Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Data Centres
News
Data centre keeps its cool with technology from Spirotech
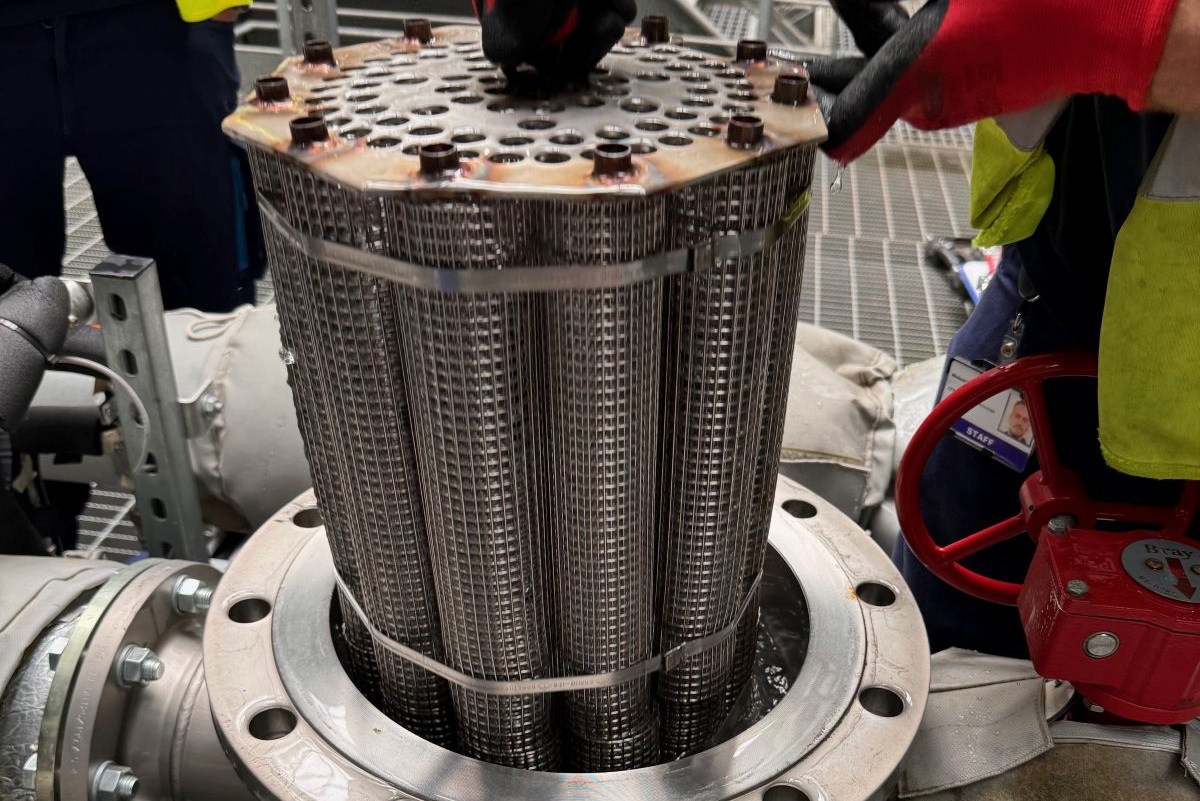
Spirotech, a water quality specialist, has fulfilled an order for 32 bespoke hi-flow SpiroTrap dirt separators for a data centre installation in Hertfordshire.
Keeping such facilities dirt-free is critical. Spirotech worked on the project with trusted contract service partner, Engineering Support Solutions (UK), based on the Slough Trading Estate in Berkshire.
ESS (UK) consulted with its prestigious data centre client and, after assessing their needs, designed the pipe connections and the bespoke sizing of the units to reduce the number of infrastructure changes to site. Spirotech supplied with this information developed the stainless-steel production units. Other specification changes included a top demountable lid for easy maintenance access and test points on inlet and outlet arms.
The ‘off-the-shelf’ models are made from carbon steel and tin and are equipped with a bottom demountable lid.
Lewis Hill, Managing Director of ESS (UK), comments, “After a series of design meetings, both on-site and with Spirotech, the adapted units were successfully manufactured within 22 weeks. We are extremely pleased with the outcome, as the final product is a highly effective, bespoke piece of equipment that perfectly meets the client’s needs.
“The data centre has three open cooling tower systems used for cooling the data halls within the building and they had strainers in place to remove the sediment being pumped around the system. However, performing maintenance on them required shutting down the cooling system, which, as you can imagine, was far from ideal for the site.
“We were pleased to have bespoke dirt separators engineered for site which has reduced down time for the client as well as provided a kit that outperforms their original design. As a business we quality assure everything we use and know that the Spirotech equipment, along with their technical ‘back-up’, won’t let us down.”
Steve Simmonds, Special Projects Engineer for Spirotech, adds, “The data centre is delighted with the installation and performance of the units. They are removing much smaller particulates than before and are, as a result, making substantial savings in terms of maintenance time and money.”
The bespoke SpiroTrap unit is able to remove very small particles from 5um and separates and removes dirt from the system whilst in operation. In case of severe pollution and/or maintenance, the unit is demountable and ensures no unnecessary downtime.
ESS UK primarily specialises in fluid movement, and offers the support, installation, maintenance, repair of pump equipment and wet waste service.
For more from Spirotech, click here.
Simon Rowley - 17 March 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Data Centres
News
Sustainable Infrastructure: Building Resilient, Low-Carbon Projects
Schneider Electric increases DC sustainability for insurance group
Schneider Electric, a specialist in the digital transformation of energy management and automation, has worked with its EcoXpert Partners, on365, to deliver a series of data centre and critical power projects to Markerstudy Group - one of the fastest growing providers of general insurance services for more than eight million customers across the UK.
