How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
Data
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
The smart city data dilemma
By Craig Stewart, CTO at SnapLogic
The concept of smart cities has been around for a while, gracing the pages of comic books and TV screens. But today smart cities are a reality, though you may not realise quite how pervasive they are just by walking down your local high street. IoT devices have enabled everything from intelligent traffic management to air quality analysis to be undertaken, and with the right tools in place officials have been able to introduce new measures to improve city conditions.
In the age of COVID-19, smart city technologies have the potential to make more of an impact than ever before. But with roll outs happening at a larger scale, it brings a new phase of data challenges to be dealt with for many city planners.
Understanding data
Today, city management teams have access to a plethora of different data sources, all thanks to the myriad of sensors across the city. But in the last 12 months, teams have often been able to use these sensors to better understand how citizens are responding to COVID-19 restrictions.
Take, for example, public transport networks. Often the most well monitored systems in the world, public transport networks generate millions of data points, covering everything from passenger numbers and peak flow, to vehicle health and climate changes. During the last year, city leaders have been able to take this data and layer it with information coming from central governments about travel restrictions and regional growths in COVID-19 cases, to not only understand if transport networks were driving COVID cases but also which routes can be reduced to reflect a reduction in demand.
One of the best examples of this came from Newcastle in the UK. The Newcastle Urban Observatory – which applies scientific techniques in measuring planned and unplanned interventions in cities – was able to track the effectiveness of UK government policy interventions by using billions of historic and real-time urban movement data points. This analysis enabled authorities to then adapt urban governance policies in response to changes in public movement.
Data volume vs data use
The very nature of smart cities often means huge data volumes. But while having data volume can be highly beneficial to understanding the nuances of changing behaviour patterns during COVID, that understanding isn’t possible if all of the data isn’t shared in the right way.
There needs to be a constant flow of information between the multiple data sources around the city. The sheer number of endpoints generating vast quantities of complex information alone could cause serious issues for any public sector IT infrastructure. But as IoT devices continue to gather invaluable data, smart cities can only thrive if the data is analysed with context while not requiring a huge uplift from IT teams or data analysts.
Adding to this challenge, we often see the full potential of smart cities unattained because after a certain point the data stops moving. Data points owned by different departments and organisations need to be properly integrated to ensure that city-dwellers are able to get the most out of smart city technology. Equipping local city administrators and the organisations that support them with the right tools is essential for the smart city vision to be fulfilled.
Smarter cities driven by automation
The manpower required to connect all of the data points and derive vital insights poses a monumental challenge. With the help of automation, smart city data can be brought together seamlessly, reducing the time and cost in managing the vast array of endpoints. This would create a city that communicates like one entity, updating in real time when changes occur.
But the data sharing on a larger, public scale is still quite restricted. There are roadblocks in the way that limit human collaboration. It is the job of the government and local city planners to make data more accessible by removing restrictions in place that stop this data from moving freely.
Having access to all of the available data, government and city officials will have a better grasp on old and new issues that plague urban areas, including pollution, vehicular and citizen traffic and managing a global pandemic. With a holistic, integrated approach organisations and governments alike will be more empowered to make any necessary changes – enabling smart cities to truly become smart and thrive, bettering the environment for us all.
Carly Weller - 18 May 2021
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
News
Why simplicity beats jargon every time
In the words of American author and motivational speaker, Tony Robbins, “complexity is the enemy of execution”. Translating even the most complicated of topics into clear, understandable language is vital to getting things done. Crosser, is designed with this philosophy in mind. Here, Crosser’s CMO and co-founder Johan Jonzon, explains why the company battles against IoT jargon.
Industrial IoT
projects are complex engagements. OT (Operational Technologies), IT and Data Science businesses are working together on the same
projects, adding buzzwords, abbreviations and technical terminology to the
jargon. All, of course, with the same goal — but different angles, meanings and
preunderstandings.
Academic research around the use of science and technology jargon indicates that it impairs a person’s ability to process scientific information, which can result in a greater resistance to persuasion, and an increased perception of risk. If people don’t understand a new technology, they are less likely to adopt it, even if it could be beneficial to business.
