How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
Security concern: IoT devices under constant attack
Cyxtera Technologies, a
secure infrastructure company, has released findings from its joint research effort
with Singapore University of Technology and Design, showing that IoT devices
are under constant attack – with more than 150 million connection attempts over
15 months.
The report titled the ‘Detection of Threats to IoT Devices
using Scalable VPN-forwarded Honeypots,’ reveals the detection of new
attacks on IoT devices, with a focus on those leveraging zero-day vulnerabilities
for specific devices.
Key
report findings include
Researchers detected more than 150 million connection attempts to 4,642 distinct IP addresses.64% of incoming connections appeared to originate in China, with another 14% from the United States. This was followed by the United Kingdom (9%), Israel (8%) and Slovakia (6%). Researchers noted that it was difficult to definitively confirm the origination of internet traffic, however, as it is possible to re-route traffic to other locations, frequently employed as an obfuscation technique.All IoT devices saw attempted logins immediately upon coming online and the number of login attempts increased steadily over time.Within days of new malware campaigns going public – such as Mirai, Satori, and Hakai – those malware families were being used to attack IoT devices from the honeypot. In many cases, the increase in activity was identifiable in the days and weeks before the malware was publicly named. 54% of connections received by the honeypot were via Telnet port, while HTTP ports received almost all of the remaining connections.IP cameras received the majority of connections in the honeypot, suggesting greater attacker interest in those IoT devices as compared to others such as printers and smart switches. Several recent, large-scale attacks on IoT devices have targeted IP cameras.
“IoT devices are an
attractive target for attackers, because they are often a security
after-thought and its harder to keep them patched and up-to-date — if patches
are even available at all,” says Alejandro Correa Bahnsen, Vice President of
Data Science at Cyxtera. “The researchers involved in this project
accurately detected several large-scale attacks targeting IoT devices
and demonstrated the frequency and speed with which these devices are targeted.
This approach can be replicated by other threat researchers to broaden our
collective knowledge about these vulnerabilities.”
New AppGate IoT Connector extends power of software-defined perimeter
In tandem with the release
of its research, Cyxtera also announced new functionality in its
flagship Zero Trust solution, AppGate SDP, which promises to extend the
benefits of network micro-segmentation and software-defined perimeter to
connected IoT devices. The company says its AppGate SDP IoT Connector
enables enterprises to enforce consistent access control policies across users,
servers, and devices to protect today’s complex and distributed resources.
IoT devices are
increasingly present in enterprise networks and are expected to grow even more
with the advent of 5G networks. According to analyst firm IDC, worldwide
technology spending on IoT is projected to reach $1.2 trillion in
2022. With the anticipated rise in IoT adoption, security issues must
be addressed head-on to fully leverage the power of smart devices in a way that
is safe and managed effectively.
“The rapid adoption of IoT devices
is outpacing the ability to secure them properly,” says Ricardo Villadiego,
General Manager, Security & Anti-Fraud at Cyxtera. “These devices are
connected to the same network as users, servers, and sensitive data, which
creates risks for the network. AppGate SDP’s IoT Connector secures
unmanaged devices, restricting lateral movement and reducing an organisation’s
attack surfaces.”
DCNN staff - 6 March 2019
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
Western Digital: Maximising user experience in the 5G era
Western Digital Corp says it’s enriching smartphone users’ mobile
experience in the 5G era with a new embedded flash drive (EFD) that provides
the speed and capacity necessary to maximise the capabilities of ultra-high-end
smartphones and mobile devices. Built on the company’s 96-layer 3D NAND, the iNAND
MC EU511 supports
Universal Flash Storage (UFS) 3.0 Gear 4/2 Lane specifications. The advanced iNAND SmartSLC Generation six propels
turbo sequential write speeds up to 750MB/s, enabling a 2-hour movie
download in only 3.6 seconds.
The 5G standard
promises ultra-fast transfer speeds, low latency, lower power consumption and
high network capacities for all mobile and edge devices. These capabilities
necessitate the high-speed data interfaces, such as UFS 3.0, transforming not
only smartphones but billions of interconnected Internet of Things (IoT)
devices.
“Smartphones are increasingly becoming the hub of all things connected,” says Oded Sagee, Senior Director, Devices, Western Digital. “High speed 5G networks are set to deliver data at up to 100X the speed of previous generations and amplify AI on many devices. Artificial Intelligence (AI) powered by integrated neural processing units (NPU) with access to big and fast data will transform how we use our smartphones. Real-time computing on the edge will be in such high demand that high standards of data capturing and accessing are fundamental. With our UFS 3.0 embedded flash drive, we are enabling users to experience the new power of 5G applications, on-demand, seamlessly and instantaneously.”