Working together with on365, a provider of resilient and energy efficient critical physical infrastructure and utility services, Schneider Electric and its longstanding EcoXpert Partners devised an upgrade and consolidation strategy for Markerstudy’s electrical infrastructure, data centres and networking systems. Equal consideration was given to the need for increased reliability, security, and energy efficiency, while helping the organisation to better manage and scale its distributed systems.
As part of the strategy, the Group chose to standardise on key components from Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure for Data Centres portfolio, including its Galaxy V-series three phase UPS’s and APC Smart-UPS RT single phase UPS, EcoStruxure Row Data Center solution, InRow DX cooling units and Chilled Water systems, APC Racks and PDUs and EcoStruxure IT Expert DCIM software.
Additionally, on365 secured a strategic five-year, Managed Service Level Agreement (SLA) to manage and maintain all critical power and cooling infrastructure on behalf of the insurance group – helping not only to improve the efficiency and resiliency of its systems, but to reduce its carbon emissions.
Sustainable expansion
Markerstudy Group was founded in 2001 and today serves over eight million customers, employing more than 7,000 people across 40 brands. In 2020 it acquired Co-op Insurance’s underwriting business, followed by BGL Insurance and Lloyd’s broker Clegg Gifford in 2021, and Atlanta Insurance in 2024. This expansion presented several technological challenges, which included integrating multiple technology systems, while managing a diverse portfolio of digital infrastructure, including several data centres and IT systems distributed across its offices and customer support centres.
The Group is fiercely committed to sustainability, aiming to reduce the energy usage and carbon emissions across its operations. To address these goals and stay updated on new technological advancements, it continues to collaborate with on365 and Schneider Electric, while working with net zero consultancy, Energise, and mapping its operations to the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHG), which earned it a Bronze sustainability rating from EcoVadis.
Modernisation strategy
Markerstudy’s strategy to standardise on Schneider Electric technologies, and to modernise its infrastructure portfolio began in 2012, when it first commissioned on365 to design and build a data centre at its Chesterfield contact centre. The data centre utilised Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure Row Data Centre solution, together with InRow DX cooling units to maximise energy efficiency, and minimise the threat of downtime from thermal shutdowns.
During 2023, on365 implemented a new main substation Transformer and Primary Switchboard to replace 30-year-old, legacy electrical equipment. Designed using IoT-enabled components for ease of monitoring and management, the new system has future-proofed Markerstudy for the integration of renewable energy at its offices, while providing key infrastructure for new EV chargers.
Additionally, on365 provided a turnkey data centre solution at Markerstudy’s Tunbridge Wells headquarters. To meet its fast-growing capacity requirements while supporting the business’ expansion, the data centre has undergone a significant technology refresh to increase the efficiency of its cooling systems. It is also using Schneider Electric Galaxy VS UPSs to enhance the resiliency of the site.
Outside of its main data centres, on365 has improved the resilience of Markerstudy’s edge computing environments across its regional office portfolio and call centres. This includes the installation of Galaxy VS UPS equipment at its Manchester office to support the critical network and the unified communications connections within its main data centres, as well as APC Smart-UPS UPS to protect the network racks on different floors of the building.
Markerstudy was also an early adopter of Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure Data Center Expert software and now uses Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure IT Expert DCIM solution, coupled with a digital services program from on365, to provide real-time monitoring, remote management and maintenance for its critical infrastructure.
Enhanced control
By working with on365 and Schneider Electric, Markerstudy has been able to establish greater control over its IT and network environments. This has enabled it to monitor and manage them for better efficiency and to lower the emissions associated with data processing and storage, as well as those associated with its IT and data centre services.
In standardising on Schneider Electric Galaxy V-series UPS and APC Smart-UPS, Markerstudy has opted for best-in-class levels of efficiency and reliability, while leveraging Green Premium technologies to help with carbon reporting. Additionally, the energy savings resulting from its new Transformer and Switchboard have contributed to Markerstudy’s sustainability ambitions, reducing the carbon footprint of its IT operations, while fast-tracking the transition of its van fleets to EVs.
“The Markerstudy board has consistently supported our investment in more efficient data centre physical infrastructure, enabling the IT Team to improve the PUE of our data centres, and accommodate our technology requirements as the company continues its growth trajectory,” says Nick Ovenden, Chief Technology Officer at Markerstudy Insurance. “Working with on365 and Schneider Electric has been central to the execution of our digital infrastructure and upgrade strategy, as well as meeting the sustainability ambitions for our IT services.”
“From day one we’ve set out to work as an extension of the Markerstudy Insurance Group,” comments Carl Richardson, Technology Manager at on365. ‘By understanding their aims and objectives and immersing ourselves in the culture of their technical team, we now deliver a nationwide service which supports the design and deployment of efficient and reliable infrastructure, and the delivery of key insurance products for its UK customers.”
“Today’s data centres and IT technologies are vital to support the UK’s thriving enterprise sector,” adds Mark Yeeles, Vice President, Secure Power division, Schneider Electric UK and Ireland. “Our work together with on365 showcases the important role of data centres as critical national infrastructure and demonstrates how our ecosystem can ensure customers like Markerstudy remain at the forefront of UK Insurance services while achieving their sustainability goals.”
Schneider Electric’s case study with Markerstudy Insurance Group and on365 is now available for download.
For more from Schneider Electric, click here.
Simon Rowley - 25 February 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Data Centres
News
Vertiv and Oxigen to develop new data centre
Vertiv, a global provider of critical digital infrastructure and continuity solutions, has announced that it is collaborating with Oxigen, a provider of data hosting, processing and distribution services, to design and implement Oxigen's largest data centre.