A cloud of confusion
The world of
industrial IoT is riddled with buzzwords and acronyms that can leave
non-experts in a cloud of confusion. Exacerbating the situation further, the
same words are used to refer to different concepts.
Take the phrase
edge computing, for example. The concept of edge computing is the same across
all sectors — to bring the processing closer to the devices that generate the
data — but its physical positioning and applications vary.
For example, within
telecommunications, the edge is described as the last physical point of
connection in cellular networks. In IT, the edge is somewhere between the data
source and the cloud, depending on the use case. And within the OT sector, edge
is often the first processing point after the machine.
On the application
side, the edge is used as the processing point for analytics, actions and
sending notifications but also for integrations and as an abstraction layer for
the machine data. The edge can also be a very good position for your advanced
machine learning algorithms. One easily understands that here is a risk of
misunderstanding.
The confusion is confirmed in the data. A 2021 McKinsey survey of industrial company executives concluded that, despite two thirds of respondents using some form of cloud technology in their operations, around 50% found its implementation more complex than initially expected.
This buzzword
confusion also adds complexity to the customer’s buying experience. Every
vendor can claim edge abilities on a generic level, because there are so many
solutions that fit into the concept. So how do you decide which vendor is right
for a designated project?
The use of jargon
is just a barrier to communication, preventing the technology from reaching
businesses it could benefit.
Making the complex simple
Avoiding jargon in
the world of edge computing and streaming analytics is a valuable tool for
enabling non-experts to understand the technology, but it only solves half the
problem. Simplicity must be carried through to the platforms themselves, to
allow users to operate the systems without extensive background knowledge and
training.
Handling huge amounts of data in real time can be challenging under even the most favorable of circumstances. However, the situation is made worse by the global IT skills shortage. According to data collated by IT training company Global Knowledge, in 2020, 78% of managers reported an IT skills gap within their business.
There is simply not
enough talent to fill global IT vacancies, which is preventing businesses from
benefiting from technological advancements. What’s more, technology is
developing at a rate faster than the end user’s ability to learn how to use it.
So, even businesses with software developers in house will struggle to keep up.
In response to this, Crosser’s Flow Studio is a low-code solution, turning existing OT and IT personnel without programming skills into citizen developers — developers without formal training or coding knowledge - enhancing the users operational and functional knowledge instead. The modular system uses a drag-and-drop methodology to allow employees to easily construct data flows with ease, from an ever-growing library of pre-built modules.
The design of the
Flow Studio is intuitive and simple, enabling collaboration between several
business divisions, including IT professionals, data scientists, product
specialists and maintenance staff. By removing unnecessary complexity, the Flow
Studio gives non-developers the ability to innovate without long or specialized
training.
Edge computing
technology is technical, but it doesn’t have to be complex. As an industry, we
need to demystify our technology and its applications by eliminating overuse of
jargon and keeping things simple. By adopting simplicity, Crosser’s products
and services empower businesses that can truly benefit from them across
industry and beyond.
Beatrice - 22 April 2021
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
News
New ABI research white paper shows the growth of LoRa
Semtech Corporation has announced the release of a commissioned white paper, “LoRa WAN and Multi-RAN Architecture Connecting the Next Billion IoT Devices,” from global tech market advisory firm, ABI Research. The report explores the rapid growth of massive Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity and real world applications leveraging multi-RAN architectures.
Vertical market evaluation was a key component to the whitepaper
research. ABI Research found that the LoRaWAN
protocol is the leading license-exempt low-power wide-area (LPWA) network
technology addressing massive IoT vertical markets, which include metering, cities,
asset tracking and logistics, commercial building automation, and home. In
addition to vertical market overviews, the white paper explores five active
LoRaWAN network implementations based on multi-RAN architectures:
Orange enables device
and data management for Cellular and non-Cellular LPWA network technologies, with the Orange Live
Objects platform. JRI-MySirius uses sensors leveraging
LoRaWAN and a Cloud-based application platform to provide turnkey temperature
monitoring for fixed and mobile assets.Ercogener developed an
end-to-end asset tracking solution that supports the LoRaWAN protocol and is
leveraged by France's national state-owned railway company.MultiTech’s programmable
gateway is the original gateway integrating LoRa® for industrial IoT
applications with support for Ethernet, 2G, 3G, 4G-LTE, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth/BLE,
and GNSS.Chevron implemented a LoRaWAN
network infrastructure to digitize a series of oil and gas fields.
