery, archiving and data security. This online service would enable organisations to retrieve data rapidly — anytime, from anywhere.
Creating an S3-compatible service was a top priority. The team wanted to support S3 applications and workflows and facilitate integration with S3 cloud storage environments. For the service’s launch, it decided to focus first on the backup use case. As a result, the underlying storage platform for the service had to integrate seamlessly with the latest version of Veeam Backup and Replication.
Isha Jain - 23 November 2023

Head office & Accounts:
Suite 14, 6-8 Revenge Road, Lordswood
Kent ME5 8UD
T: +44 (0)1634 673163
F: +44 (0)1634 673173