Vertiv’s power and thermal solutions deliver scalability and energy efficiency, and its services also provide comprehensive support, helping to position Oxigen as a benchmark for high-performance data centres in Spain.
Oxigen’s second and largest data centre, situated in Sant Cugat del Vallès, boasts an impressive 6,000m² (64,583 feet) of space - including a 3,000m² (32,292 feet) operations clean room - and has the capacity for up to 800 racks with multiple power and customisation options. This scope allows Oxigen to quickly adapt to market needs, such as continuously evolving AI projects. While the current infrastructure occupies only a portion of the available space, the facility is ready for expected growth. The data centre is designed in line with Uptime Institute's Tier III criteria, which certifies that the facility meets high standards of availability and redundancy, enabling enhanced resilience and connectivity.
Vertiv's technology - which is essential for the smooth and continuous operations of this data centre - includes:
• A high-performance Vertiv Liebert AFC chiller, which provides precise temperature and flow of the cooling fluid.• Vertiv Liebert CRV row-based cooling equipment, which allows humidity and temperature adjustment and is located near the most demanding racks.• Vertiv Powerbar iMPB busbar systems, which allow power to be distributed to the equipment racks, significantly increasing flexibility and scalability for the future.
Vertiv has also provided Vertiv Critical Insight, a vendor-agnostic software that allows authorised personnel to visualise everything happening in the data centre in real time, enabling continuous monitoring of any critical digital infrastructure and its deployments onsite or remotely. Critical Insight notifies the personnel monitoring the systems of the current conditions of the equipment, trends and analysis. It provides recommendations on personnel actions as the equipment reaches baseline thresholds. Any adjustments needed can then be completed by the appropriate engineers physically onsite or remotely if controls management can be done.
This mix of adaptable technologies, along with energy consumed coming from 100% renewable resources, enables increased energy efficiency and cost savings.
Benjamin Rovira, CEO of Oxigen, says, "We have been working with the Vertiv team for more than 20 years, during which they have always demonstrated exceptional professionalism and delivered state-of-the-art technology. Knowing both their products and their team well and having always achieved strong results, we trust their ability to adapt to our evolving requirements. They are an ideal partner.”
The Oxigen data centre has 6MW of total power and up to 20 kW per rack to serve industries including the pharmaceutical, industrial, technological, education and public sectors. Oxigen customers expect their critical digital infrastructure to provide continuous uptime to support significant processing capability, consistent cooling and stored electricity - especially at peak hours.
Jordi Gonzalez Sandalinas, Enterprise Account Manager at Vertiv, comments, "The collaboration with Oxigen is testament to the ability of our solutions to adapt and expand with the customer’s needs. Our focus on energy efficiency, coupled with flexibility and ongoing support, allows Oxigen to grow without compromising the quality or security of its services.
"Over the years, we have built strong trust and demonstrated a deep knowledge of Oxigen’s needs, in addition to providing a broad and innovative portfolio of technologies. This is why the company has placed its full trust in Vertiv’s service team for the maintenance and management of the equipment."
For more from Vertiv, click here.
Simon Rowley - 18 February 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Data Centres
News
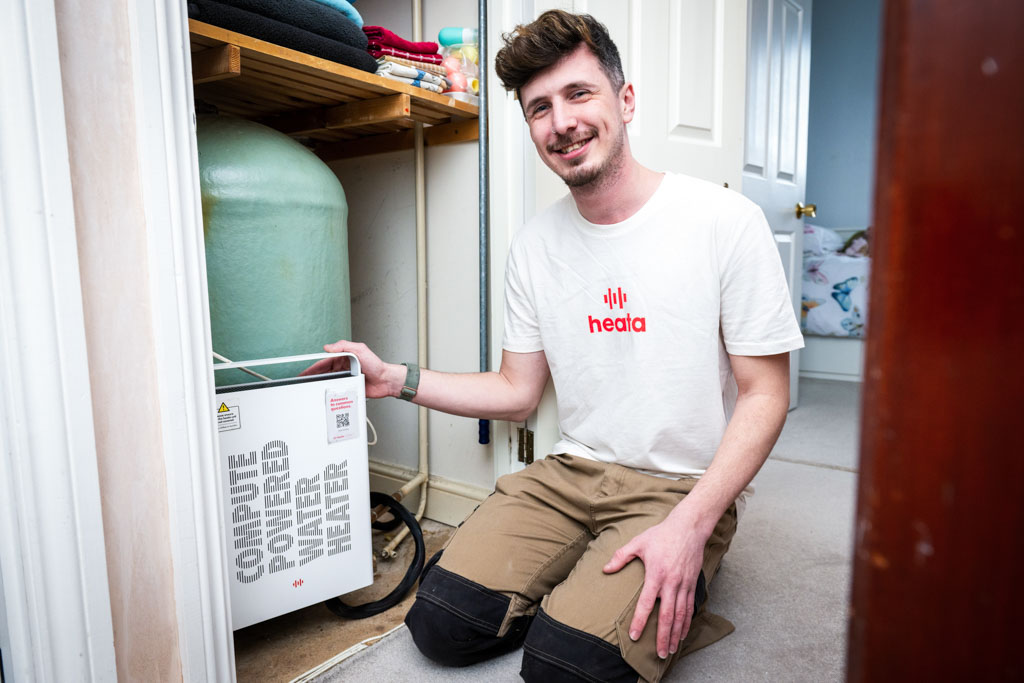
heata and British Gas project to deal with DC waste heat
This month, a pioneering trial backed by British Gas will see heat generated from computing servers recycled to provide free hot water in homes, using ground-breaking technology developed by UK firm, heata.