“The future of IoT connectivity requires flexible solutions that address a wide spectrum of vertical IoT applications, use cases and device types,” says Marc Pegulu, Vice President of IoT Applications in Semtech’s Wireless & Sensing Products Group. “LoRa and the LoRaWAN open protocol enable interoperability and seamless connection between the many devices that can exist in a single environment. As a technology provider, our job is to create solutions that make deployment and use easier for people."
The study concluded that LoRa devices will play an important role as a
key LPWA network technology now and in the future as the IoT continues to
connect physical devices to digital assets. Additional key takeaways
highlighted in the white paper include:
5G
and non-cellular network technology will co-exist: In the
future, LoRaWAN and 5G will co-exist in the form of hybrid networks or multi-RAN
architectures. Full
5G will take longer than expected: 5G is not capable of addressing
massive IoT in the near term. 5G networks and the device hardware supporting
the Release 17 specifications will not be commercially available until early
2024.LoRa
leads in LPWA technology: By 2026, LoRa is expected to be the leading
non-cellular LPWA network technology and will account for over a one-fourth
share of all LPWA network connections and more than half of all non-cellular
LPWA connections. Total
non-cellular LPWA connections in 2026 are expected to reach 1.3 billion. LoRa
is moving beyond enterprise applications: Consumer
applications leveraging LoRa are beginning to take off. Traditional
architecture is witnessing competition from LPWA network technologies,
providing direct device-to-Cloud connectivity for a growing number of smart
home devices.
Beatrice - 10 February 2021
Data
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
Data collected from IoT devices will breed the next new Uber or Netflix
What organisations can do with data is set to dramatically shift in 2021 and beyond, according to IoT connectivity specialist Eseye, as more IoT devices are deployed and the data they generate dwarfs that collected through traditional online channels.
Eseye predicts that data mined from user interactions with things rather than digital services will create a wealth of rich data, bigger and more detailed than online data ever was, enabling new business models, the creation of new products and services and new levels of understanding of human behaviour.
Services like Amazon,
Facebook and Netflix capture a wealth of consumer usage and behaviour data
which is stored, analysed and used to digitise and reinvent shopping, social
interactions and entertainment as custom personalised, data-driven services.
This has had an extraordinary effect on the creation of new personalised
services and new disruptive business models. As radical a change as this was,
now IoT data is set to power unprecedented levels of innovation over the coming
years.
According to Eseye, this
innovation will be seen not just in the next generation of classic IoT devices,
which will become much more interactive and personalised to real time
behaviour, but also in the development of a new set of devices created through
the fusion of multiple sensors, cellular connectivity to the cloud and advanced
AI techniques. This combination will enable near real time predictions of what
services should be dynamically configured into those devices to maximise
revenue and collect even more data and deliver huge value.
“IoT companies that see the
potential, not just in the device but also in the data collected, will be the
big winners,” comments Nick Earle, CEO, Eseye. “As we come out of the pandemic,
organisations will be looking for new ways to innovate, and IoT data has the
potential to disrupt business models and processes in practically every
industry. Disruption, by its nature, comes from places we haven’t even dreamed
of, but it can be radical. For example, the people who invented the internet
could never have predicted the emergence of services such as Uber and Netflix.
Likewise, we can only speculate around what IoT entrepreneurs will come up with
once they have access to data from billions of devices capturing rich
intelligence on every aspect of our lives and businesses. We predict it will be
an even bigger wave of innovation than the first wave of IoT adoption.”
One of Eseye’s customers is already using rich data to predict diseases before they happen. A leading digital therapeutics provider manufactures and sells a next-generation clinical-grade wearable, which delivers actionable insights powered by machine learning, deep neural networks and AI on real time disease trajectory. This helps clinicians predict and prevent serious medical events. For example, chronic diseases, like heart failure, can lead to billions of pounds of unnecessary hospitalisations and re-admissions. Therefore, the potential benefits across the healthcare sector if this model becomes widely adopted are enormous.