Powered by the higher performance of a UFS 3.0 flash interface, 5G mobile devices will provide greater performance and lower latency for applications such as augmented reality, virtual reality (AR/VR) and mobile gaming. Additionally, high network speeds will enable consumers to quickly download and view ultra-high-resolution photos and 4K/8K media on mobile devices.
DCNN staff - 26 February 2019
Artificial Intelligence in Data Centre Operations
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
What to expect from Mobile World Congress 2019
There is now under a week to go until the biggest names in
the mobile industry descend on Barcelona for Mobile World Congress (MWC), 25-28
February. With everything from eSIM, the IoT to 5G and smart cities, DCNN takes
a look at what industry specialists predict to be the defining trends at world’s
largest mobile show.
eSIM goes full steam ahead, and into the enterprise
Manuel Zepeda, Division President, Caribbean and Latin America, Amdocs
“2018 was a pivotal moment for eSIM and consumer adoption. With Apple using eSIM technology in the iPhone X, and a growing number of mobile operators across the globe supporting the technology, it’s only a matter of time before eSIM-only becomes the standard in devices.
“At MWC this
year, we can expect to see discussions focused on how operators can offer eSIM
technology to the enterprise. For example, eSIM technology can be used by
enterprises that use machine-to-machine technology. eSIM enables remote
provisioning, so a company would not need to install a physical SIM card into
each piece of hardware, which can be a painstaking task. This can make areas
like public utility (like water and gas meters) much easier to manage and gives
communication providers a new revenue opportunity by providing the
connectivity.
“By working
closely with device manufacturers, communication providers can guarantee that
they are creating a smooth onboarding process for eSIM technology in the
enterprise. Mobile World Congress will be a hot bed of discussions about how
eSIM can be used across a broad range of vertical sectors.”
IoT connectivity requirements to be fulfilled by 4.5G
Ingo Flomer, VP Business Development and Technology, Cobham Wireless
As the
IoT expands, so too does the scale of projects and applications. The industrial
IoT (IIoT) is characterised by sites with a high volume of connected devices
and sensors – such as processing plants, mining and oil exploration, shipping
ports – which require always-on, ultra-low latency, ultra-reliable and
ultra-secure cellular connectivity. Signal in these environments often supports
mission critical applications and needs to penetrate industrial-grade
infrastructure, and hardware needs to withstand often harsh environments.
Connectivity must be robust and reliable: failures, poor coverage and outages
could risk to revenues and safety.I
What
does this mean for Mobile World Congress? Whilst in the future, it’ll be 5G
that facilitates the IIoT, this year we’ll see a demand from the IIoT sector
for 4.5G, which offers the speed and latency to cope with most of today’s IIoT
demands. 4.5G technology can co-exist with 5G when the networks arrive and will
continue to be used for years to come. There will therefore be a demand for
coverage systems that can support 4.5G today and can support 5G when the
technology arrives. Whilst a lot of the hype at MWC will be around
5G, there will also be a huge amount of discussion regarding how today’s
technology can support critical IoT systems.
5G will create a culture clash between traditional tech and vertical sectors
Pio Suh, Managing Director, IPCom
“At MWC this
year, 5G handset launches and networks will steal the limelight. However, there
will also be a big focus on how 5G can unlock opportunities in vertical sectors.
Automotive, healthcare, smart cities, agriculture, manufacturing – it’s these
industries where the lucrative businesses cases lie, and which are driving the
development of technologies.
“This
has been great for these sectors while business cases were purely hypothetical.
However, at MWCwe can expect to see some innovations come to fruition, and
with them the issues and complexity of how to license patent bearing devices of
these 5G technologies. For example, major car manufacturers will need to research,
negotiate and finally obtain necessary patent licenses for their connected
cars. This is something very new to them as traditionally major car
manufacturers left it to their suppliers to deal with IP.
“Vertical
sectors hoping to capitalise on 5G and the IoT will suddenly have to become
technical experts and intellectual property (IP) pros. Failure to successfully
navigate the landscape could result in litigation, which could stifle progress.
These parties will require guidance, education, and a clear-cut route to fairly
obtaining and using IP related to 5G.”
The race for 5G commercialisation begins in the RAN
Steve Papa, CEO, Founder, Parallel Wireless
“At MWC this
year, operators and vendors from across the globe will be competing to
demonstrate they are leading the race for 5G commercialisation. We’ve already
seen debate in the US market, as T-Mobile and Verizon have fired shots at
AT&T for claiming that a service that they are marketing as 5G, is in-fact
just supercharged 4G.