The trial marks a huge milestone for heata founders, Chris Jordan and Michael Paisley, who hope their technology could help tackle the fuel poverty crisis, as well as being one of the solutions to one of the biggest environmental challenges of today - dealing with the waste heat generated by data centres.
heata’s technology, which was developed as part of an innovation project with British Gas, allows heat generated from intensive data processing (typically undertaken in a data centre) to be channelled directly into a hot water cylinder in the home; reducing bills for the homeowner, and avoiding the need for the energy intensive cooling needed in a typical data centre.
What this looks like in reality is a small compute unit attached to the hot water cylinder. This is part of the heata network - a ‘virtual data centre’ - and can process data for cloud computing customers whilst providing free hot water for the homeowner.
Each heata unit can provide up to 4kWh of hot water per day, saving households up to £340 per year. British Gas has this month launched a 10 unit trial running its own data processing workloads on the heata units in their employee’s homes, providing their employees with free hot water as a by-product of British Gas’s data processing.
Chris Jordan, Co-Founder of heata, says, “Waste heat is a big problem for data centres, leading to significant energy costs for cooling. Yet heat is valuable. On the other side of the coin you have an energy crisis and people struggling to heat their homes. Our unique technology brings those two things together. We’ve created a distributed ‘virtual data centre’ where the servers are attached to domestic hot water cylinders, enabling the heat generated by the data processing to be reused to provide free hot water in the home.
“British Gas launching this trial is a huge step and we would love to see other firms following their lead. By making a small change to where you process your data, businesses can have an impact on fuel poverty and the planet. Being able to say you have reduced your compute carbon footprint and provided free hot water to people during an energy crisis is hugely powerful for companies who take pride in their sustainability and social impact.
Paul Lodwidge, Head of Energy Product & Propositions at British Gas, adds, “Innovative projects like this are another example of how the UK is becoming a leader in cutting carbon emissions. heata is a true pioneer in the way it has developed a solution that can reuse waste heat and deliver significant cost and carbon savings. We’re proud to be able to support them with this latest trial and will work together to share insights and learnings that will enable the business to scale-up its offering.”
Simon Rowley - 13 February 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Data Centres
Hyperscale Data Centres: Scale, Speed & Strategy
News
Yondr breaks ground on third phase of London campus
Yondr Group, a global developer, owner and operator of hyperscale data centres, has broken ground on the third building of its London data centre campus in Slough.
Once completed, the 40MW data centre will bring the total capacity of the London campus to just over 100MW, making it one of the largest in the UK. The ground-breaking brings the site of a derelict paint factory back into commercial use, and the event follows completion of the first 30MW building at the London campus in July last year. An additional 30MW data centre is currently in the construction phase on site.
Yondr’s third building on the London campus has been designed to BREEAM ‘Very Good’ standards, to deliver both reliable data capacity and sustainability. The new facility will be energy efficient in line with the company’s sustainability strategy and 2030 target for Scope 1 and 2 carbon neutrality. Solar panels will be installed on the building’s roof and the facility will boast industry-leading power utilisation efficiency (PUE).
Plans for the building were developed in close collaboration with Slough Borough Council and the Canal & River Trust, with the goal of realising a building that actively enhances biodiversity and improves the canal side, with a focus on aesthetics and active transport access for local residents.A green wall facing out towards the canal is one of the ways in which aesthetics and sustainability have been integrated into the project, as part of a strategy of blending the building with its surroundings. The green wall has been designed on an independent structure to overcome the technical requirements of the data centre and it will provide both visual and acoustic shielding, in addition to contributing to biodiversity.
Yondr’s commitment to sustainability will extend beyond the border of the site for the new data centre, with the planting of trees and shrubs which have been specially selected to be sympathetic to local plant species and wildlife. A new walking and cycle route will contribute to the health and fitness of the local community and help to reduce vehicular traffic by creating a convenient cut-through.
In a further step to create a positive impact in the local area, Yondr conducted a community-needs assessment which highlighted challenges children face in accessing outdoor learning opportunities. To help bridge this gap, Yondr has provided funding for six classes from local schools for a day of hands-on learning at the Iver Environment Centre – allowing the children to immerse themselves in biodiversity, conservation, and the importance of protecting the environment.
Peter Hill, VP of Design & Construction EMEA at Yondr, comments, “The plans for this third building on our London campus show a clear evolution of our data centre design and delivery capabilities. It demonstrates just how far we have come in embracing sustainability to deliver our carbon neutrality goals and bring forward exemplar data centre developments.
“Breaking ground on this project is a milestone not just for this building, but also for our London campus and our increasingly strong presence in Europe. I’d like to thank everyone who has helped progress this project through the design and planning stage, as well as those who have joined us to celebrate today, and I look forward to a smooth construction process and handover next year.”
The facility is expected to be completed in mid-2026.
For more from Yondr Group, click here.