Another example is how IoT
is helping vulnerable people remain independent through condition monitoring,
whereby such devices use personal health data combined with behavioural
patterns, and analytics predict when changes in care regimes might be required.
These are just two examples of millions of potential applications.
“In 2020 the pandemic has accelerated many of the IoT trends we predicted last year. That’s because an economic slowdown, like we are experiencing, puts enormous pressure on enterprises to reduce costs and increase customer delivered value. IoT does both of these things, and so the pressure for adoption is growing. This sudden need for new technological approaches has happened at a time when IoT is reaching a level of cost and maturity that allows for mainstream adoption. This will increase the ability to collect rich data from these next generation IoT devices, delivering unimaginable insights to power innovation in years to come,” adds Nick.
This is just one of 10 IoT
predictions that Eseye is forecasting for 2021 and beyond. Others include how
IoT can deliver real time visibility into the food supply chain with technology
advances such as printing IoT circuits, batteries, and cellular connectivity
onto flexible labels. It’s exploring how IoT – as it becomes more integrated
into consumer and industrial products – can provide brands with a direct line
to customers, collapsing supply chains to bring original equipment
manufacturers closer to consumers.
Furthermore, Eseye is also analysing how mobile network
operators (MNOs) are adapting to compete globally and why a federation approach
creates a more viable economic model for MNOs to deliver IoT, as well as the
emergence of virtual MNOs. Eseye announced its global alliance of MNOs, The
AnyNet Federation, in 2019 and over the last year the AnyNet Federation has
grown to 12 MNO members, a number which Eseye expects to further grow in 2021.
Beatrice - 28 January 2021
Data
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
Data Centre Security: Protecting Infrastructure from Physical and Cyber Threats
Data Centre Software for Smarter Operations
Essential Disaster Recovery News for Data Centres
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
Infrastructure Management for Modern Data Centres
Scalable Network Attached Solutions for Modern Infrastructure
Tech firm strengthens asset recovery links
A leading Internet of Things (IoT) solutions
company has appointed a new head of global risk as part of its expanding
security operations.
And the recruitment bolsters the firm’s fledgling
reputation in asset recovery, which has amounted to a staggering value of over
£5m across the past four years.
Seeking to enhance business protection following a rapid increase in high-value asset attacks across the UK, Smarter Technologies has enlisted Mark Roche into its ranks. A highly trained specialist with over 20 years of experience in covert operations, Roche is considered one of an elite group trained to manage high-value asset recovery operations.
“In the cat-and-mouse game of fighting criminal activity, it’s our goal to always be one step ahead of the criminals,” comments Roche on his appointment.
“We are building and strengthening an expert team
to tackle asset recoveries across a global network.”
Smarter Technologies already works with recognised institutions such as the Ministry of Defence and Royal Airforce, delivering real-time asset tracking through its secure Orion Data Network.
And now with Roche among the ranks, the business
is set to excel in helping SME's, blue chip companies and police forces across
the country.
“The issue is that police forces sometimes don’t have the resources to deal with asset theft" adds Roche.
“When it comes to their resource allocation and
prioritisation between the theft of an asset and a case that involves potential
preservation of life, the latter will always come first.”
“My process involves liaising with police force
wherever that asset was stolen from, working with the troops on the ground and
locating the tracker to a precise location.”
One police force that is already familiar with the
benefits Roche can bring in his field is Essex and Kent Police.
“I have worked with Mark Roche for a number of years, and he has had significant impact in reducing crime and improving recovery rates,” says Jason Hendy, head of serious and organised crime, Essex and Kent Police.
“Mark has helped catch more criminals with his
equipment than any other company we know. He is also known now as an expert
tracker across many police forces and trains officers on tracking.
“We look forward to continuing our association to ensure we maintain our position at the forefront of detection and the successful prosecution of criminal behaviour.”
Beatrice - 3 December 2020
Data
Data Centre Infrastructure News & Trends
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
Innovations in Data Center Power and Cooling Solutions
Abtec to shift to industry 4.0 with appointment of Head of industrial IoT
As Abtec Building Technologies seek to enhance its service offering to industrial and commercial customers, the award-winning smart buildings provider has announced the appointment of Kieron O’Toole as Head of Industrial IoT.