“Today,
5G is primarily concerned with radio access network (RAN) technology, as the
3GPP specifications for the core network have not yet been finalised. Being
first to market with 5G is, therefore, about how quickly operators can
introduce 5G radios into their networks and integrate them with legacy 2G, 3G
and 4G infrastructure.
“In
order to rapidly deploy 5G, the telecom industry is exploring virtualised RAN
(vRAN) and open RAN (oRAN) technology. By virtualising and opening the RAN to
multiple vendors, service providers can reduce the cost of all generations of
deployments, from 2G to 5G. They can then deliver 5G coverage by making
deployments easy and affordable to install and maintain, while sustaining a
high quality of service for customers. Operators that take this approach will
be in a strong position to win the race for early 5G commercialisation.”
5G security comes to the fore
John English, Director of Marketing, Service Provider Solutions, Netscout
“5G has
dominated the agenda at MWC for several years. However, while much
attention has been paid to the increased speeds and innovation the next
generation of communications will bring, discussions around 5G security have
been much less prominent.
“From
our conversations with mobile operators, we know how seriously they’re taking
security. In Barcelona this year, we will therefore see the operator community
come together to discuss how to address critical security challenges. With 5G
driving the adoption of virtualized network infrastructures such as containers
and distributed cloud models, much of the conversation will focus on how
carriers can secure and assure services in this increasingly complex
environment.
“At the
heart of these discussions will be the need for a pervasive security model that
offers comprehensive insight on both service performance and security. In
parallel with this, end-to-end visibility into the entire network
infrastructure will become a critical component of security strategies. Only by
having visibility into the entire 5G environment, including both public and
private cloud, will carriers be able to identify whether devices are behaving
in a suspicious or malicious manner. Armed with this insight, they can identify
potential threats, and rapidly rectify issues before they impact services.”
Smart cities will take centre stage at MWC
Richard Baker, CEO, GeoSpock
“At MWC19
we’ll see plans and prototypes for smart city infrastructure demo-ed and mapped
by exhibitors, with the Country/Territory pavilions and GSMA’s Innovation City
offering stages for playing out ideas for connected environments. This will
span everything from autonomous vehicles to utilities management in smart
office blocks, showcasing the benefits smart cities can bring.
“However,
for smart cities to evolve from the ideas stage to reality, there are
significant data challenges that must be addressed. Much of the data needed to
inform smart city planning currently exists in siloes. Lacking the ability to
join the dots between data sets, stakeholders will be unable to derive value
from smart city projects.
“What’s
needed is an approach which marries both macro-level and micro-level views of
the urban environment: visibility of every element and end-point in a smart
city, and the ability to map this onto expansive real-world environments, in
real time. Information on crime locations, for instance, can be mapped with
street lighting provision to identify hotspots. Resulting patterns can then be
used to inform urban planning and better secure our cities. Visualising and
contextualising data will enable a ‘data-first approach’ to planning and
development, ensuring connected infrastructure and services are tailored to
their citizens’ needs.
“Operators’
attentions at MWC will also be focused on smart city developments, as
they seek to enter new verticals and generate new revenue opportunities. Not
only can operators provide the connectivity that will underpin cities, they’ll
also have access to unprecedented volumes of data from devices and sensors on
their networks. This data could become one of operators’ biggest assets and
enable them to transform from dumb data pipes to powerful data vendors.”
DCNN staff - 20 February 2019
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
MWC: Nokia launches off-the-shelf IoT packages to help operators address new vertical markets
In advance of
Mobile World Congress, Nokia has launched off-the-shelf Internet of Things
(IoT) packages to help operators win new business in vertical IoT markets. In
addition to enabling operators to achieve a fast time to market, the packages
promise to simplify the set-up and operations of enterprise IoT services.
Built on the Nokia Worldwide IoT Network Grid (WING)
infrastructure that provides the necessary global IoT connectivity and services
support, the applications include IoT sensors, user applications and business
models suited to specific sectors. Nokia WING's managed service approach also
offers a pay-as-you-grow business model, giving operators the flexibility to
quickly scale up IoT services as required.
The new market-ready solutions for WING eliminate the challenges
facing operators developing their own IoT services. These include the need for
specialised expertise, the complexities of combining fragmented IoT
connectivity infrastructure and the risk and effort of setting up and working
with multiple service providers globally. Nokia works with best-in-class
partners on Nokia WING vertical applications portfolio and continues to develop
the IoT ecosystem.