Simon Rowley - 12 February 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Data Centres
News
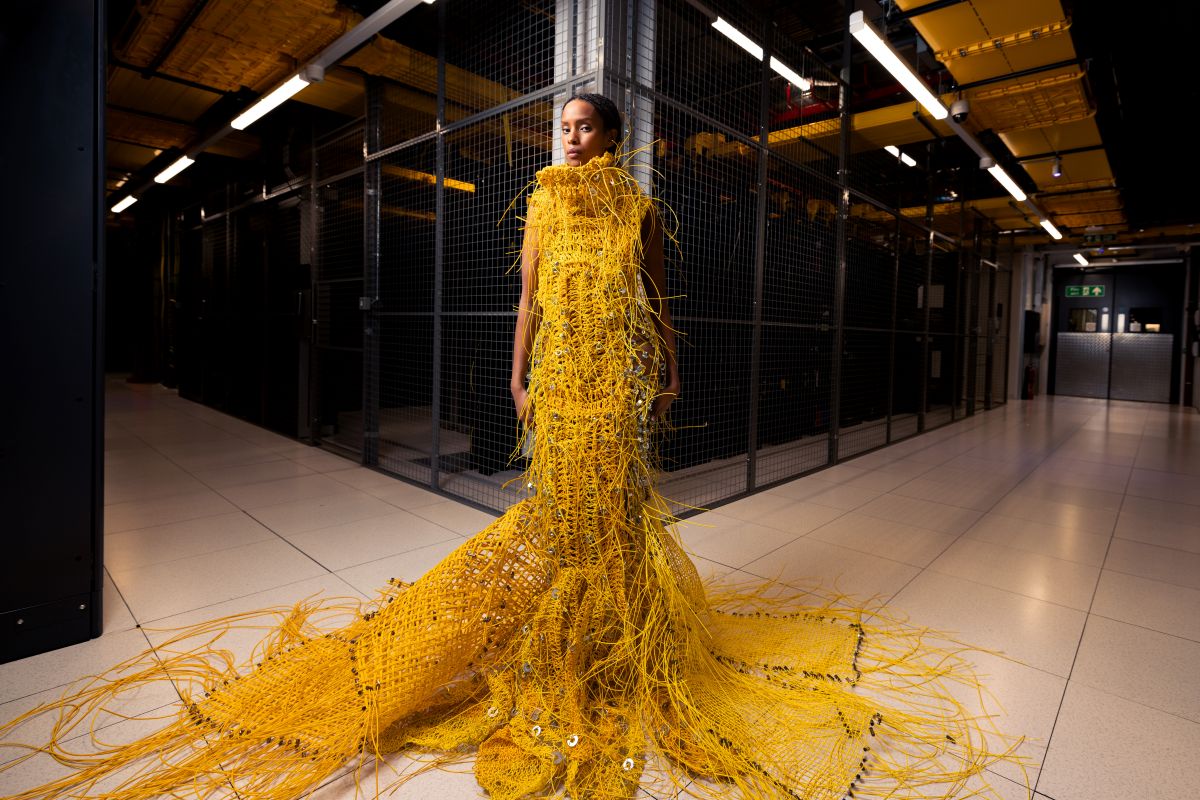
Designers create garment made from data centre materials
Ahead of London Fashion Week, designer, Maximilian Raynor, and data centre company, Equinix, have taken wearable tech to a different dimension with the creation of a one-off garment that brings the internet to life by using recycled materials in new and innovative ways.
Merging high fashion with sustainability, the dress (which was developed with the codename 'Project Max') is made entirely from discarded data centre materials - including 3,600m of internet cables, metal nuts and bolts - to showcase the ‘personification of the internet herself'. The garment reportedly took in the region of 640 hours to create.
Bruce Owen, President EMEA at Equinix, explains, “We have worked with designer, Maximilian Raynor, to bring the internet to life through a visually striking piece of design in the form of a dress made from materials at our London data centres. By bridging the gap between physical and virtual, we wanted to create something tangible that works as a unique talking point to highlight the many thousands of connections that are created by Equinix to support economies and societies every day.
“The design pays homage to the physicality of the vital infrastructure that makes up the internet. Rather than some sort of weird magic or unexplainable force that just happens to work, it’s a physical, intricate network of cables, traversing land and sea and creating physical connections housed in Equinix data centres worldwide.
“People have never been more aware of the impact of digital on their lives – especially with the explosion in advancements of technologies like AI, cloud, and quantum that all rely on these physical hubs to expand and collaborate. It’s no coincidence that a key theme at Davos last week centred around the Intelligent age and what that means for economies and societies worldwide.
“Ultimately, this is a light-hearted way of exploring something important. We want the campaign to showcase the internet’s real-world impact on people’s daily lives and businesses, as well as its vital role in the UK economy. Whether that is the development of new drugs to cure disease, or the way we pay for our food - both online and in shops, or even the way we keep people connected to each other over vast distances. By highlighting the value that data centres bring to society, we aim to answer questions surrounding data centre operations and generate global awareness for our fast-growing and ever-important industry.”
For more from Equinix, click here.
Simon Rowley - 7 February 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
News
UK advances gigabit broadband expansion
Ultra-fast broadband has been rolled out in remote areas of Scotland as part of the Government's initiative to improve connectivity around the UK.
Connectivity on the Scottish islands has long been a challenge due to their remote locations, but Openreach engineers, working on the Scottish government's Reaching 100% (R100) programme, have now brought full-fibre broadband to Tiree and Iona.
This deployment required careful planning with local organisations to protect wildlife and the natural landscape. The upgrade is seen as transformative, linking islanders to the global digital economy. Further rural Scottish communities are set to benefit from the R100 programme in the coming months, aligning with the government's goal of full digital inclusion.
Meanwhile, in North Yorkshire, Quickline is rolling out gigabit broadband under the £5bn Project Gigabit programme, launched in 2021 to boost economic recovery and regional development. Targeting areas overlooked by commercial providers, the initiative ensures underserved locations gain access to high-speed internet.
Five months into its North Yorkshire contract, Quickline has delivered access to nearly 5,000 homes and businesses, including the first 46 premises under contract and an extra 4,800 through commercial expansion. The North Yorkshire contract aims to provide broadband to 36,000 funded premises, with an additional 50,000 connections through commercial expansion. Across all its Project Gigabit contracts, Quickline is set to connect 170,000 subsidised homes and businesses in Yorkshire and Lincolnshire, rising to 360,000 with commercial builds.