In his role, O'Toole will lead the business unit responsible for the design and management of IoT, and data infrastructure for commercial customers - from edge to core to cloud. This allows Abtec to deliver greater expertise and value in smart buildings and the new wave of smart factories being implemented. The Industrial IoT service brings together Abtec’s range of digital services including IT/OT converged data networks; high availability data centres and WAN; cyber security; intelligent lighting, heating and access control; CCTV; presence tracking; and 24/7 infrastructure and energy management.
These digital
foundations reduce operational cost and risk for customers, but they also form
the bedrock of wider Industry 4.0 programmes such as digital twins, supply
chain integration, machine learning and AI optimisation, whilst enabling a
world of new Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) sensors and applications to
be deployed.
Prior to joining
Abtec at the beginning of October, Kieron has worked extensively across the
industrial and enterprise ICT environments in systems engineering and
businesses improvement roles for organisations such as Polestar Interactive and
BT Global Services. He is also a member of Aston University’s Industrial
Advisory Board and the Institute of Consulting.
Of his
appointment, Kieron comments: “It is an exciting time to be joining Abtec
Building Technologies. Industrial IoT will play a transformative role in
customer experience and production efficiency and will enable new ways of
working across the entire supply chain. Using my knowledge and experience, I am
looking forward to being part of Abtec leveraging its unique expertise, assets
and service wrap in the industrial market to provide our customers a reliable
data infrastructure partner.”
Dave Watkins, Director of Abtec Building Technologies, concludes: “We are delighted that Kieron has joined Abtec in this new role. He has a proven track record in delivering results, and his expertise will add value to our business as we grow our Industrial IoT service offering.”
Beatrice - 17 November 2020
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
National 5G test centre opens at Maynooth University
RadioSpace, a new €1.5 million national test centre for next-gen wireless technologies such as 5G and IoT, has been opened at Maynooth University in Ireland.
The new 5G test centre, which is one
of the first of its kind in Europe, has been designed to provide a range of
services to developers of 4G mobile networks, IoT-enabled products, 5G and
mmWave devices.
RadioSpace, will be open to enterprises,
SMEs and start-ups, and will provide a unique, large scale, interference-free
facility for scientists and engineers from industry and universities, in
Ireland and internationally.
The facility consists of a
specially constructed anechoic chamber that provides perfect isolation for
radio signals. Nothing can enter, and nothing can leave. With advanced
test equipment and specialist engineers, this allows for very sensitive
measurements to be made, essential for the development of modern wireless
devices.
RadioSpace connects industry and
academic researchers. The aim, to address the full range of challenges in
developing new technologies and products for the next generation of wireless
devices.
The €1.5 million facility, which
has received €638,000 funding from Science
Foundation Ireland (SFI), is part of Connect - the world-leading SFI Research
Centre for future networks and communications.
This service is available to
SMEs, and access can be facilitated via the Enterprise
Ireland Innovation voucher scheme. This ensures that both SMEs and larger
organisations can avail of the technology and expertise of researchers in
Maynooth University.
According to Professor Philip
Nolan, President of Maynooth University, “This facility will serve as the
National 5G Test Centre for Ireland, providing a space for next-generation
wireless technologies to be tested, refined and applied on an international
scale. I’m pleased to say that RadioSpace will be available to all those who
can make good use of it, from leading researchers and innovators to students
just starting their careers, from the largest multinational to the smallest of
start-ups. Until now Irish industry working in this space has needed look
abroad to avail of similar facilities and I’m proud we are now in a position to
provide this centre of excellence right here in Maynooth.”