The four new solutions announced today by Nokia include:
Smart Agriculture as-a-Service: Sensors capture environmental, soil and crop data that is
then analysed to provide insights that help farmers manage crops more
effectively, potentially saving costs on irrigation, pesticides and
fertilizers.Livestock Management
as-a-Service: Tracking devices and
biosensors monitor animal health and welfare to provide ranchers with early
alerts if abnormalities are detected, protecting valuable livestock and
improving yields.Logistics as-a-Service: IoT sensors enable tracking of the global movement and
condition of goods through the complete supply chain to help enterprises
instantly identify incidents and even predict future events to optimize
delivery and logistics process efficiency.Asset Management as-a-Service: Connecting products anywhere in the world enables their
status and performance to be monitored centrally, helping enterprises provide a
better service to their business and consumer customers.
Nokia is trailing Agriculture as-a-Service with an African
operator and working with a leading services and consulting firm on Asset
Management as-a-Service to help them offer more advanced services.
Brian Partridge, Vice President, 451 Research, says, "Nokia
addresses a wide spectrum of challenges through its WING IoT
infrastructure-as-a-service so its early traction with customers isn't a
surprise. Most telecom operators desire a more prominent role in the IoT value
chain that builds upon secure and reliable domestic or global connectivity.
Nokia's announced plans to offer end-to-end vertical applications on top of the
WING global infrastructure is a logical next step. We believe that this
approach benefits Nokia's WING telecom customers and the enterprises they serve
in addition to vertical application partners who can benefit from WING's market
scale and go-to market channels."
DCNN staff - 20 February 2019
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
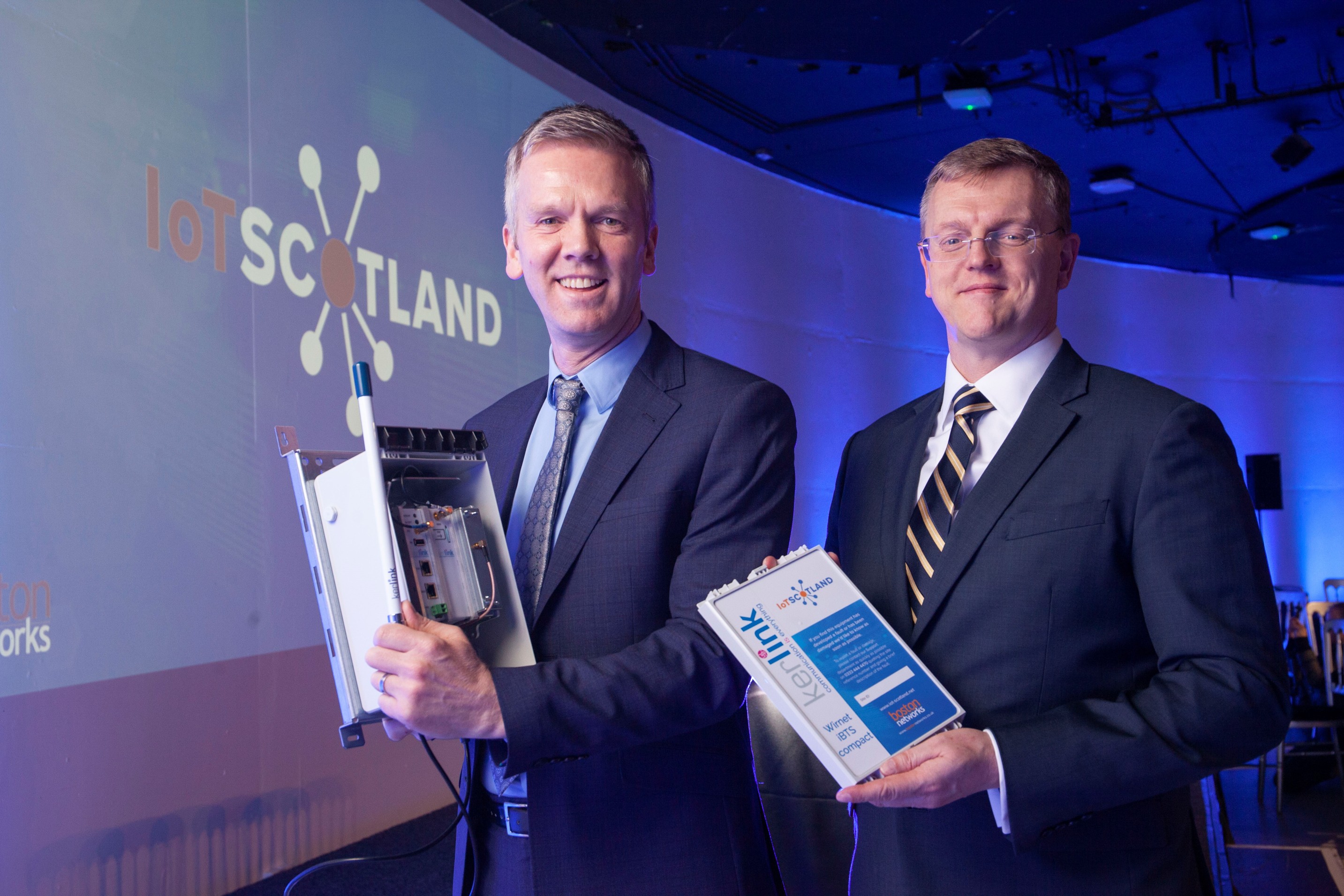
Boston Networks launches transformational IoT Scotland
Boston Networks,
the Glasgow-headquartered smart integrated solutions business has launched the
UK's most advanced Internet of Things (IoT) network – fittingly at Glasgow
Science Centre.