Elizabeth Anderson, CEO of the Digital Poverty Alliance, says, "The ongoing rollout of gigabit connectivity can make a transformative difference to the lives of people across the UK, providing fast broadband access to online digital services. Tasks such as online banking, e-learning and booking a digital healthcare appointment are made almost impossible for those without connectivity, so these broadband rollout schemes are vital for the British people. However, the affordability of these services is key - with faster packages often costing much more and being out of reach for those on lower incomes."
"Scotland, especially, has proved difficult to reach for broadband providers due to its rural nature, but the success of the Tiree rollout highlights the roadmap for creating a connected Scotland. We'd hope to see the Scottish government placing affordable connectivity as a central point within their digital inclusion strategy work, committing substantial investment into high-speed, affordable infrastructure in rural areas to ensure digital quality for all."
Simon Rowley - 4 February 2025
Cooling
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Data Centres
News
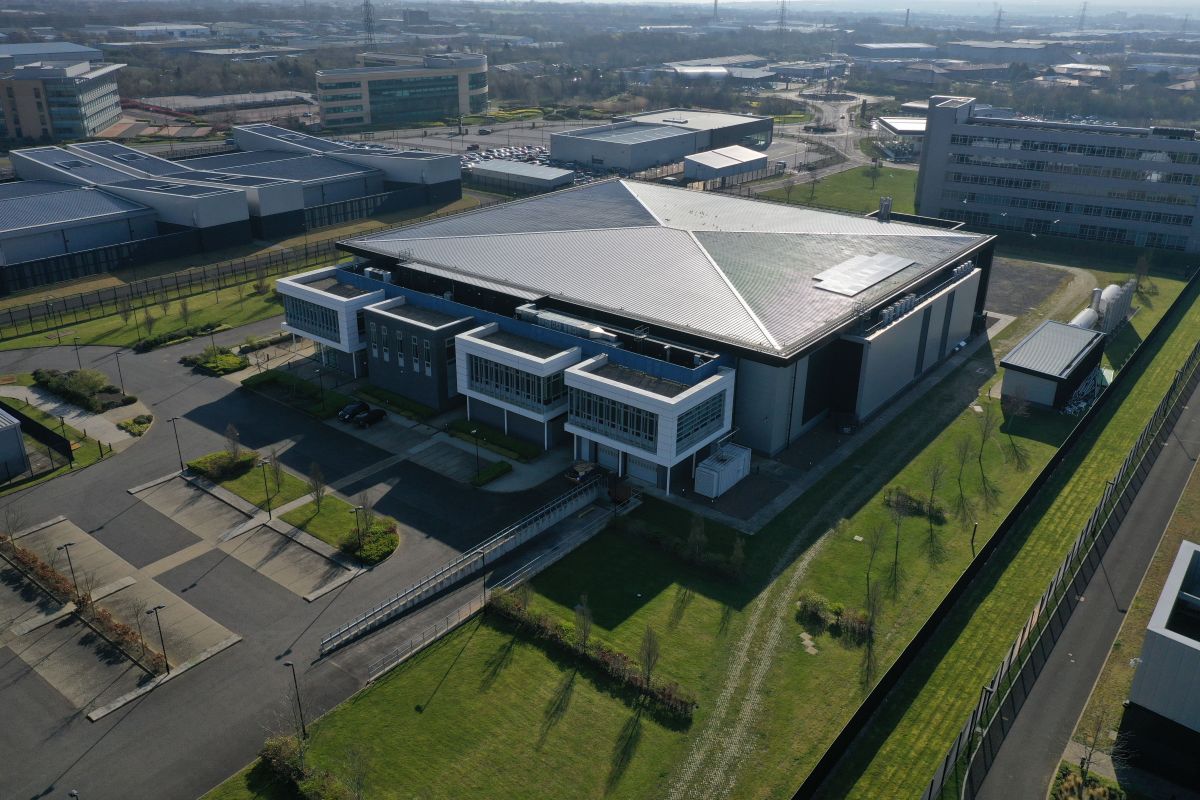
Immersion cooling OCP completed at Stellium data centre
Stellium Datacenters, a colocation operator and provider of data centre infrastructure innovations, has announced the launch of an Open Compute Project (OCP) Proof of Concept at its HPC hyperscale data centre near Newcastle.
This follows the integration phase of an immersion cooling system into Stellium’s OCP-Ready certified infrastructure in collaboration with Submer and its partners. Based on OCP design and engineering protocols, Submer’s installation represents the first ORv3 showcase deployed in Europe, a specification within the broader OCP concept that focuses on rack design and power supply regulation.
In combination with ExxonMobil’s DC 3235 Super fluid, the compute is powered by MiTAC’s Capri 2 servers with AMD CPUs and server components provided by Circle B. Other key contributions to the project so far include TE Connectivity busbars, Murata power shelves, an Edge-Corenetwork switch, and FormericaOE immersion fibre cables.
“As one of the first OCP-Ready data centres in the UK, Stellium is delighted to be at the heart of this significant engineering achievement, which is being followed with great interest by existing and prospective customers,” says Ed Bissell, Sales & Marketing Director, Stellium Datacenters. “With Submer and our OCP Partners, we are leading the way in immersion cooling technology capable of cost-effectively addressing the exponential cooling demands of high performance AI and ML computing. Our joint collaboration is an exemplar of how to achieve this goal and without compromise when it comes to reliability, processing performance and energy efficiency.”
Oriol Chavanel, Submer Ecosystem Enablement Tech. Lead & OCP Lead, adds, “For Submer, having finally deployed this configuration this offers an opportunity to show an ORv3 configuration to current and future end customers. For those who are considering Immersion OCP-related solutions, visiting the facility will allow them to see a real hyper-converged set-up.”