DCNN staff - 5 June 2019
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
Sony's new IoT chipset promises a 60 mile range
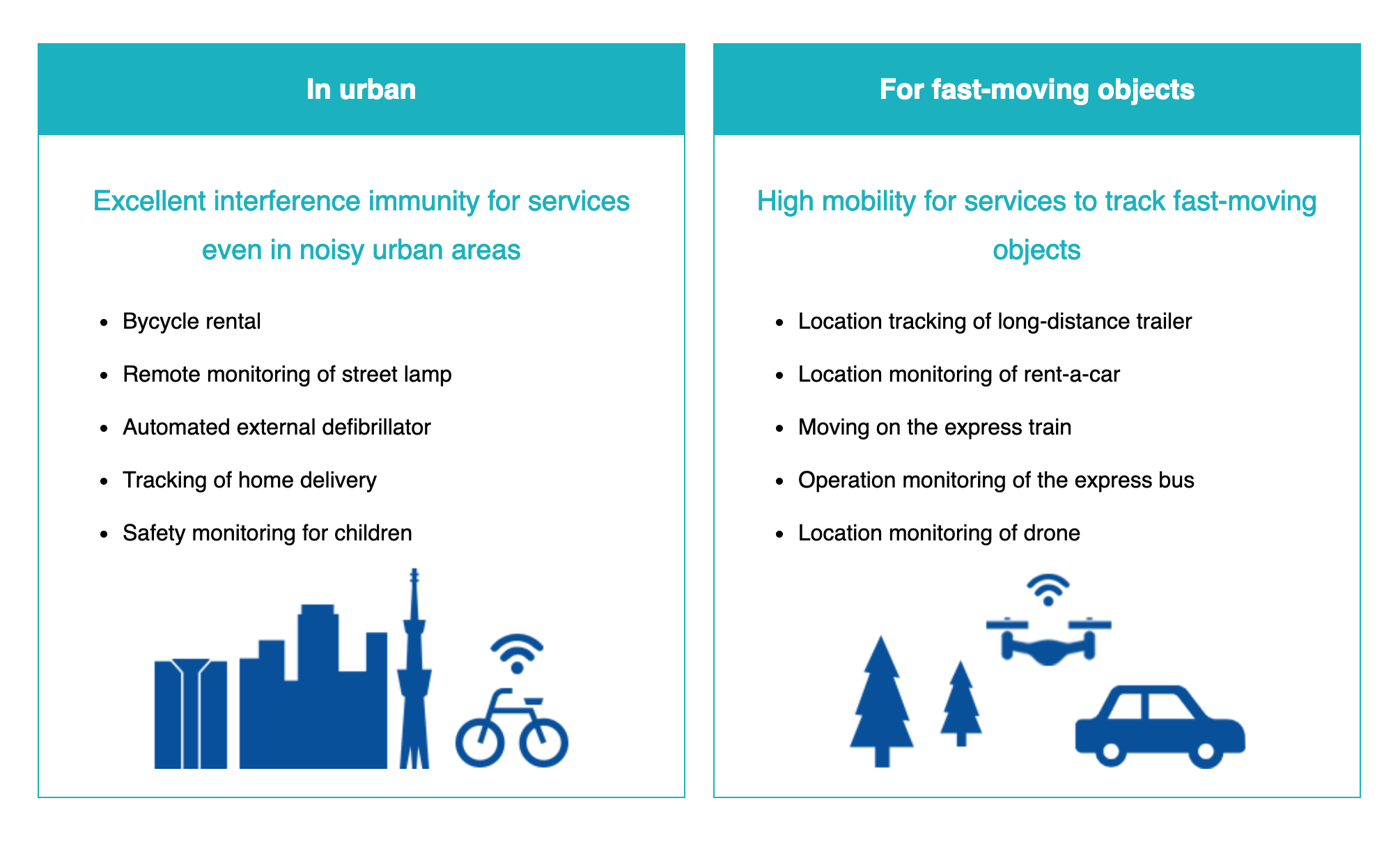
Despite huge advancements in networking technology, it’s still commonplace for the average consumer living in a large home to complain about their Wi-Fi signal. Whether it’s devices refusing to connect to the network, or the cliff-edge drop in internet speeds, networking range is still a major factor when building a smart home. Thankfully, it may not be a factor for much longer, as Sony has developed a brand-new IoT chipset that promises a range of 60 miles.