IoT Scotland is said to provide a wide area wireless sensor network for applications and services to collect data from devices and send that data without the need for cellular or Wi-Fi, supporting businesses to develop new and innovative applications, changing the way they work.
The six-million-pound network, which
will work via 500 LoRa (Long Range) wireless gateways situated throughout
Scotland, is part funded by £2.7 million from the Scottish Government, with
further support from Scottish Enterprise, Highland and Islands Enterprise (HIE)
and private sector investment from Boston Networks itself.
At the launch it was announced that
Glasgow will be over 99% covered via 22 gateways which are being installed
across the city – which, the company says, makes it the most LoRa covered city
in the UK, with the potential to become the smartest.
Argyll and Bute Council has also
signed up as an early adopter which is said to see early installations in Oban
and Helensburgh, and negotiations are also said to be underway with other local
councils and other organisations throughout the country with a full roll-out
planned by March 2021. Boston Networks will install and manage all of these
devices.
IoT Scotland promises to enable
businesses and public sector organisations to monitor and potentially control
the status, efficiency and productivity of their assets and equipment,
scheduling maintenance and improving production.
Boston Networks Chief Technology
Officer, Falk Bleyl comments, “We are excited to be leading this pioneering
project to build and operate the IoT network and drive the commercialisation of
the Internet of Things across Scotland.
"There will be a forecasted 25
billion IoT devices connected by 2025, and only a small number will be
connected to the internet using 3G, 4G or Wi-Fi. LoRa networks like IoT
Scotland are going to become increasingly important – they have the potential
to be as disruptive to businesses as the internet has been already to our daily
lives.
"IoT Scotland will be the most
advanced in the UK, can revolutionise the use of smart technologies and will be
rolled out in cities, towns and rural areas across the country. It allows a
wide range of users, from public sector organisations to small IoT start-ups to
multinationals to focus on the deployment of sensors and applications, rather
than network build.
"There is already interest from
other parts of the UK in what we're doing here in Scotland, and there is
potential for us to roll-out similar infrastructure elsewhere."
DCNN staff - 13 February 2019
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
IIoT trends for 2019
Industry 4.0, the Fourth Industrial Revolution or the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Regardless of the phrase used to describe digitalisation in manufacturing, there’s no denying that a shift has already taken place. Stefan Reuther, chief sales officer at COPA-DATA, gives his three predictions for industrial automation in 2019…
Manufacturers have long felt the
pressure to invest in new technologies. In the so-called age of Industry 4.0,
this pressure has been heightened by an influx of products and initiatives, all
claiming to help manufacturers digitise their operations. Unfortunately, some
of these schemes are nothing more than a waste of money.
Don’t get me wrong, there is certainly value
in investing in technology to enable digitalisation in factories’ practices.
However, rushed approaches have led to some manufacturers making haphazard investments.
For example, some have delegated digitalisation to third parties and as a
result, are not in charge of their own automation.
Before embarking on a digitalisation scheme,
manufacturers should first examine which technology is practical to their
facility. A good place to begin is to listen to the people on the factory
floor. Understanding how technology can practically help workers can ensure
that investments are pragmatic.
Another thing to consider is simplicity,
by reducing complexity of processes and gaining a clearer overview and full
control. Manufacturers should choose technology that is easy to understand,
implement and scale up in the future. Moving into 2019, digitalisation should
be approached in a more practical manner — a steady, incremental transformation
is better than a failed one.
Less data hoarding, more data use
Software is another area that has been constantly
hallmarked as a method to speed up manufacturing digitalisation. However,
before investing in software for data collection, manufacturers should begin
2019 by implementing a coherent data strategy.