Steve Helvie, VP of Emerging Markets, Open Compute Project, comments, “We are excited to see this collaboration between OCP Members, Stellium Datacenters, Submer, MiTAC, Exxon Mobil, AMD, Murata and other key partners, driving innovation through this Proof of Concept for immersion cooling. Efforts like these exemplify the power of the Open Compute Project community working together to advance sustainable, energy-efficient solutions for the data centre industry. By working together to explore new approaches, these partners are not only validating cutting-edge technologies, but also contributing to the evolution of open infrastructure to meet the demands of a rapidly growing market.”
Stellium, Submer, OCP Partners and OCP representatives will be hosting an open day at Stellium’s data centre on 12 February to showcase the immersion cooling installation to existing and prospective customers.
For more from Stellium, click here.
Simon Rowley - 31 January 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Data Centres
Liquid Cooling Technologies Driving Data Centre Efficiency
News
Sustainable Infrastructure: Building Resilient, Low-Carbon Projects
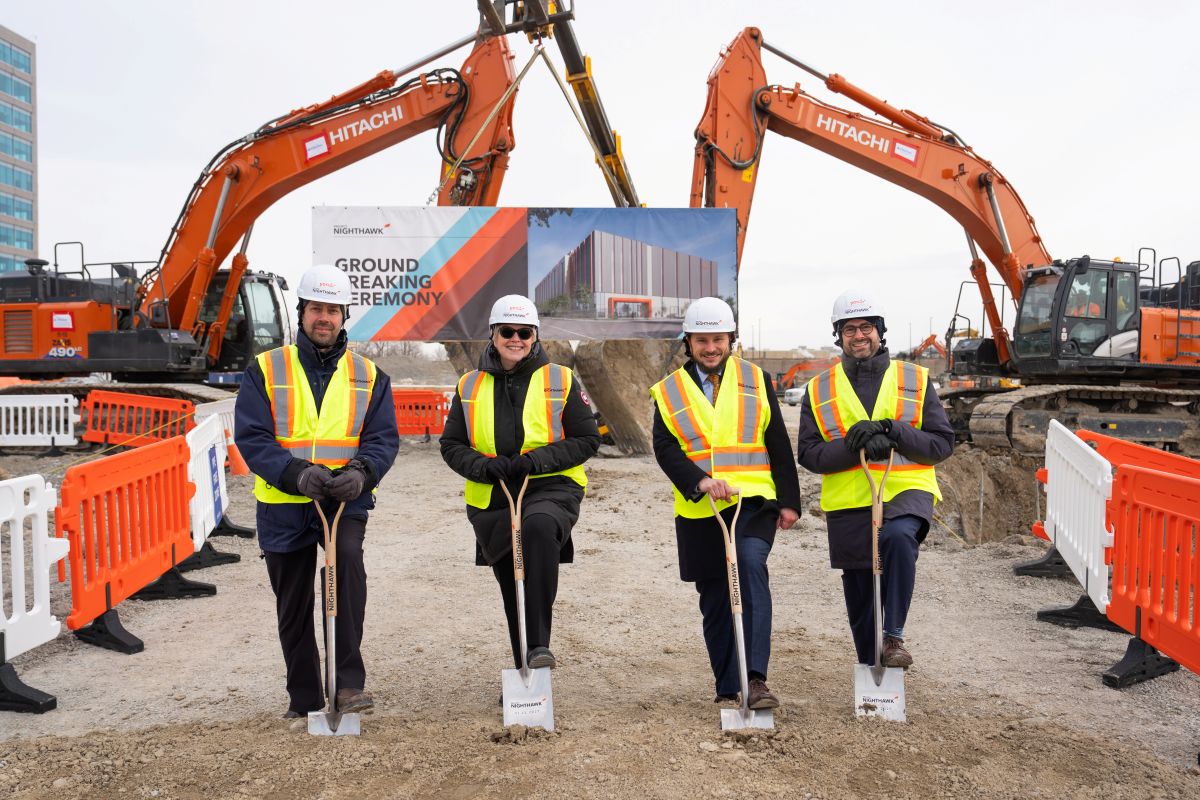
Yondr Group holds ground-breaking for Toronto data centre
Yondr Group, a global developer, owner and operator of hyperscale data centres, has held a ground-breaking ceremony to mark the start of work on site for its 27MW Toronto data centre.
The project, which Yondr is building on a 4.5-acre site, is the company’s first development in Canada. It forms part of Yondr’s global expansion, as the business continues to deliver reliable and resilient data centre capacity at speed and at scale, with projects currently completed or in progress in North America, Europe and Asia.
The ground-breaking in Toronto follows the completion of the company’s 48MW data centre project in Northern Virginia, and the first ready for service (RFS) milestone for the company’s 40MW Frankfurt data centre last November.
The ceremony was attended by Councillor Shelley Carroll of Don Valley North, who gave a speech highlighting the city’s thriving digital economy and emphasised Toronto’s vision of becoming a global hub for innovation and talent. The event also brought together key stakeholders all united in their vision of building a more connected and future-proofed Toronto.
Situated in a strategic location within Canada’s emerging data centre hub, the project comprises a three-storey, 27MW data centre, which is scheduled to achieve RFS by mid-2026. The project has been designed by Yondr to follow the Toronto Green Standard, the city’s sustainable design and performance requirements for new developments, and this aligns with the company’s environmental goals and target for achieving net zero for scope 1 and 2 carbon emissions by 2030.
The building will feature a closed loop cooling design, which means once the chilled water loop is filled, the facility will not need to consume water for cooling. Once completed, the project will have bike parking, electric vehicle charging points and will open up pedestrian walkways. The environmentally friendly landscaping plan will have native and pollinator plants, and the building’s glass will be bird-friendly, helping birds to see the building as a barrier and avoid collisions.