A 60-mile range for an IoT chipset is crazy considering not even the largest estates in the country occupy that much land. In fact, the crazy range of Sony’s CXM1501GR chipset could theoretically mean that someone in central London would be able to connect to an IoT-enabled device in Cambridge, and still have range to spare. Thankfully, this chipset has plans much grander than simply controlling a homeowner’s heating or lighting.
Don’t jump on the hype train just yet
Despite a reported 60-mile range, don’t jump onto the hype train straight away, as there’s quite a few technicalities to cover first. While it’s true that users won’t have to be connected to a Wi-Fi network or have a phone signal in order to communicate with IoT devices equipped with Sony’s chipset, they will have to be within range of a dedicated low-power wide area (LPWA) ELTRES network mast, which Sony plans to roll-out by the end of the year. These masts enable the transfer of low-bit data across a wide area, without sucking up huge amounts of power – ideal for IoT applications.
The CXM1501GR’s huge range comes from the fact that it transmits in the 920MHz band, which is similar to what is offered by a standard 2G mobile signal. While Sony says that its IoT-enabled chipset is capable of 60 miles of range, in the real-world, that’s likely to be much less. That’s because it’ll have to deal with physical barriers, such as walls and trees, as the signal makes its journey. Despite this, there are some major benefits with using this low frequency band.
How can Sony’s new chipset be used?
Sony believes that by taking IoT devices off traditional networks, it will enable them to run more efficiently. This is especially true in an urban environment, where Sony’s new chipset won’t be required to compete with other devices for bandwidth. This is a problem that is supposed to be solved by 5G, but it’s clear that Sony wants to give IoT devices their very own network.
For city dwellers, Sony’s new chipset should allow for a myriad of use cases, such as – tracking home deliveries, monitoring street lamps, keeping tabs on children, and even helping run a city’s bicycle rental program. It’s in rural locations where the Sony CXM1501GR chipset reallt shines, however.
Not only can Sony’s chipset transmit data over large distances with very little power, but they also come equipped with GPS/GNSS sensors to obtain time and position data. This means that these IoT chips will be invaluable in assisting with search and rescue operations, while it can also be used to keep track of drones, rental vehicles, buses, and trains. In fact, Sony believes that the possibilities are truly endless for its IoT chipset.
While Sony may believe in its chipset, the company is not yet ready to commit to an international roll-out. The network is set to initially roll-out in the company’s native of Japan later this year, but if the technology proves to be viable, then we could be seeing it roll-out globally in just a few years time.
DCNN staff - 29 May 2019
Artificial Intelligence in Data Centre Operations
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
News in Cloud Computing & Data Storage
Ford and Autonomic collaborates with AWS to advance vehicle connectivity
Ford, Autonomic and Amazon Web Services (AWS), have announced
that they have formed a collaboration which aims to advance the availability of
cloud connectivity services, as well as connected car application development
services for the transportation industry.
Through this collaboration, Autonomic’s Transport Mobility Cloud
(TMC) will be powered by AWS and be used as the standard connected car solution
for Ford vehicles.
Ford Mobility and Autonomic say they selected AWS for its global
availability, and the breadth and depth of AWS’ portfolio of services,
including; Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning, analytics, and compute
services.
The collaboration with AWS promises to allow additional
partnership and business opportunities for automakers, public transit
operators, large-scale fleet operators, and software developers.
As a Technology Partner in the AWS Partner Network (APN),
Autonomic says it will also work with Independent Software Vendors (ISVs) and
System Integrators (Sis) to offer vehicle connectivity services and
capabilities for developing connected vehicle cloud services, vehicle features,
and mobile applications to automotive manufacturers and mobility application
developers.
Marcy Klevron, President at Ford Mobility says, “This
collaboration will significantly expand our opportunity to deliver the very
best experiences to Ford vehicle and mobility customers. I am excited that our
future cloud standard for connected vehicle solutions will be powered by AWS in
addition to Autonomic’s Transportation Mobility Cloud. Working with AWS and
Autonomic, Ford and our mobility partners will have access to the
industry-leading mobility platform.”
The collaboration represents an expansion of the existing
relationships between Ford, Autonomic and AWS.