Rather than simply collecting and
storing data, manufacturers must identify the results that they want to achieve
and decide how data can help them to meet these business objectives.
Consider this as an example. Let’s say a
manufacturer wants to improve return on investment (ROI) in the facility by
reducing the amount of materials wasted from production. To identify areas of
improvement, manufacturers would need to collect production data and compare
this with data from Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP).
Without a pre-determined strategy like
this, manufacturers run the risk of simply collecting and storing hordes of
data. There’s no value in data if it is left to gather dust. Over the next
twelve months, we hope to see data strategies become an integral part of
manufacturing. That said, data strategies are only comprehensible when using
the correct software.
The software evolution
Recent years have seen a shift in the
amount of investment manufacturers assign to software. Traditionally, hardware
would have received the largest bulk of cash, but this is beginning to change —
particularly as more advanced software platforms emerge.
Software for manufacturing facilities is
no longer limited to Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Supervisory
Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA). The realm of industrial software is
experiencing a convergence of IT and operational technologies (OT), giving
birth to new platforms which integrate a plethora of different areas — including
enterprise data from the corporate level, through to field and process level
automation.
While this may sound more complicated
than traditional systems, these platforms often boast better design, visualisation,
calculation logic and ergonomics than their predecessors. This makes the
operation of systems safer, simpler and more transparent.
Software is the driver of what is so commonly
referred to as Industry 4.0. As a result, it is no surprise that we are likely
to see increased investment in integrated platforms like these over the next
twelve months.
The age of conceptualising the
possibilities of manufacturing digitalisation is over. During the next twelve months,
the products and initiatives hailed as ways to transform manufacturing
facilities will finally be put to practical use.
DCNN staff - 9 January 2019
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
Beyond the cloud: First integrated VIoT platform launched
Digital Barriers, a provider of edge-intelligent video solutions to security and defence organisations worldwide, and Cloudview, a visual data specialist whose cloud service provides a secure platform for the storage and management of video from unlimited numbers of cameras, have announced the world’s first fully integrated visual IoT (VIoT) platform.
The platform is said to combine ultra-low bandwidth secure live streaming with a fully scalable, resilient, easy to deploy cloud platform, in the form of EdgeVis from Digital Barriers and Cloudview’s Visual Data Platform.
When connected to one or many CCTV, body worn or mobile cameras, the new VIoT platform promises to massively reduce the size of the data transmitted, while analytics will generate new insights into what is happening at a particular location; why it is happening, and what might happen next. The results are encrypted and sent to a secure cloud infrastructure, which consolidates, stores and manages visual data from multiple sources. This data can then be securely accessed by any authorised user from any device and any location.
The platform targets a video analytics market that will see a compound annual growth rate of more than 50% over the next five years, according to McKinsey, and a seven-fold increase in video surveillance internet traffic, according to Cisco.
Beyond surveillance, the new VIoT platform will be developed to access a broader range of Visual IoT solutions, including smart city, healthcare, automotive and industrial applications.
“Sight is our most powerful sense and by adding it to the IoT, we open a huge range of possibilities,” explains Cloudview CEO and co-founder James Wickes. “With Cloudview, there’s no need for the expense and disruption caused by the wholesale replacement of legacy infrastructure. Our partnership with Digital Barriers means we can now deliver our service using much less bandwidth, as well as providing edge analytics that will speed up the provision of critical information by reducing the need for constant human intervention to manually find and analyse it.”
“We have proven that our video streaming is more efficient and cost-effective than any other on the market,” adds Zak Doffman, Digital Barriers CEO.
“We have combined edge analytics and live streaming as a real-time game changer. Until now it has not been available with a fully integrated backend. Now this joint offering resolves that. This is completely unique on the market: AI-based capture and analysis of video at the edge, low-bandwidth streaming of video to the cloud, plugging into the exponential growth in cloud, AI and IoT.”
DCNN staff - 2 January 2019
Data
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
Digi International Brings IoT Expertise, Edge Computing to Electronica 2018 in Munich
Digi International, a global provider of Internet of Things
(IoT) connectivity products and services, has announced that it is highlighting
its Digi XBee3 series of smart edge IoT modules and modems, with a particular
emphasis on the Digi XBee3 Cellular with NB-IoT, at electronica 2018 in Munich,
Germany.
Digi is showcasing its solutions with several demonstrations of the latest embedded technology and is also sharing its expertise by leading multiple educational sessions.
Electronica is taking place at the Messe München Exhibition Center from November 13-16, 2018. Digi is exhibiting in Hall B5 at Booth 263.