As part of its social impact initiatives, Yondr has partnered with the University of Toronto to fund a scholarship programme. ‘The Yondr Group Scholarship’ will be available to undergraduate students at the university entering courses in Computer Science, the Rotman Commerce business programme, Life Sciences, or Mathematical & Physical Sciences.
Successful applicants will receive $5,000 per year for five years, with the first awards being made to students starting their studies at the beginning of the 2025/26 academic year this coming autumn.
Kent Andersson, Program Controls Director for the Americas at Yondr Group, says, “Our Toronto data centre forms a key part of our strategy for North America, where there is an urgent need to increase capacity to support the digital economy. This project will play a key role in providing the infrastructure needed to support cutting-edge cloud computing and connectivity, and enable the development of AI and future technologies in Canada and beyond.
“We would like to thank the Canadian authorities, including the City of Toronto and our strategic partners, for supporting a positive approach to bringing this project from concept to site, and I look forward to seeing the data centre take shape on site over the coming months.”
For more from Yondr Group, click here.
Simon Rowley - 31 January 2025
Data Centre Build News & Insights
Data Centre Projects: Infrastructure Builds, Innovations & Updates
Enterprise Network Infrastructure: Design, Performance & Security
News
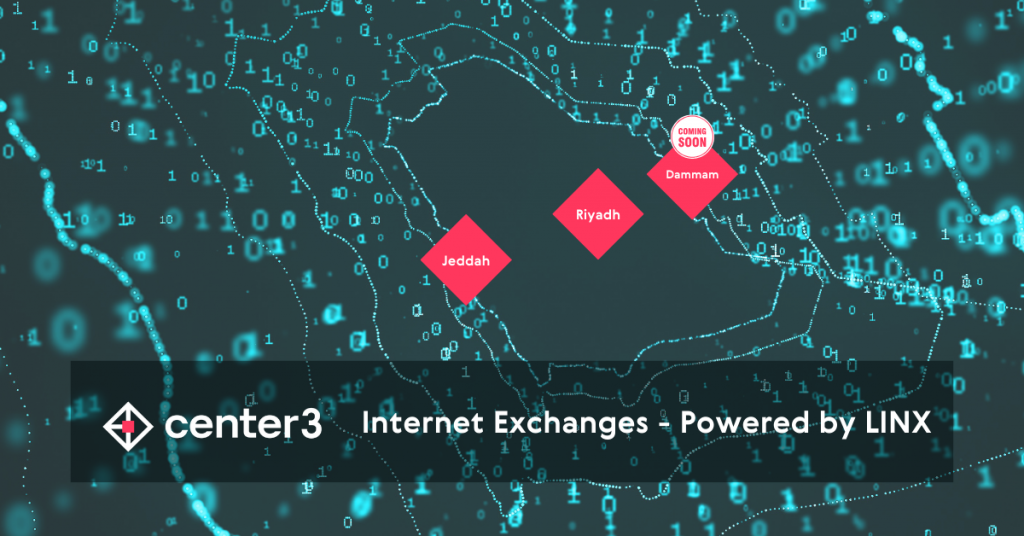
LINX IXP in Jeddah completes capacity upgrades
The London Internet Exchange (LINX) has completed its 100G capacity upgrade project in Jeddah, following an increase in customers and port demands at the interconnection hub in KSA.
LINX has been powering Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) for Center3, its strategic partner in Saudi Arabia, since 2018. Jeddah was the first port of call for this deployment and since then, LINX peering services have gone live in Riyadh and teams are preparing to deploy in Dammam this year.
Jeddah is one of the main landing stations for subsea cables in the Middle East, distributing global content locally and providing convenient onward connectivity to Asia, Europe and Africa.
The IXP in Jeddah creates a neutral and central meeting point in the MG1 (MENA Gateway) data centre for carriers, cloud, content providers, enterprise networks and more to peer their network traffic locally and improve end user online performance. The IXP also offers lower latency, increased control and resilience, and increased security and redundancy.
Halil Kama, Regional Director for LINX in the Middle East, comments, “We are pleased to be upgrading our internet exchange capacity with an additional 16x 100G port capability due to customer demand in Jeddah. This enhancement further strengthens Jeddah’s role as a digital gateway, ensuring faster, more efficient connections for networks and users across the region.”
With regular traffic peaks over 650Gbps, networks connected into the IXP in Jeddah need to ensure their ports have the capacity to cope with the spikes in online traffic often generated by sporting events or gaming upgrades.
There were 36.84 million internet users in Saudi Arabia in January 2024, with an impressive internet penetration rate of 99% of the total population at the start of 2024. Additionally, Kepios analysis indicates that internet users in Saudi Arabia increased by 527,000 (1.4%) between January 2023 and January 2024.
The rapid evolution of the digital scene in Saudi Arabia is fuelled by its Vision 2030 strategy. The growth in sports and event tourism has generated a greater need for lower latency streaming solutions, and with talks that Saudi Arabia’s Public Investment Fund (PIF) could acquire a minority stake in sports streaming service, DAZN, this demand is set to continue to increase.
AWS has also just announced Jeddah as a new CloudFront Edge location and plans to invest more than $5.3 billion (£4.3bn) in the long term to develop Saudi Arabi as an AWS cloud region.
With an increase in partnerships, investments and services comes a further demand for capacity and continued and reliable low latency interconnection solutions.
For more from The London Internet Exchange, click here.
Simon Rowley - 30 January 2025

Head office & Accounts:
Suite 14, 6-8 Revenge Road, Lordswood
Kent ME5 8UD
T: +44 (0)1634 673163
F: +44 (0)1634 673173