DCNN staff - 3 May 2019
Artificial Intelligence in Data Centre Operations
Data
Data Centre Operations: Optimising Infrastructure for Performance and Reliability
How the Internet of Things Is Shaping Data Centre Operations
UK in pole position in £62 billion self-driving car race
The UK
is in pole position in the global race to market for connected and autonomous
vehicles (CAVs), with a £62 billion boost to the UK economy by 2030 up for
grabs, according to a major new report published by the Society of Motor
Manufacturers and Traders (SMMT) and Frost & Sullivan.
The report
titled: Connected
and Autonomous Vehicles: Winning the Global Race to
Market, analyses the wide-ranging
societal and economic benefits to be achieved by gradually increasing
CAVs on our roads.
The report
identifies that the UK is in a strong position to capitalise, with more than
£500 million already committed by industry and
government to CAV R&D and testing.
Autonomous driving trials are taking place across many major towns and cities, and
we are home to four major CAV test beds and three additional sites focused on
highways, rural and parking, with more than 80 collaborative R&D projects
underway. The next game-changing step is to move from testing CAV technologies
to deployment in the real world.
Advanced
driver assistance systems (ADAS) such as Autonomous Emergency Braking and
Collision Warning are already available on the majority of new cars registered
in the UK. Combined with the
gradual introduction of automated vehicles from 2021, this will deliver massive safety benefits. Over the next
decade, the technology is set to prevent 47,000 serious accidents and save
3,900 lives.
At the same time, some 420,000 new jobs will be created, including in the automotive industry and other sectors such as telecoms and digital services. Driving commuters, meanwhile, will gain back the equivalent of a full working week thanks to more ‘downtime’ and smoother traffic flows during their commute.
The UK is in pole position in the £62 billion self-driving car race
The report pinpoints three critical areas that will help CAV rollout and in which the UK has a significant advantage: supportive regulation, enabling infrastructure and an attractive market. With the world’s first insurance legislation for autonomous vehicles already in place, the most comprehensive review of road transport underway and more miles across motorways, urban and rural roads able to be driven autonomously, the UK is already ahead of global rivals in its readiness to commercialise self-driving technology. The report ranks the UK above other major automotive countries, including Germany, US, Japan and South Korea as a global destination for the mass rollout of CAVs.
To
realise this potential, however, the conditions must be right, and sustained
support from government will be vital – particularly if we are to meet its
ambition to get autonomous vehicles on to UK roads in 2021.
The report’s
key recommendations for government include updating road traffic laws,
improving 4G coverage across all road networks, encouraging local authorities
to work with industry to implement urban mobility services and influencing
future harmonisation of international regulations to ensure these new vehicles
can operate seamlessly between the UK and abroad.
Crucially,
however, the UK’s departure from the EU must be orderly with a deal that
supports both the industry and technological collaboration, especially in data.
A ‘no deal’ Brexit will result in lasting damage to the UK’s reputation as a
politically stable destination for inward investment, putting the benefits
identified in the report at risk.
Mike Hawes, SMMT Chief Executive, says, “A transport revolution stands before us as we move to self-driving cars and the UK is in pole position in this £62 billion race. Government and industry have already invested millions to lay the foundations, and the opportunities are dramatic – new jobs, economic growth and improvements across society. The UK’s potential is clear. We are ahead of many rival nations but to realise these benefits we must move fast. Brexit has undermined our global reputation for political stability and it continues to devour valuable time and investment. We need the deadlock broken with ‘no deal’ categorically ruled out and a future relationship agreed that reflects the integrated nature of our industry and delivers frictionless trade.”
Sarwant Singh, Senior Partner and Head of Mobility, Frost & Sullivan, adds, “The UK already has the essential building blocks – forward thinking legislation, advanced technology infrastructure, a highly skilled labour force, and a tech savvy customer base – to spearhead CAV deployment over the next decade. However, it will require sustained and coordinated efforts by all key stakeholders, especially the government, to realise the significant annual economic benefits forecast for the UK from CAV deployment by 2030 and drive the vision of safe, convenient and accessible mobility for all.”
DCNN staff - 10 April 2019

Head office & Accounts:
Suite 14, 6-8 Revenge Road, Lordswood
Kent ME5 8UD
T: +44 (0)1634 673163
F: +44 (0)1634 673173