The Digi XBee3 series is designed to support IoT innovation and computing capability at the network edge. Digi XBee3 provides MicroPython programmability and dual-mode radios, with the ability to upgrade via software to Bluetooth LE, enabling local device connectivity from a smartphone or tablet.
Digi XBee3 adopts a modular approach to IoT connectivity that includes options for Zigbee, Wi-Fi, or cellular, including LTE-M and NB-IoT. Digi XBee3 enables innovative IoT solutions that can be more quickly developed, prototyped and mass-produced for optimal return on investment, says its creator.
These solutions can be deployed, provisioned and monitored with Digi XCTU and Digi Remote Manager (DRM), Digi’s centralised, secure device management platform.
In addition to providing insight into device and network health, DRM automates updates, accesses data directly from the edge and integrates data into open APIs to provide users with deeper insights.
Additionally, Digi is previewing its Digi ConnectCore 8X
system-on-modules (SOMs) and SBCs. Digi is an NXP early access partner, and the
small module will utilise the NXP i.MX 8X processor family based on ARM Cortex-A35
and Cortex-M4F cores.
“When people come to electronica, they expect to see not
just new technology, but how it can help them solve their business challenges,”
says Chris Bowen, vice president, EMEA, at Digi International. “Digi addresses
connection and networking needs with a full range of embedded hardware options,
software specifically developed to optimize IoT deployments and expert services
to ensure customer success. Digi is not just connecting the things in the IoT,
we’re offering data, insights and management tools to maximize performance and
drive business value.”
Product Demonstrations
Remote IoT Connectivity with Digi XBee3
Cellular: This demonstration will showcase remote device management between
a Digi XBee3 Cellular device and the cloud-based Digi Remote Manager by
remotely monitoring and controlling devices located in multiple locations
directly from the trade show floor.Digi XBee3 End-to-End IoT Networking: Digi
will present the latest advancements in the Digi XBee3 platform, including
multi-protocol support (Zigbee, CAT-1, LTE-M, NB-IoT + Bluetooth LE), with
an IoT networking solution composed of Digi XBee3 modules, Digi XBee industrial
gateways and network/device management tools. These updates enable new use
cases for improved installation, local control diagnostics and configuration.
The network and device management element will use a new XCTU® Mobile
application for the Digi XBee configuration via a phone or tablet.SteadyServ iKeg: This application
demonstration will show the SteadyServ iKeg using sensors to measure keg
volume, analyze the data locally with a Digi ConnectPort gateway, then send the
analysis into the cloud over a Zigbee connection. The iKeg application presents
the cloud-based information to bar managers to help accurately inventory and
proactively order more when beer runs low.
Educational Sessions
Selecting Cellular LPWAN Technology for the
IoT: Presented by Mark Tekippe, Digi International Director of Product
Management, Embedded and RF, on Wednesday, November 14. As part of the IoT
Track, this session will address selecting the best connectivity technology for
low-power, low-bandwidth requirements in the IoT, touching on LTE Cat 1, LTE-M,
NB-IoT and more.What is Edge Compute?: Presented by
Andreas Burghart, Digi International Solution Sales Engineer, on Thursday,
November 15. As part of the Machine Learning Track, this session dives into how
bringing intelligence to the edge demands a different way of thinking about
existing IT infrastructures. Touchstones include extending compute capabilities
intelligently, opening up new opportunities and revenue streams with more
compute power, and improving time to market.Yocto Project Linux as a Platform for
Embedded Systems Design: Presented by Alex Gonzalez, Supervisor, Software
Engineering; Digi International, on Thursday, November 15. As part of the
software track, this session covers a wide-range of issues when selecting an
operating system for an embedded system including acquisition cost, source code
availability, and its broad architecture support. All these factors lead to a
significantly improved time-to-market and a reduction in platform design risk
and effort.
Co-exhibitors and Partner Participation
As well as at its own booth, Digi is exhibiting solutions
and will be showcased throughout the venue with partners including Mouser (Hall
C3, Booth 550), Digi-Key Electronics (Hall B5, Booth 165), Atlantik (Hall C4,
Booth 222), CODICO (Hall C4, Booth 402), Avnet Silica (Hall C5, Booth 101) and
Arrow (Hall C4, Booth 412).
In-booth infoMouser will include Digi’s XBee XGI Industrial
Gateways and Digi XBee & Silicon Labs Giant Gecko Kit in its “Future
Cities” virtual reality demonstration in both the Digital Twinning and Smarter
Edge sections.Atlantik will feature a ConnectCore 8X in their
booth.CODICO will display Digi TransPort and NB-IoT
modules in its booth.
Dan Sait - 13 November 2018
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
Ambient Commerce: Driving expenditure on IoT technology
Ambient commerce is an important use case for the Internet of Things (IoT) and promises to be a game changing retail technology, according to GlobalData, a data and analytics company.
The company’s latest report from its thematic research team says that ambient Commerce, which combines technology with the physical space associated with retail stores, will offer a whole new way to shop.
Ed Thomas, principal analyst for technology thematic research at GlobalData, says, “The worlds of online and offline retail are merging, and ambient commerce sits in the middle. This is why Amazon and Alibaba, the world’s dominant online retailers, have both invested billions in acquiring stakes in physical retailers. Having gained a physical foothold on the high street, these retailers are now heightening the retail experience by experimenting with ambient commerce in stores.”
Ambient commerce describes a new form of shopping which makes use of sensors, coupled with artificial intelligence (AI), to help customers select and pay for their goods, without the need for keyboards or cash registers.
Two main models are emerging in the ambient commerce value chain: the Amazon Go version of ambient commerce, where computer vision, sensors and machine learning technologies enable customers to ‘grab and go’; and the Chinese version of ambient commerce – popularised by Alibaba, Tencent and JD.com – which uses less in-store IoT infrastructure, but is likely to take off faster because it is based on existing smartphone technology, coupled with QR codes.
GlobalData says its research has found that ambient commerce will drive expenditure on IoT connected devices and on IoT software and services in the retail sector. With the company estimating that the retail sector will spend $5.3 billion on IoT software and services, up from $2.7 billion in 2018 by 2020. Over the next two years, the retail sector will emerge as the fifth largest spender on IoT software and services after the government, transportation, utilities and manufacturing sectors.
Thomas adds, “We can expect many more strategic alliances and M&A deals as old-world companies seek to join the new ambient world, and the insurgents broaden their bases and round out their tech infrastructures.”
DCNN staff - 30 October 2018
Data
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
Twentytwo: A smart London development
In 1990, there were just 10 ‘megacities’ (cities of over 10 million). By 2015, that figure had jumped to 28, accounting for 12% of the world’s urban inhabitants. People are moving to urban centres attracted by the lifestyle and range of opportunities they offer; with more people on the pavements and soaring land prices, new buildings need to head skywards.
When completed next year, Twentytwo, a new development located minutes from the new London Liverpool Street Crossrail station, is expected to stand 278 metres tall and showcase a number of new construction solutions in a challenging historic and densely populated urban environment. It is anticipated that developers, planners and architects from around the world will look to Twentytwo as a model case in building smarter, faster and safer.
Driving tall building innovation
The ability to build higher has long been linked to advances in elevator technologies.
Today, elevators are integral to constructing megastructures and moving the millions of tenants who use these buildings. The lift being installed in the building is set to use AI, video analytics and other advanced techniques to move people smarter, faster and more intelligently. Using IoT and data analytics to improve maintenance effectiveness, maximise equipment uptime, identify proactive maintenance and repairs, and machine learning to fine tune dispatching 24/7 365 days a week.
Another smart benefit is eCall, which is said to put the elevator in the palm of your hand; allowing you to call the elevator from anywhere in the building so that it is waiting for you when you get to the lift lobby. Finally, facial recognition and gait analysis, credential ‘handshake’ all geared to seamless interaction where things happen ‘automagically’.
Twentytwo has over 1,100 men, women and engineers working on the site and, when fully occupied, will be home to a 12,000-strong workers and visitors so the elevator solution is critical. For this reason, the developers turned to Otis for its SkyBuild elevator system.
Otis SkyBuild & Twentytwo Bishopsgate
Installed at the beginning of construction, the SkyBuild elevator is said to facilitate movement of crews and tools quickly and safely – at around eight times faster than a standard goods lift – without the need of a crane or external lift or exposure to weather (which can also stall construction). According to the company the elevator’s unique hydraulic piston system enables the lift’s mechanical system to climb one floor at a time in step with the building’s construction. When complete, the SkyBuild elevators at Twentytwo are anticipated to quickly transition for service as SkyRise elevators, Otis’ premier elevator for the world’s tallest buildings, bringing the Twentytwo’s total elevator count to 57.
The City of London’s medieval street layout and estimated 400,000 daily commuter population pose additional challenges at Twentytwo. By moving people and materials around the site quickly, SkyBuild is said to enable developers to reduce the disruption to the local environment and community caused by goods delivery.
DCNN staff - 29 October 2018

Head office & Accounts:
Suite 14, 6-8 Revenge Road, Lordswood
Kent ME5 8UD
T: +44 (0)1634 673163
F: +44 (0)1634 673173